Abstract
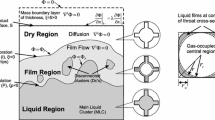
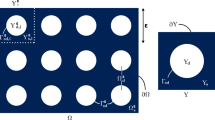
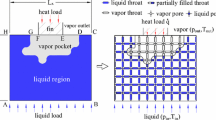
A multiscale network model is presented to model unsaturated moisture transfer in hygroscopic capillary-porous materials showing a broad pore-size distribution. Both capillary effects and water sorption phenomena, water vapour and liquid water transfer are considered. The multiscale approach is based on the concept of examining the porous space at different levels of magnification. The conservation of the water vapour permeability of dry material is used as scaling criterion to link the different pore scales. A macroscopic permeability is deduced from the permeabilities calculated at the different levels of magnification. Each level of magnification is modelled using an isotropic nonplanar 2D cross-squared network. The multiscale network simulates the enhancement of water vapour permeability due to capillary condensation, the hysteresis phenomenon between wetting and drying, and the steep increase of moisture permeability at the critical moisture saturation level. The calculated network permeabilities are compared with experimental data for calcium silicate and ceramic brick and a good agreement is observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blunt, M., King, J. M. and Scher, H.: 1992, Simulation and theory of two-phase flow in porous media, Phys. Rev. A 46(12), 7680-7699.
Chandler, R., Koplik, J., Lerman, K. and Willemsen, J. F.: 1982, Capillary displacement and percolation in porous media, J. Fluid Mech. 119, 249-267.
Diaz, C. E., Chatzis, I. and Dullien, F. A. L.: 1987, Simulation of capillary pressure curves using bond correlated site percolation on a simple cubic network, Transport in Porous Media 2(3), 215-240.
Constantinides, G. N. and Payatakes, A. C.: 1989, A three dimensional network model for consolidated porous media: basic studies, Chem. Engng. Comm. 81, 55-81.
Crank, J.: 1989, The Mathematics of Diffusion, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Crausse, P., Bacon, G. and Bories, S.: 1981, Etude fondamentale des transfers couplés chaleur-masse en milieu poreux, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 24(6), 991-1004.
Descamps, F.: 1997, Continuum and discrete modelling of isothermal water and air transfer in porous media, PhD Thesis, Catholic University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
Dullien, F. A. L.: 1979, Porous Media: Fluid Transport and Pore Structure, Academic Press, New York.
Durner, W.: 1994, Hydraulic conductivity estimations for soils with heterogeneous pore structure, Water Resour. Res. 30, 211-223.
Fatt, I.: 1956, The network model of porous media: III. The dynamic properties of networks with tube radius distribution, Trans. AIME Petrol. Div. 207, 164-177.
Gummerson, R. J., Hall, C., Hoff, W. D., Hawkes, R., Holland, G. N. and Moore, W. S.: 1979, Unsaturated water flow within porous materials observed by NMRimaging, Nature 281, 56-57.
Ioannidis, M. A. and Chatzis, I.: 1993, Network modelling of pore structure and transport properties of porous media, Chem. Engng. Sci. 48(5), 951-972.
Jerauld, G. R., Hatfield, J. C., Scriven, L. E. and Davis, H. T.: 1984, Percolation and conduction on Voronoi and triangular networks: a case study in topological disorder, J. Phys. C 17, 1519-1529.
Kamp, C. L.: 1988, Le transfert d´humidité dans la pâte de ciment durcie, Chantier Suisse 19(5), 419-424.
Koplik, J.: 1982, Creeping flow in two-dimensional networks, J. Fluid Mech. 119, 219-247.
Koplik, J. and Lasseter, T. J.: 1985, Two-phase flow in random network models of porous media, Soc. Petrol. Engng. J. 25, 89-100.
Lenormand, R., Toboul, E. and Zarcone, C.: 1988, Numerical models and experiments on immiscible displacements in porous media, J. Fluid Mech. 189, 165-187.
Lin, C. and Cohen, M. H.: 1982, Quantitative methods for microgeometric modelling, J. Appl. Phys. 53, 4152-4165.
Neimark, A. V.: 1989, Multiscale percolation systems, Sov. Phys. JETP 69(4), 786-791.
Payatakes, A. C. and Dias, M. M.: 1984, Immiscible microdisplacement and ganglin dynamics in porous media, Rev. Chem. Engng. 85-174.
Philip, J. R.: 1955, Numerical solution of equations of the diffusion type with diffusivity concentration-dependent, Trans. Faraday Soc. 51, 885-892.
Philip, J. R. and de Vries, D. A.: 1957, Moisture movement in porous materials under temperature gradients, Trans. Am. Geophys. Un. 38, 222-232.
Prat, M.: 1995, Isothermal drying of non-hygroscopic capillary-porous materials as an invasion percolation process, Int. J. Multiphase Flow 21(5), 875-892.
Quenard, D.: 1989, Adsorption et transfer d´humidité dans les matériaux hygroscopiques. Approche du type percolation et expérimentations, PhD Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse, Toulouse, France.
Sahimi, M.: 1993, Flow phenomena in rocks: from continuum models to fractals, percolation, cellular automata, and simulated annealing, Rev. Modern Phys. 65, 1393-1534.
Schirmer, R.: 1938, Die Diffusionszahl von Wasserdampf-Luftgemischen und die Verdampfungsgeschwindigkeit, VDI Beiheft Verfahrestechnik 6, 170.
Soll, W. E. and Celia, M. A.: 1993, A modified percolation approach to simulating three-fluid capillary pressure-saturation relationships, Adv. Water Res. 16, 107-126.
Wilkinson, D. and Willemsen, J. F.: 1983, Invasion percolation: a new form percolation theory, J. Phys. A 16, 3365-3376.
Wilson, K. G.: 1971, Renormalization and critical phenomena, Phys. Rev. B 4(9), 174-184.
Wise, W. R.: 1992, A new insight on pore structure and permeability, Water Resour. Res. 28, 189-198.
Xu, K., Daian, J.-F. and Quenard, D.: 1997, Multiscale structures to describe porous media, Part I: theoretical background and invasion by fluids, Transport in Porous Media 26, 51-73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carmeliet, J., Descamps, F. & Houvenaghel, G. A Multiscale Network Model for Simulating Moisture Transfer Properties of Porous Media. Transport in Porous Media 35, 67–88 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006500716417
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006500716417