Abstract
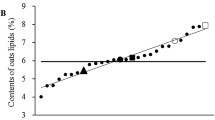
Numerous factors affect plasma cholesterol and, therefore, representpotential interferences with the specific effects of diet on lipid metabolism.After casein intake, serum cholesterol levels depend on many experimentalconditions in rats, such as the type of casein, the presence or absence ofcholesterol in the diet, the age and strain of rat, the diet composition, thenutritional status. The effect of fasting duration on selected parameters wasstudied in adult male Wistar rats fed a 20% casein and 1% cholesterol-based diet. No changes were observed in total serum, lipoproteins-B andHDL cholesterol and in triglyceride values after an 8 h-fast compared tonon-fasted animals. A significant decrease was induced in total andlipoproteins-B cholesterol with a 12 h-fast. A prolonged fast resulted ina significant decrease in these parameters and in triglycerides and inHDL-cholesterol levels.Fasted animals fed heated soybean meal instead of casein did not display amarked decrease in serum lipids. It appeared that the fasting effect wasmore marked in animals fed casein than in animals fed soybeans. Theseresults showed the importance of experimental conditions such as nutritional status ofanimals when blood samples are taken in studies of the hypocholesterolemiceffect of soy protein compared to casein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Terpstra AHM, Hermus RJJ, West CE (1983) The role of dietary protein in cholesterol metabolism. World Rev Nutr Diet 42: 1–55.
Sugano M (1983) Hypocholesterolemic effect of plant protein in relation to animal protein: mechanism of action. In: Gibney MJ, Kritchevsky D (eds), Animal and Vegetable Proteins in Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerosis. New York: Alan R Liss, pp 51–84.
Forsythe WA, Green MS, Anderson JJB (1986) Dietary protein effects on cholesterol and lipoprotein concentration: a review. J Am Coll Nutr 5: 533–549.
Sugano M, Beynen AC (1990) Dietary Proteins, Cholesterol Metabolism and Atherosclerosis (Monographs on Atherosclerosis, Vol 16), Basel: Karger.
Beynen AC (1990) Comparison of the mechanisms proposed to explain the hypocholesterolemic effect of a soybean protein versus casein in experimental animals. J Nutr Sci Vit 36 (Suppl II): S87–S93.
Guermani L, Villaume C, Bau HM, Mejean L, Nicolas JP (1992) Effect of different kinds of dietary casein on blood cholesterol and triglycerides in pair fed rats. Nutrition 8: 101–104.
Cohn JS, Kimpton WG, Nestel PJ (1984) The effect of dietary casein and soy protein on cholesterol and VLDL metabolism in the rat. Atherosclerosis 52: 219–231.
Austin GE, Mazincki E, Sgoutas D (1984) Comparison of phosphotungstate and dextran sulfate-Mg++ precipitation procedures for determination of HDL-cholesterol. Clin Biochem 17: 166–169.
Cohn JS, McNamara JR, Cohn SD, Ordovas JM, Scharfer EJ (1988) Postprandial plasma lipoprotein changes in human subjects of different ages. J Lipid Res 29: 469–479.
Rifai N, Merrill JR, Holly RG (1990) Postprandial effect of a high fat meal on plasma lipid, lipoprotein cholesterol and apolipoprotein measurements. Ann Clin Biochem 27: 489–493.
Hauton JC (1992) Athérosclérose et obésité: incertitudes et perspectives. Méd Nutr 28: 209–223.
Aoyama Y, Hitomi-Ohmura E, Yoshida A (1991) Effect of a dietary excess of histidine and subsequent starvation on serum lipids in rats. Agric Biol Chem 55: 1161–1162.
Weingand KW, Daggy BP (1991) Effects of dietary cholesterol and fasting on hamster plasma lipoprotein lipids. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 29: 425–428.
Calandra S, Pasquali I, Ronchetti E, Gherardi C, Fornieri I, Tarugi P (1977) Chemical and morphological changes of rat plasma lipoproteins after a prolonged administration of diets containing olive oil and cholesterol. Atherosclerosis 28: 369–387.
Field JF, Kam NTP, Mathur SN (1990) Regulation of cholesterol metabolism in the intestine. Gastroenterology 99: 539–551.
