Abstract
1. Fenestrated vessels can be reversibly induced in brain by agents that stimulate urokinase production. This plasminogen activator, like vascular endothelial growth factor and metalloproteinases, is secreted by tumor cells and may account for induction of fenestrated vessels. Why only some of the brain's barrier vessels are converted to fenestrated vessels is unknown.
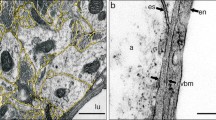
2. The structures responsible for the filtering of solutes by fenestrated vessels may be the same as those of continuous, less permeable vessels: the glycocalyx on the surfaces of the endothelial cells and the subendothelial basal lamina.
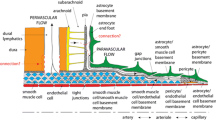
3. Solutes leaving the cerebral ventricles immediately enter the interstitial clefts between the cells lining the ventricles. A fraction of a variety of solutes, injected into CSF compartments, is retained by subendothelial basal lamina, from which the solutes may be released in a regulated way.
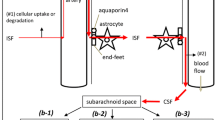
4. The brain's CSF and interstitial clefts are the conduits for nonsynaptic volume transmission of diffusible signals, e.g., ions, neurotransmitters, and hormones. This type of transmission could be abetted by a parallel, cell-to-cell volume transmission mediated by gap junctions between astrocytes bordering CSF compartments and parenchymal astrocytes.
5. The width and contents of the interstitial clefts in fetal brain permit cell migration and outgrowth of neurites. The contents of the narrower and different interstitial clefts of mature brain permit solute convection but must be enzymatically degraded in order for cells to migrate through it.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Adamson, R. H. (1990). Permeability of frog mesenteric capillaries after partial pronase digestion of the endothelial glycocalyx. J. Physiol. 428:1-13.
Asher, R., Perides, G., Vanderhaeghen, J.-J., and Bignami, A. (1991). Extracellular matrix of central nervous system white matter: Demonstration of an hyaluronate-protein complex. J. Neurosci. Res. 28:410-421.
Beck, T., Lindholm, D., Castrén, E., and Wree, A. (1994). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects against ischemic cell damage in rat hippocampus. J. Cer. Blood Flow Metab. 14:689-692.
Bernstein, J. J., and Woodward, C. A. (1995). Glioblastoma cells do not intravasate into blood vessels. Neurosurgery 36:124-132.
Bignami, A., and Asher, R. (1992). Some observations on the localization of hyaluronic acid in adult, newborn and embryonal rat brain. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 10:45-57.
Bignami, A., and Dahl, D. (1994). Glial Cells in the Central Nervous System and Their Reaction to Injury, Medical Intelligence Unit, R. G. Landes, Austin, TX, p. 109.
Blasberg, R. G., Patlack, C., and Fenstermacher, J. D. (1975). Intrathecal chemotherapy: Brain tissue profiles after ventriculo-cisternal perfusion. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 195:73-83.
Bosman, F. T., Havenith, M., and Cleutjens, J. P. (1985). Basement membranes in cancer. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 8:291-304.
Brightman, M. W. (1965a). The distribution within the brain of ferritin injected into cerebrospinal fluid compartments. I. Ependymal distribution. J. Cell Biol. 26:99-123.
Brightman, M. W. (1965b). The distribution within the brain of ferritin injected into cerebrospinal fluid compartments. II. Parenchymal distribution. Am. J. Anat. 117:193-219.
Brightman, M. W. (1968). The intracerebral movement of proteins injected into blood and cerebrospinal fluid of mice. Prog. Brain Res. 29:19-37.
Brightman, M. W., and Reese, T. S. (1969). Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J. Cell Biol. 40:648-677.
Broadwell, R. D. (1992). Pathways into, through, and around the fluid-brain barriers. NIDA Res. Monogr. 120:230-258.
Broadwell, R. W., and Sofroniew, M. V. (1993). Serum proteins bypass the blood brain fluid barriers for extracellular entry to the central nervous system. Exp. Neurol. 120:245-263.
