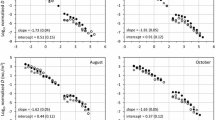
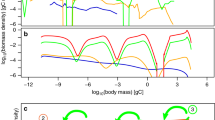
Abstract
We studied the use of size distributions as a response variable in limnological experiments. Previous quantifications of size distributions were incomplete or difficult to use in experimental settings, and we developed a multivariate approach that more fully describes the shape and biomass of planktonic and benthic size distributions. We re-evaluate the hypothesis that fish affect the shape and nutrients affect the biomass of size distributions, and show that the multivariate approach is more responsive to detecting treatment effects. In a mesocosm experiment, we use this new quantification and analysis of size distributions to detect the main and interactive effects of nutrient addition and sediment type on both benthic and pelagic size distributions. Size distributions in both habitats responded to the nutrient and sediment treatments, indicating linkage since a treatment applied in one habitat affected the size distribution in the opposite habitat. Since size distributions reduce each habitat into a common currency, we were able to examine the nature of the linkage. The relative response of each habitat to the nutrient treatment was different with regard to the shape of the distributions, while the relative response to the sediment treatment was different with regard to the biomass in the distributions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens, M. A. & R. H. Peters, 1991. Patterns and limitations in limnoplankton size spectra. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 48: 1967–1978.
Almond, M. J. R., E. Bentzen & W. D. Taylor, 1996. Size structure and species composition of plankton communities in deep Ontario lakes with and without Mysis relicta and planktivorous fish. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 53: 315–325.
APHA, 1995. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 19th edn. In Eaton, A.D., L. S. Clesceri & A. E. Greenberg (eds), Washington, DC: 4.106-4.116 Baca, R. M., 1998. The use of size distributions in ecological experiments. PhD dissertation, University of Mississippi; 168 pp.
Bak, R. P. M. & E. H. Meesters, 1998. Coral population structure: the hidden information of colony size-frequency distributions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 162: 301–306.
Bock, R. D., 1975. Multivariate Statistical Methods in Behavioral Research, McGraw-Hill, New York, 623 pp.
Cattaneo, A., 1993. Size spectra of benthic communities in Laurentain Streams. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 50: 2659–2666.
Cuker, B. E., P. T. Gama & J. M. Burkholder, 1990. Type of suspended clay influences lake productivity and phytoplankton community response to phosphorus loading. Limnol. Oceanogr. 35: 830–839.
Cuker, B. E. & L. Hudson, Jr., 1992. Type of suspended clay in-fluences zooplankton response to phosphorus loading. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37: 566–576.
Drenner, R. W. & J. D. Smith, 1991. Biomass-dependent effects of mosquitofish on zooplankton, chlorophyll and the size distribution of particulate phosphorus. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 24: 2382–2386.
Drenner, R. W., S. T. Threlkeld & M. D. McCracken, 1986. Experimental analysis of the direct and indirect effects of an omnivorous filter-feeding clupeid on plankton community structure. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 43: 1935–1945.
Drenner, R. W., S. T. Threlkeld, J. D. Smith, J. R. Mummert & P. A. Cantrell, 1989. Interdependence of phosphorus, fish, and site effects on phytoplankton biomass and zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 34: 1315–1321.
Duplisea, D. E., S. R. Kerr & L. M. Dickie, 1997. Demersal fish biomass size spectra on the Scotian Shelf, Canada: species replacement at the shelfwide scale. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 54, 1725–1735.
Gaedke, U., 1992. The size distribution of plankton biomass in a large lake and its seasonal variability. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37: 1202–1220.
García, C.M., F. Echevarría & F.X. Niell, 1995. Size structure of plankton in a temporary, saline inland lake. J. Plankton Res. 17: 1803–1817.
Gerlach, S. A., A. E. Hahn & M. Schrage, 1985. Size spectra of benthic biomass and metabolism. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 26: 161–173.
Kirk, K. L. & J. J. Gilbert, 1990. Suspended clay and the population dynamics of planktonic rotifers and cladocerans. Ecology 71: 1741–1755.
Koenings, J. P., R. D. Burkett & J. M. Edmundson, 1990. The exclusion of limnetic Cladocera from turbid glacier-meltwater lakes. Ecology 71: 57–67.
Hanson, J. M., 1990. Macroinvertebrate size-distributions of two contrasting freshwater macrophyte communities. Freshwat. Biol. 24: 481–491.
Hanson, J. M., E. E. Prepas & W. C. Mackay, 1989. Size distribution of the macroinvertebrate community in a freshwater lake. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 46: 1510–1519.
Jónasson, P. M., 1978. Zoobenthos of lakes. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 20: 13–37.
Jonasz, M. & G. Fournier, 1996. Approximation of the size distribution of marine particles by a sum of log-normal functions. Limnol. Oceanogr. 41: 744–754.
Lazzaro, X., R. W. Drenner, R. A. Stein & J. D. Smith, 1992. Planktivores and plankton dynamics: effects of fish biomass and planktivore type. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 49: 1466–1473.
Lean, D. R. S., 1973. Phosphorus dynamics in lake water. Science 179: 678–680.
Mazumder, A., D. J. McQueen, W. D. Taylor & D. R. S. Lean, 1988. Effects of fertilization and planktivorous fish (yellow perch) predation on size distribution of particulate phosphorus and assimilated phosphate: large enclosure experiments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33: 421–430.
McCauley, E. & F. Briand, 1979. Zooplankton grazing and phytoplankton species richness: field tests of the predation hypothesis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24: 243–252.