Polonovski J (1989) Régulation de l'absorption intestinale du cholestérol. Cah Nutr Diet 24: 19–25.
Brown MS, Goldstein JL, Dietschy JM (1979) Active and inactive forms of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in the liver of the rat. J Biol Chem 12: 5144–5149.
Gallo LL, Clark SB, Myers S, Vahouny GV (1984) Cholesterol absorption in rat intestine: Role of cholesterol esterase and acyl coenzyme A: Cholesterol acyltransferase. J Lipid Res 25: 604–612.
Martinez MJ, Ruiz JI, Lacort, Ochoa B (1991) Diurnal variations of rat liver enzymes catalyzing cholesterol ester hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1085: 106–111.
Jeske DJ, Dietschy JM (1980) Regulation of rates of cholesterol synthesis in vivo in the liver and carcass of the rat measured using (3H) water. J Lipid Res 21: 364–376.
Swift LL, Soulé PD, Gray ME, LeQuire VS (1984) Intestinal lipoprotein synthesis. Comparison of nascent Golgi lipoproteins from chow-fed and hypercholesterolemic rats. J Lipid Res 25: 1–13.
Wolfe BM, Grace DM (1987) Substitution of mixed amino acids resembling soy protein for mixed amino acids resembling casein in the diet reduces plasma cholesterol in slowly, but not rapidly fed nor fasted baboons. Metabolism 36: 223–229.
Vahouny GV, Chalcarz W, Satchithanandam S, Adamson I, Klurfeld DM, Kritchevsky D (1984) Effect of soy protein and casein intake on intestinal absorption and lymphatic transport of cholesterol and oleic acid. Am J Clin Nutr 40: 1156–1164.
Vahouny GV, Adamson I, Chalcarz W, Satchithanandam S, Muesing R, Klurfeld DM, Tepper SA, Sanghvi A, Kritchevsky D (1985) Effects of casein and soy protein on hepatic and serum lipids and lipoprotein lipid distributions in the rat. Atherosclerosis 56: 127–137.
Kritchvesky D (1990) Protein and atherosclerosis. J Nutr Sci Vit 36 (Suppl II): S81–S86.
Pailler FM, Lanteaume MTh, Alonso A, Yvert JP, Schmit JM (1986) Induction d'une hypercholestérolémie chez le rat Wistar: résultats des bilans biochimiques pratiques et comparaison avec les données bibliographiques. Méd Nutr 22: 167–172.
Critchfield JW, Ney D, Schneeman B, Rucker R (1990) Protein quality: plasma cholesterol and apolipoprotein levels in the rat. Nutr Res 10: 655–661.
Laraki L, Pelletier X, Debry G (1991) Effects of dietary cholesterol and phytosterol overload on Wistar rat plasma lipids. Ann Nutr Metab 35: 221–225.
Sautier C, Flament C, Doucet C, Suquet JP (1986) Effects of eight dietary proteins and their amino acid content on serum hepatic and faecal steroids in the rat. Nutr Rep Int 34: 1051–1057.
Sautier C, Dieng K, Flament, Doucet C, Suquet JP, Lemonnier (1983) Effects of whey protein, casein, soya-bean and sunflower proteins on the serum, tissue and faecal steroids in rats. Br J Nutr 49: 313–319.
Doucet C, Flament C, Sautier C, Lemonnier D (1987) Effect of an hypercholesterolemic diet on the level of several serum lipids and lipoproteins in nine rat strains. Reprod Nutr Dev 27: 897–906.
Sugano M, Ishiwaki N, Nagata Y, Imaizumi K (1982) Effects of arginine and lysine addition to casein and soya-protein on serum lipids, apolipoproteins, insulin and glucagon in rats. Br J Nutr 48: 211–221.
Nagata Y, Ishiwaki N, Sugano M (1982) Studies on the mechanism of antihypercholesterolemic action of soy protein and soy protein-type amino acid mixtures in relation to the casein counterparts in rats. J Nutr 112: 1614–1625.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guermani-Nicolle, L., Villaume, C., Bau, HM. et al. The cholesterol-lowering property of soybeans fed to rats is related to the fasting duration. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 56, 239–249 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011144031646
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011144031646