Abstract
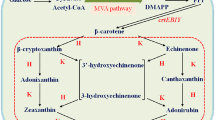
Metabolic engineering of the early non-mevalonate terpenoid pathway of Escherichia coli was carried out to increase the supply of prenyl pyrophosphates as precursor for carotenoid production. Transformation with the genes dxs for over-expression of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase, dxr for 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase and idi encoding an isopentenyl pyrophosphate stimulated carotenogenesis up to 3.5-fold. Co-transformation of idi with either dxs or dxr had an additive effect on ß-carotene and zeaxanthin production which reached 1.6 mg g−1 dry wt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht M, Takaichi S, Misawa N, Schnurr G, Böger P, Sandmann G (1997) Synthesis of atypical cyclic and acyclic hydroxy carotenoids in Escherichia coli transformants. J. Biotechnol. 58: 177–185.
Borovkov AY, Rivkin MI (1997) pBBR1MCS: XcmI-containing vector for direct cloning of pcr products. BioTechniques 22: 812–814.
Johnson EA, Schroeder WA (1995) Microbiol carotenoids. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 53: 119–178.
Kajiwara S, Fraser PD, Kondo K, Misawa N (1997) Expression of an isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase gene enhances isoprenoid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochem. J. 324: 421–426.
Misawa N, Satomi Y, Kondo K, Yokoyama A, Kajiwara S, Daito T, Ohtanai T, Miki W (1995) Structure and functional analysis of a marine bacterial carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster and astaxanthin biosynthetic pathway proposed at the gene level. J. Bacteriol. 177: 6575–6584.
Neudert U, Martínez-Férez I, Fraser PD, Sandmann G (1998) Expression of an active phytoene synthase from Erwinia uredovora and biochemical properties of the enzyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1392: 51–58.
Ohnuma S, Suzuki M, Nishino T (1994) Archebacterial ether-linked lipid biosynthetic gene. Expression, cloning, sequencing and chracterization of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 14792–14797.
Ruther A, Misawa N, Böger P, Sandmann G (1997) Production of zeaxanthin in Escherichia coli transformed with different carotenogenic plasmids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 48: 162–167.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Sandmann G, Albrecht M, Schnurr G, Knörzer O, Böger P (1999) The biotechnological potential and design of novel carotenoids by gene combination in Escherichia coli. Trends Biotechnol. 17: 233–237.
Sprenger GA, Schorken U, Wiegert T, Grolle S, Graaf AA, Taylar SV, Begley TP, Bringer-Meyer S, Sahm H (1997) Identification of a thiamin-dependent synthase in Escherichia coli required for the formation of the 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate precursor to isoprenoids, thiamin and pyridoxal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 94: 12857–12862.
Takahashi S, Kuzuyama T, Watanabe H, Seto H (1998) A 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase catalyzing the formation of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 95: 9879–9884.
Wang C-W, Oh M-K, Liao J (1999) Engineered isoprenoid pathway enhances astaxanthin production in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioengin. 62: 235–241.
Weiner JH, Limire BD, Elmer ML, Bradley RD, Douglas G (1984) Overproduction of fumarate reductase in Escherichia coli induces a novel intracellular lipid-protein organelle. J. Bacteriol. 158: 590–596.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albrecht, M., Misawa, N. & Sandmann, G. Metabolic engineering of the terpenoid biosynthetic pathway of Escherichia coli for production of the carotenoids β-carotene and zeaxanthin. Biotechnology Letters 21, 791–795 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005547827380
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005547827380