Menzel, D. W. & N. Corwin, 1965. The measurement of total phosphorus in seawater based on the liberation of organically bound fractions by persulfate oxidation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 10: 280–282.
Morin, A. & D. Nadon, 1991. Size distribution of epilithic lotic invertebrates and implications for community metabolism. J. n. am. Benthol. Soc. 10: 300–308.
Peters, R. H., 1983. Size structure of the plankton community along the trophic gradient of Lake Memphremagog. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 40: 1770–1778.
Platt, T. & K. Denman, 1977. Organisation in the pelagic ecosystem. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunt. 30: 575–581.
Plumb, R. H., Jr, 1981. Procedure for handling and chemical analysis of sediment and water samples. USEPA/COE, Technical Report EPA/CE-81-1.
Prairie, Y. T, 1996. Evaluating the predictive power of regression models. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 53: 490–492.
Ramsay, P. M., S. D. Rundle, M. J. Attrill, M. G. Uttley, P.R. Williams, P.S. Elsmere & A. Abada, 1997. A rapid method for estimating biomass size spectra of benthic metazoan communities. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 54: 1716–1724.
Rasmussen, J. B., 1993. Patterns in the size structure of littoral zone macroinvertebrate communities. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 50: 2192–2207.
Real, M., F. Sabater & J. A. Morguí, 1992. Significant physiographic disturbances in the Ebro basin reservoirs (N.E. Spain) reflected by Oligochaeta size spectra. Hydrobiologia 235/236 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 75): 363–374.
Rhew, K., R. M. Baca, C. A. Ochs & S. T. Threlkeld, 1999. Interaction effects of fish, nutrients, mixing and sediments on autotrophic picoplankton and algal composition. Freshwat. Biol. 42: 99–109.
Rodríguez, J., F. Echevarría & F. Jiménez-Gómez, 1990. Physiological and ecological scalings of body size in an oligotrophic, high mountain lake (La Caldera, Sierra Nevada, Spain). J. Plankton Res. 12: 593–599.
Rodríguez, J. & M. M. Mullin, 1986. Relation between biomass and body weight of plankton in a steady state oceanic system. Limnol. Oceanogr. 31: 361–370.
Rojo, C. & J. Rodríguez, 1994. Seasonal variability of phytoplankton size structure in a hypertrophic lake. J. Plankton Res. 16: 317–335.
Ruiz, J., 1994. The measurement of size diversity in the pelagic ecosystem. Sci. Mar. 58: 103–107.
SAS Institute, 1988. SAS/STAT User's Guide 6.03, SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, 1028 pp.
Schwinghamer, P., 1981. Characteristic size distributions of integral benthic communities. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 38: 1255–1263.
Schwinghamer, P., 1984. Observations on size-structure and pelagic coupling of some shelf and abyssal benthic communities. In Gibbs. P. E. (ed.), Proceedings of the Nineteenth European Marine Biology Symposium in Plymouth, Devon, U.K., Cambridge University Press: 347–359.
Sheldon, R. W. & T. R. Parsons, 1967. A continuous size spectrum for particulate matter in the sea. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 24: 909–915.
Sheldon, R. W., A. Prakash & W. H. Sutcliffe, Jr, 1972. The size distribution of particles in the ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17: 327–340.
Sprules, W. G., J. M. Casselman & B. J. Shuter, 1983. Size distribution of pelagic particles in lakes. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 40: 1761–1769.
Sprules, W. G. & A. P. Goyke, 1994. Size-based structure and production in the pelagia of Lakes Ontario and Michigan. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 51: 2603–2611.
Sprules, W. G. & M. Munawar, 1986. Plankton size spectra in relation to ecosystem productivity, size and perturbation. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 43: 1789–1794.
Stevens, J., 1992. Applied Multivariate Statistics for the Social Sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, 629 pp.
Strayer, D., 1986. The size structure of a lacustrine zoobenthic community. Oecologia 69: 513–516.
Tabachnick, B. G. & L. S. Fidell, 1996. Using Multivariate Statistics, Harper Collins Publishers Inc., New York, 880 pp.
Threlkeld, S. T., 1994. Benthic-pelagic interactions in shallow water columns: an experimentalist's perspective. Hydrobiologia 275/276: 293–300.
Tittel, J., B. Zippel, W. Geller & J. Seeger, 1998. Relationships between plankton community structure and plankton size distribution in lakes of northern Germany. Limnol. Oceanogr. 43: 1119–1132.
Van Veldhoven, P. P. & G. P. Mannaerts, 1987. Inorganic and organic phosphate measurements in the nanomolar range. Anal. Biochem. 161: 45–48.
Vidondo, B., Y. T. Prairie, J. M. Blanco & C. M. Duarte, 1997. Some aspects of the analysis of size spectra in aquatic ecology. Limnol. Oceanogr. 42: 184–192.
Warwick, R. M., N. R. Collins, J. M. Gee & C. L. George, 1986. Species size distributions of benthic and pelagic Metazoa: evidence for interaction? Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 34: 63–68.
Warwick, R. M. & I. R. Joint, 1987. The size distribution of organisms in the Celtic Sea: from bacteria to Metazoa. Oecologia 73: 185–191.
Zar, J. H., 1984. Biostatistical Analysis. Second edn. Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewood Cliffs, 718 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baca, R.M., Threlkeld, S.T. Using size distributions to detect nutrient and sediment effects within and between habitats. Hydrobiologia 435, 197–211 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004118000669
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004118000669