Abstract
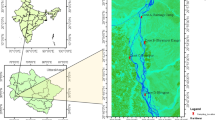
Phytoplankton of the River Seonath, a major tributary of Mahanadi river system, was studied for 15 months together with physical–chemical variables in relation to a pollution gradient. Multivariate analysis and ordination by Principal Components Analysis of the physical–chemical variables and phytoplankton density indicated a community replacement along a pollution gradient. The dominant benthic diatom community, mainly comprising Achnanthes trigibba and A. affinis of the upstream was replaced by Chlorophycea at the middle stretch and Cyanophycea at the downstream sites. Chlorella, Scenedesmus and Coelastrum dominated among Chlorophyceae in the middle stretch in the highly polluted sites, followed by the Cyanophycean assemblage of Microcystis and Merismopedia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, T. F. H. & J. H. Koonce, 1973. Multivariate approaches to algal strategiems and tactics in systems analysis of phytoplankton. Ecology 54: 1234–1246.
American Public Health Association, 1980. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Sewage and Industrial Wastes APHA, AWWA, WPCF Washington: 1193 pp.
Del Giorgio, P. A., A. L. Vinocur, R. J. Lombardo & H. G. Tell, 1991. Progressive changes in the structure and dynamics of the phytoplankton community along a pollution gradient in a lowland river a multivariate approach. Hydrobiologia 224: 129–154.
Golterman, H. L. & R. S. Clymo, 1971. Methods for Chemical Analysis of Freshwater. Blackwell, London: 166 pp.
Govindan, V. S. & B. B. Sunderesan, 1979. Seasonal succession of algal flora in the region of Adyar River. Indian. J. Envir. Health 21: 131–142.
Joy, C. M., K. P. Balkrishnan & A. Joseph, 1990. Physicochemical aspects of a tropical river receiving industrial effluents In Trivedy, R. K. (ed.), River Pollution in India, Ashish Publishing House, New Delhi: 219–236.
Khanna, D. R., 1993. Ecology and pollution of Ganga River. Ashish Publishing House, New Delhi: 290 pp.
Krishnamurthi, C. R., K. S. Bilgrami., T. M. Das & R. P. Mathur, 1991. The Ganga: a Scientific Study. Northern Book Center, New Delhi, India: 246 pp.
Laxminarayana, J. S. S., 1965 Studies on the phytoplankton of the River Ganges, Varanasi, India. Hydrobiologia 25: 119–175.
Nandan, S. B. & R. J. Patel, 1992. Ecological studies of algae. In Mishra S. R. & D. N. Saksena (eds), Aquatic Ecology. Ashish Publishing House, New Delhi: 331 pp.
O'Farrel, I., 1994. Phytoplankton ecology and limnology of the Salado River (Buenos Aires, Argentina). Hydrobiologia 271: 168–178.
O'Farrel, I. & Izaguirre, 1994. Phytoplankton ecology and limnology of the River Uruguay Lower Basin (Argentina). Arch. Hydrobiol. 99: 155–179.
O'Farrel, I., Izaguirre & A. Vinocur, 1996. Phytoplankton ecology of the Lower Parana River (Argentina). Arch. Hydrobiol. 115: 75–89.
Pahwa, D. V. & S. N. Mehrotra, 1966. Observations on fluctuations in the abundance of plankton in relation to certain hydrobiological conditions of River Ganga. Proc. Nat Acad. Sci. India 36: 157–159.
Pielou, E. C., 1984. The Interpreatation of Ecological Data. Wiley, New York: 263 pp.
Rai, L. C., 1978. Ecological studies of algal communities of river Ganges at Varanasi. Ind. J. Ecol. 5: 1–6.
Rai, S. V. R., V. P. Singh & L. P. Mall, 1978. Pollution studies of river Khan (Indore) India. I Biological assessment of pollution. Wat. Res. 12: 555–559.
Sabata, B. C. & M. Nayar, 1995. River Pollution in India. Ashish Publishing House New Delhi: 223 pp.
Sabater, S., F. Sabatar & X. Tomas, 1987. Water quality and diatom community in two Catalan Rivers N. E. Spain. Wat. Res. 21: 90–911.
Sabater, S. & F. Sabatar, 1988. Relationship between diatom assemblages and physico-chemical variables in the river Ter. (N.E. Spain). Int. Rev. ges. Hydrobiol. 73: 171–179.
Sabater, S. & F. Sabater, 1992. Longitudinal changes of benthic algal biomass in a mediteranean river during two high production periods. Arch. Hydrobiol. 124: 475–487.
Shukla, A. C. & Anjum 1991, Biological aspects of Ganga river ecosystem In Gopal, B. & Asthana (eds), Aquatic Sciences in India South Asian Publ. New Delhi: 93–109.
Unni, K. S., 1996. Ecology of River Narmada. Ashish Publishing House, New Delhi: 371 pp.
Venkateswarlu, V., 1970 An ecological study of algae of river Moosi. iv Periodicity of some common species of algae. Hydrobiologia 35: 45–64.
Wetzel, R. G. & G. Likens, 1979 Limnological Analysis. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia: 357 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unni, K.S., Pawar, S. The phytoplankton along a pollution gradient in the river Mahanadi (M.P. state) India – a multivariate approach. Hydrobiologia 430, 87–96 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004025231206
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004025231206