Abstract
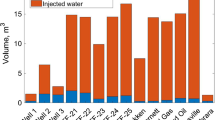
The first field data, collected over an 11 year period, are presented which indicate the possible effect of asphalt precipitation on the permeability and injectivity index of a fractured carbonate oil reservoir. The asphalt aggregates were formed during enhanced oil recovery by injection of a rich gas into the reservoir. The data indicate that, while at the initial stages of the operations the permeability and injectivity index decrease, at later times they appear to oscillate with the process time, with apparent oscillations' periods that depend on the heterogeneity of the reservoir. Two classes of plausible mechanisms that give rise to such oscillatory behavior are discussed. One relies on the changes in the structure of the reservoir's fractures, while the other one is based on asphalt precipitation in the reservoir. Computer simulations of flow and precipitation of asphalt aggregates in a pore network model of the reservoir are carried out. The results appear to support our proposition that asphalt formation and precipitation in the reservoir are the main mechanism for the observed behavior of the injectivity index. We also develop a stochastic continuum model that accurately predicts the time-dependence of the reservoir's permeability and injectivity index during the gas injection process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennet, C. O. and Myers, J. E.: 1974, Momentum, Heat, and Mass Transfer, 2nd edn, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Burke, N. E., Hobbs, R. E. and Kashou, S.F.: 1990, Measurement and modeling of asphaltene precipitation, J. Pet. Tech. 42, 1440.
Boduszynski, M. M.: 1987, Composition of heavy petroleums. 1. Molecular weight, hydrogen deficiency, and heteroatom concentration as a function of atmospheric equivalent boiling point up to 1400 °F, Energy & Fuels 1, 2.
Carnahan, N. F.: 1989, Paraffin deposition in petroleum production, J. Pet. Tech. 41, 1024.
Carnahan, N. F., Quintero, L., Pfund, D. M., Fulton, J. L., Smith, R. D., Capel, M. and Leontaritis, K.: 1993, A small angle X-ray scattering study of the effect of pressure on the aggregation of asphaltene fractions in petroleum fluids under near-critical solvent conditions, Langmuir 9, 2035.
Chang, C. and Fogler, H. S.: 1993, SPE Paper 25185.
Craft, B. C., Hawkins, M. F. and Terry, R. E.: 1990, Applied Petroleum Reservoir Engineering, 2nd edn, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey.
Dabir, B., Nematy, M., Mehrabi, A. R., Rassamdana, H. and Sahimi, M.: 1996, Asphalt flocculation and deposition: III. The molecular weight distribution, Fuel 75, 1633.
David, A.: 1973, Asphaltene flocculation during solvent simulation of heavy oils, AIChE Symp. Series, 69, 56.
Dickie, J. P., Haller, M. N., and Yen, T. F.: 1969, Electron microscopic investigations on the nature of petroleum asphaltics, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 29, 475.
Espinat, D. and Ravey, J. C.: 1993, SPE Paper 25187.
Fan, L. T., Nassar, R., Hwang, S. H. and Chou, S. T.: 1985, Analysis of deep bed filtration data: Modeling as a birth-death process, AIChE J. 31, 1781.
Goldman, A. J., Cox, R. G. and Brenner, H.: 1967, Slow viscous motion of a sphere parallel to a plane wall: I. Motion through a quiescient fluid, Chem. Eng. Sci. 22, 637.
Hirschberg, A., deJong, L. N. G., Schipper, B. A. and Meijer, J. G.: 1984, Influence of temperature and pressure on asphaltene flocculation, Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 24, 283.
Imdakm, A. O. and Sahimi, M.: 1991, Computer simulation of particle transport processes in flow through porous media, Chem. Eng. Sci. 46, 1977.
Katz, D. L. and Beu, K. E.: 1945, Nature of asphaltic substances, Ind. Eng. Chem. 37, 195.
Kawanaka, S., Park, S. J. and Mansoori, G. A.: 1991, Organic deposition from reservoir fluids: a thermodynamic predictive technique, SPE Reser. Eng. 6, 185.
Koots, J. A. and Speight, J. G.: 1975, Relation of petroleum resins to asphaltenes, Fuels 54, 179.
Lapidus, L. and Pinder, G. F.: 1982, Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations in Science and Engineering, Wiley, New York.
Leontaritis, K. J.: 1989, SPE Paper 18892.
Lichaa, P. M. and Herrera, L.: 1975, Electrical and other effects related to the formation and prevention of asphaltenes deposition, SPE Paper 5304.