Casley-Smith, J. R., and Mart, P. E. (1970). The relative antiquity of blood capillaries and lymphatics, and their significance for the uptake of large molecules: An electron microscopical investigation in an elasmobranch. Experientia (Separatum) 26:508-510.
Cifuentes, M., Fernandez-Llebrez, P., Perez, J., Perez-Fiares, J. M., and Rodriguez, E. M. (1992). Distribution of intraventricularly injected horseradish peroxidase into cerebrospinal compartments of the rat spinal cord. Cell Tissue Res. 270:485-494.
Clough, G. (1991). Relationship between microvascular permeability and ultrastructure. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 55:47-69.
Coomber, B. L., Stewart, P. A., Hayakawa, E. M., Farrell, C. L., and Del Maestro, R. F. (1988). A quantitative assessment of microvessels ultrastructure in C6 astrocytoma spheroids transplanted to brain and to muscle. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 47:29-40.
Cornell-Bell, A. H., Finkbeiner, M. S., Cooper, M. S., and Smith, S. J. (1990). Glutamate induces calcium waves in cultured astrocytes:Long-range glial signaling. Science 247:470-473.
Cserr, H. F, Cooper, D. N., Suri, P. K., and Patlack, C. S. (1981). Efflux of radiolabeled polyethylene glycols and albumin from rat brain. Am. J. Physiol. 240:F319-F328.
Debbage, P. L. (1996). A systematic histochemical investigation in mammals of the dense glycocalyx glycosylations common to all cells bordering the interstitial fluid compartment of the brain. Acta Histochem. 98:9-28.
Dermietzel, R. (1998). Gap junction wiring: A “new” principle in cell-to-cell communication in the nervous system? Brain Res. Rev. 26:176-183.
Dermietzel, R., Thurauf, N., and Kalweit, P. (1983). Surface charges associated with fenestrated brain capillaries. II. In vivo studies on the role of molecular charge in endothelial permeability. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 84:111-119.
Dobrogowska, D. H., Lossinsky, A. S., Tarnawski, M., and Vorbrodt, A. W. (1998). Increased bloodbrain barrier permeability and endothlelial abnormalities induced by vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Neurocytol. 27:163-173.
Dunker, R. O., Harris, A. B., and Jenkins, D. P. (1976). Kinetics of horseradish peroxidase migration through cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 118:199-217.
Enkvist, M. O., and McCarthy, K. D. (1994). Astroglial gap junction communication is increased by treatment with either glutamate or high K+ concentration. J. Neurochem. 62:489-495.
Esser, S., Wolburg, K., Wolburg, H., Breier, G., Kurzchalia, T., and Risau, W. (1998). Vascular endothelial growth factor induces endothelial fenestrations in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 140:947-959.
Evered, D., and Whelan, J. (eds.) (1989). TheBiology of Hyaluronan, Ciba Foundation, Wiley, Chichester.
Fang, J., Wang, Y., and Krueger, J. M. (1998). Effects of interleukin-1β on sleep are mediated by the type I receptor. Am. J. Physiol. 274:R655-R660.
Fenstermacher, J. D., Ghersi-Egea, J. F., Finnegan, W., and Shen, J. L. (1997). The rapid flow of cerebrospinal fluid from ventricles to cisterns via subarachnoid velae in the normal rat. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. (Wien) 70:285-287.
Gash, D., Sladek, J. R., Jr., and Sladek, C. D. (1980). Functional development of grafted vasopressin neurons. Science 210:1367-1369.
Giese, A., Rief, M. D., Loo, M. A., and Berens, M. E. (1994). Determinants of human astrocytoma migration. Cancer Res. 54:3897-3904.
Gross, P. M., Sposito, N. M., Pettersen, S. E., and Fenstermacher, J. D. (1986). Differences in function and structure of the capillary endothelium in gray matter, white matter and a circumventricular organ of rat brain. Blood Vessels 23:261-270.
