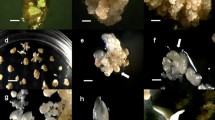
Abstract
Different NAA plus kinetin or BA combinations were tested on Francia Pernod fennel seedlings for callus induction and plant regeneration. Callogenesis from hypocotyls was obtained in all auxin/cytokinin-containing media. The organogenic response was observed especially in presence of NAA plus kinetin. The highest frequency of shoot regeneration was found when the auxin and kinetin were used at a 1:1 ratio. Moreover, a prolonged culture period increased shoot formation. Somatic embryogenesis was tested on several fennel populations. The results gave evidence of the genotypic importance. Two different protocols were used for somatic embryo induction. Using the first protocol among the different fennel genotypes tested, only Francia Pernod showed embryogenic capacity. In this case, from a primary non-embryogenic callus cultured for 12 months in presence of 2,4-D, an embryogenic secondary callus was produced. When transferred to the medium without 2,4-D (agarized or liquid), this gave embryogenic plants in high frequency. As far as the second embryogenic method is concerned, secondary embryogenic callus developed only in the presence of 2,4-D plus kinetin in Francia Pernod genotype. Thereafter, the replacement of those growth regulators by GA3 into the medium greatly increased the somatic embryo development, especially in `Francia Pernod', but also in `Aboca erbe' callus, a population with a very poor embryogenic capacity. In Francia Pernod, the primary and secondary (embryogenic) calli showed different morphological and histological responses, either when the secondary callus was induced by 2,4-D alone or by 2,4-D plus kinetin. Ontogenetic processes leading to somatic embryo formation are described in this context.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemanno L, Berthouly M & Michaux-Ferrière N (1996) Histology of somatic embryogenesis from floral tissues cocoa. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 46: 187–194
Anzidei M, Vivona L, Schiff S & Bennici A (1996) In vitro culture of Foeniculum vulgare: callus characteristics in relation to morphogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 45: 263–268
Becker H (1970) Untersuchungen zur Frage der Bildung flüchtiger Stoffwechselprodukte in Calluskulturen. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanzen 161: 425–441
Button J, Kochba J & Bornman CH (1974) Fine structure of an embryoid development from embryogenic ovular callus of 'shamouti' Orange (Citruss inensis Osb.). J. Exp. Bot. 25: 446–457
Culafic L, Budimir S, Vujicic R & Neskovic M (1987) Induction of somatic embryogenesis and embryo development in Rumex acetosella L. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 11: 133–139
Du Manoir J, Desmarest P & Saussay R (1985) In vitro propagation of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Miller). Sci. Hortic. 27: 15–19
Feder N & O'Brien TP (1968) Plant microtechnique: some principles and new method. Am. J. Bot. 55: 123–142
Fisher DB (1968) Protein staining of ribboned epon sections for light microscopy. Histochemie 16: 92–96
Garcia-Rodriguez MJ, Paupardin C & Saussay R (1978) Sur la formation d'un tissu sécréteur et la synthèse d'anéthole par des tissus de Fenouil (Foeniculum vulgare Miller var. Dulce) cultivés in vitro. CR Acad. Sci. Paris 287: 693–696
Gibbons IR & Grimstone AV (1960) On the flagellate structure in certain flagellates. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 7: 697–716
Hunault G (1981) La culture in vitro des tissus de Fenouil (Foeniculum vulgare Miller). Premières observations sur le comportement des explantats primitifs et des cals. CR Acad. Sci. Paris 293: 553–558
Hunault G (1984) In vitro culture of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.) from cell suspension to mature plant. Sci. Hortic. 22: 55–65
Hunault G, Desmarest P & Du Manoir J (1989) Foeniculum vulgare Miller: Cell culture, regeneration, and the production of anethole. In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol. 7, Medicinal and Aromatic Plants II (pp 185–211). Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg
Hunault G & Du Manoir (1992) Micropropagation of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Miller). In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol 19, High-Tech and Micropropagation III (pp 199–217). Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg
Hunault G & Maatar A (1995) Enhancement of somatic embryogenesis frequency by giberellic acid in fennel. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 41: 171–176
Kononowicz H & Janick J (1984) Response of embryogenic callus of Theobroma cacao L. to gibberellic acid and inhibitors of gibberellic acid synthesis. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 113: 359–366
Jensen WA (1962) Botanical Histochemistry-Principles and Practice. WH Freeman, San Francisco (p 96).
Lakshmi Sita G (1986) Sandalwood (Santalum album L). In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol I, Trees I (pp 363–374). Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg
Lu C & Vasil IK (1985) Histology of somatic embryogenesis in Panicum maximum (Guinea grass). Am. J. Bot. 72: 1908–1913
Maheshwari SC & Gupta GRP (1965) Production of adventitious embryoids in vitro from stem callus of Foeniculum vulgare. Planta 67: 384–386
Martoja R & Martoja M (1967) Initiation aux Techniques de l'Histologie Animale. Masson et Cie, Paris
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 479–497
Nagmani R, Becwar MR & Wann SR (1987) Single-cell origin and development of somatic embryos in Picea abies (L.) Karst. (Norway spruce) and P. glauca (Moench) Voss (white spruce). Plant Cell Rep. 6: 157–159
Paupardin C, Garcia-Rodriguez MJ & Bricout J (1980) Multiplication végétative de quelques plantes aromatiques: problèmes possés par la production d'essence. C.R. Acad. Agric. Fr. 66: 658–666
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17: 208–212
Theiler-Hedtrich R & Kägi AC (1991) Cloning in vitro and somatic embryogenesis in Foeniculum vulgare Mill. (Fennel) of 'Zefa fino' and 'Zefa tardo'. Acta Hortic. 300: 287–291
Thorpe TA (1993) In vitro organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis: physiological and biochemical aspects. In: Roubelakis-Angelakis KA & Tran Thanh Van (eds) Morphogenesis in Plants (pp 19–38). Plenum Press, New York
Toonen MAJ & de Vries SC (1996) Initiation of somatic embryos from single cells. In: Wang TL & Cuming A (eds) Embryogenesis – The Generation of a Plant (pp 173–189). Bios Scientific Publisher, UK
Vieitez AM & Barciela J (1990) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from embryonic tissues of Camellia japonica L. Plant Cell Tiss. Org: Cult. 21: 267–274
Vieitez FJ, Ballester A & Vieitez AM (1992) Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from cell suspension cultures of Fagus sylvatica L. Plant Cell Rep. 11: 609–613
Xiao XG & Branchard M (1993) Embryogenesis and plant regeneration of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) from hypocotyl segments. Plant Cell Rep. 13: 69–71
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anzidei, M., Bennici, A., Schiff, S. et al. Organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis in Foeniculum vulgare: histological observations of developing embryogenic callus. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 61, 69–79 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006454702620
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006454702620