Lihoreau, C., Briant, J. and Tindy, R.: 1967, Influence de la pression sur la flocculation des asphaltenes, Revue Inst. Francais Pét. 22, 797.
Liu, Y. C., Sheu, E. Y., Chen, S. H. and Storm, D. A.: 1995, Fractal structure of asphaltene in toluene, Fuel 74, 1352.
Litwinisyzn, J.: 1966, Colmatage-scouring in the light of stochastic birth-death, Bulletin De ´LAcadémie Polanaise Des Sciences, Serie des Sciences Techniques 14, 561.
Long, X. N. and Coombe, D. A.: 1997, Modeling asphaltene precipitation during primary depletion, Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 2, 170.
MacMillan, D. J., Tackett, J. E., Jr., Jessee, M. A. and Monger-McClure, T. G.: 1995, A unified approach to asphaltene precipitation: Laboratory measurement and modeling, J. Pet. Techn. 47, 788.
Monger, T. G.: 1984, The impact of oil aromaticity on carbon dioxide flooding, SPE/DOE Paper 12708.
Monger, T. G. and Fu, J. C.: 1987, The nature of CO2-induced organic deposition, SPE Paper 16713.
Monger, T. G. and Khakoo, A.: 1981, The phase behavior of CO2-appalacian oil systems, SPE Paper 10269.
Mozaffarian, M., Dabir, B., Sohrabi, M., Rassamdana, H. and Sahimi, M.: 1997, Asphalt flocculation and deposition: IV. Dynamic evolution of the heavy organic compounds, Fuel 76, 1479.
Preckshot, G. W., DeLisle, N. G., Cottel, C. E. and Katz, D. L.: 1943, Asphaltic substances in crude oils, Trans. AIME 151, 188.
Rassamdana, H., Dabir, B., Nematy, M., Farhani, M. and Sahimi, M.: 1996, Asphalt flocculation and deposition: I. The onset of precipitation, AIChE J. 41, 10.
Rassamdana, H., Farhani, M., Mozaffarian, M., Dabir, B. and Sahimi, M.: 1999, Asphalt flocculation and deposition: V. Phase behavior in miscible and immiscible injections, Energy & Fuels 13, 176.
Rassamdana, H. and Sahimi, M.: 1996, Asphalt flocculation and eposition: II. Formation and growth of fractal aggregates, AIChE J. 42, 3318.
Sahimi, M.: 1995, Flow and Transport in Porous Media and Fractured Rock, VCH, Weinheim, Germany.
Sahimi, M. and Imdakm, A. O.: 1991, Hydrodynamics of particulate motion in porous media, Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 1169.
Sahimi, M., Rassamdana, H. and Dabir, B.: 1997, Asphalt formation and precipitation: Experimental studies and theoretical modelling, Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 2, 157.
Sheu, E. Y., Liang, K. S., Sinha, S. K. and Overfield, R. E.: 1992, Polydispersity analysis of asphaltene solutions in toluene, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 153, 399.
Speight, J. G.: 1991, The Chemistry and Technology of Petroleum, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Standing, M. B.: 1977, Volumetric behavior of oil field hydrocarbon systems, SPE Paper 45154.
Storm, D. A., Sheu, E. Y. and DeTar, M. M.: 1993, Macrostructure of asphaltenes in vacuum residue by small-angle X-ray scattering, Fuel 72, 977.
Tuttle, R.M.: 1983, High-pour-point and asphaltic crude oils and condensates, J. Pet. Tech. 35, 1192.
Wu, J., Prausnitz, J. M. and Firoozabadi, A.: 1998, Molecular-based thermodynamics of asphalteneoil equilibria, AIChE J. 44, 1188.
Yarborough, L.: 1979, Application of a generalized equation of state to petroleum reservoir fluids, in: K. C. Chao and R. L. Robinson (eds), Equations of State in Engineering and Research, American Chemical Society, Washington.
Yen, T. F.: 1974, Structure of petroleum asphaltene and its significance, Energy Sources 1, 447.
Yen, T. F. and Chilingarian, G. V. (eds): 1994, Asphaltenes and Asphalts, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahimi, M., Mehrabi, A.R., Mirzaee, N. et al. The Effect of Asphalt Precipitation on Flow Behavior and Production of a Fractured Carbonate Oil Reservoir During Gas Injection. Transport in Porous Media 41, 325–347 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006759524127
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006759524127