Guan, X., Cravatt, B. F., Ehring, G. R., Hall, J. E., Boger, D. L., Lerner, R. A., and Gilula, N. B. (1997). The sleep-inducing lipid oleaminde deconvolutes gap junctions communication and calcium wave transmission in glial cells. J. Cell Biol. 139:1785-1792.
Herron, G. S., Banda, M. J., Clark, E. J., Gavrilovic, J., and Werb, Z. (1986). Secretion of metalloproteinases by stimulated capillary endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 261:2814-2818.
Hirano, A., and Matsui, T. (1975). Vascular structures in brain tumors. Hum. Pathol. 6:611-621.
Hoffman, D., Breakefield, X. O., Short, M. P., and Aebischer, P. (1993). Transplantation of a polymerencapsulated cell line genetically engineered to release NGF. Exp. Neurol. 122:100-106.
Jaeger, C. B. (1987). Morphological and immunocytochemical characteristics of PC12 cell grafts in rat brain. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 495:334-350.
Kaya, M., Chang, L., Truong, A., and Brightman, M. W. (1996). Chemical induction of fenestrae in vessels of the blood-brain barrier. Exp. Neurol. 142:6-13.
Kooistra, T. J., Opdenberg, J. P., Toet, K., Hendricks, H. F. J., Van den Hoogen, R. M., and Emeis, J. J. (1991). Stimulation of tissue-type plasminogen activator synthesis by retinoids in cultured human endothelial cells and rat tissue in vivo. Thromb. Haemostas. 65:565-572.
Krueger, J. M., Obal, F., Opp, M., Toth, L., Johannsen, L., and Cady, A. B. (1990). Somnogenic cytokines and models concerning their effects on sleep. Yale J. Biol. Med. 63:157-172.
Laske, D. W., Morrison, P. E., Lieberman, M., Corthesy, M. E., Reynolds, J. C., Stewart-Henney, P. A., Koong, S.-S., Cummins, A., Paik, C. H., and Oldfield, E. H. (1997). Chronic interstitial infusion of protein to primate brain: Determination of drug distribution and clearance with single photon emission computerized tomography imaging. J. Neurosurg. 87:586-594.
Laws, E. R., Jr., Goldberg, W. J., and Bernstein, J. J. (1993). Migration of human malignant astrocytoma cells in the mammalian brain: Scherer revisited. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 11:691-697.
Levick, J. R., and Smaje, L. H. (1987). An analysis of the permeability of a fenestra. Microvasc. Res. 33:233-256.
Lund-Johansen, M., Rucklidge, G. J., Milne, G., and Bjerkvig, R. (1991). A metalloproteinase capable of destroying cultured brain tissue isolated from rat glioma cells. Anticancer Res. 11:1001-1006.
McBain, C. J., Traynelis, S. F., and Dingledine, R. (1990). Regional variation of extracellular space in the hippocampus. Science 249:674-677.
Milhorat, T. H., Nobandegani, F., Miller, J. I., and Rao, C. (1993). Noncommunicating syringomyelia following occlusion of central canal in rats. J. Neurosurg. 78:274-279.
Morrow, B. A. Starcevic, V. P., Keil, L. C., and Severs, W. B. (1990). Intracranial hypertension after cerebroventricular infusions in conscious rats. Am. J. Physiol. 258:R1170-R1176.
Naparstek, Y., Cohen, I. R., Fuks, Z. V. I., and Vlodavsky, I. (1984). Activated T lymphocytes produce a matrix-degrading heparan sulphate endoglycosidase. Nature 310:241-244.
Nicholson, C., and Rice, M. E. (1986). The migration of substances in the neuronal microenvironment. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 481:55-71.
Pappas, G. D., and Sagen, J. (1988). Fine structural correlates of vascular permeability of chromaffin cell transplants in CNS pain modulatory regions. Exp. Neurol. 102:280-289.
Pino, R. M., and Essner, E. (1981). Permeability of rat choriocapillaris to hemoproteins. Restriction of tracers by fenestrated endothelium. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29:281-290.
Reith, A., and Rucklidge, G. J. (1992). Invasion of brain tissue by primary glioma: Evidence for the involvement of urokinase-type plasminogen activator as an activator of type IV collagenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 186:348-354.
Renkin, E. M. (1992). Cellular and intercellular transport pathways in exchange vessels. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 146:S28-S31.
Rennels, M. L., Gregory, T. F., Blaumanis, O. R., Fujimoto, K., and Grady, P. A. (1985). Evidence for a paravascular fluid circulation in the mammalian central nervous system, provided by the rapid distribution of tracer protein throughout the brain from the subarachnoid space. Brain Res. 326:47-63.
Roberts, W. G., and Palade, G. E. (1995). Increased microvascular permeability and endothelial fenestration induced by vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Cell Sci. 108:2369-2379.
Rosenstein, J. M., and Brightman, M. W. (1983). Circumventing the blood-brain barrier with autonomic grafts to brain surfaces. Science 221:879-881.
Sawaya, R., and Highsmith, R. (1988). Plasminogen activator activity and molecular weight patterns in human brain tumors. J. Neurosurg. 68:73-79.
Silver, R., LeSauter, J. L., Tresco, P. A., and Lehman, M. N. (1996). A diffusible coupling signal from the transplanted suprachiasmatic nucleus controlling circadian locomotor rhythms. Nature 382:810-813.
Stewart, P. A., and Hayakawa, K. (1994). Early ultrastructural changes in blood-brain barrier vessels of the rat embryo. Dev. Brain Res. 78:25-34.
Stoodley, M. A., Jones, N. R., and Brown, C. J. (1996). Evidence for rapid fluid flow from the subarachnoid space into the spinal central canal in the rat. Brain Res. 707:155-164.
Timpl, R. (1994). Proteoglycans of basement membranes. EXS 70:123-144.
Toole, B. P., Goldberg, R. L., Chi-Rosso, G., Underhill, C. B., and Orkin, R. W. (1984). Hyaluronate cell interactions. In Trelstad, R. L. (ed.), The Role of Extracellular Matrix in Development, Alan Liss, New York, pp. 43-66.
Unemori, E. N., Ferrara, N., Bauer, E. A., and Amento, P. (1992). Vascular endothelial growth factor induces interstitial collagenase expression in human endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 153:557-562.
Vladovsky, I., Miao, H. Q., Medalion, B., Danagher, P., and Ron, D. (1996). Involvement of heparan sulfate and related molecules in sequestration and growth promoting activity of fibroblastic growth factor. Cancer Metastas. Rev. 15:177-186.
Wakai, S., Meiselman, S., and Brightman, M. W. (1986). Muscle grafts as entries of blood-borne proteins into the extracellular space of the brain. Neurosurgery 18:548-554.
Weindl, A. (1973). Neuroendocrine aspects of circumventricular organs. In Ganong, W. F., and Martini, L. (eds.), Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, Oxford Press, New York, pp. 3-32.
Yan, Q., Matheson, C., Sun, J., Radeke, M. J., Feinstein, S. C., and Miller, J. A. (1994). Distribution of intracerebral ventricularly administered neurotrophins in rat brain and its correlation with Trk receptor expression. Exp. Neurol. 127:23-36.
Yanagishita, M. (1993). Function of proteoglycans in the extracellular matrix. Acta Pathol. Jpn. 43:283-293.
Yang, P., Yin, X., and Rutishauser, U. (1992). Intercellular space is affected by the polysialic acid content of NCAM. J. Cell Biol. 116:1487-1496.
Yoshida, Y., Yamada, M., Wakabayashi, K., and Ikuta, F. (1988). Endothelial fenstrae in the rat fetal cerebrum. Dev. Brain Res. 44:211-219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brightman, M.W., Kaya, M. Permeable Endothelium and the Interstitial Space of Brain. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20, 111–130 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006944203934
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006944203934