Abstract
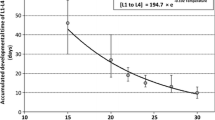
Larval development and seasonal regulation in a spring-emerging gomphid dragonfly, Asiagomphus pryeri (Selys), was investigated mainly by repeated sampling in the field and also by laboratory experiments. Eggs exhibited direct development. Larval duration was usually 3 or 4 years. Larvae in the penultimate instar (i.e. F-1) that entered the final instar (F-0) synchronously in their third autumn emerged in the following spring but F-1 of the same age-cohort that failed to enter F-0 in the autumn did not emerge in the following spring (i.e. cohort splitting); they had a smaller head width, underwent a supernumerary ecdysis and entered F-0 in the following autumn together with a cohort one year younger. Reduction of temporal variation in emergence, which lasted about 3 weeks, from late May to mid June, was achieved by synchronized entry to F-0 in the previous autumn. No additional synchronisation was detected in the overwintering F-0 population. Long-day photoperiod (LD 15:9; corresponding to the summer solstice) induced in F-1 intense diapause which was terminated by intermediate photoperiod (LD 13:11; the equinox). In nature, such photoperiodic responses apparently mediate the synchronous entry to F-0 in autumn. Discussion on the mechanisms of seasonal regulation is made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando, H., 1962. The comparative embryology of Odonata with special reference to a relic dragonfly Epiophlebia superstes Selys. Jap. Soc. for Promotion of Sci., Tokyo, 205 pp.
Aoki, T., 1991. A survey record on the gomphid fauna of Kobe City, Hyogo Prefecture. Gracile 46: 13–17 (in Japanese).
Aoki, T., 1993. Larval development in Asiagomphus pryeri (Selys) in nature I. Tombo 36: 35–38 (in Japanese).
Aoki, T., 1994. Larval development in Asiagomphus pryeri (Selys) in nature II. Hatching, larval period, number of instars and emergence. Tombo 37: 31–36 (in Japanese).
Bennett, S. & P. J. Mill, 1993. Larval development and emergence in Pyrrhosoma nymphula (Sulzer) (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae). Odonatologica 22: 133–145.
Corbet, P. S., 1954. Seasonal regulation in British dragonflies. Nature 174: 655, 777.
Corbet, P. S., 1957. The life history of the Emperor Dragonfly Anax imperator Leach (Odonata: Aeshnidae). J. Anim. Ecol. 26: 1–69.
Corbet, P. S., 1962. A biology of dragonflies. Witherby, London, 247 pp.
Corbet, P. S. & I. F. Harvey, 1989. Seasonal regulation in Pyrrhosoma nymphula (Sulzer) (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae) 1. Seasonal development in nature. Odonatologica 18: 133–145.
Corbet, P. S., I. F. Harvey, J. Abisgold & F. Morris, 1989. Seasonal regulation in Pyrrhosoma nymphula (Sulzer) (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae) 2. Effect of photoperiod on larval development in spring and summer. Odonatologica 18: 333–348.
Danks, H. V., 1987. Insect dormancy: an ecological perspective. Biol. Survey of Canada Monograph 1, 439 pp.
Fukui, M., 1982. Dragonflies at Tsudagawa-River. Suruga no Konchu 116: 3401–3412 (in Japanese).
Hamada, K. & K. Inoue, 1985. The dragonflies of Japan in colour. Kodansha, Tokyo, 371 pp (in Japanese).
Ingram, B. R. & C. E. Jenner, 1976. Life histories of Enallagma hageni (Walsh) and E. aspersum (Hagen) (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae). Odonatologica 5: 331–345.
Ishida, S., K. Ishida, K. Kojima & M. Sugimura, 1988. Illustrated guide for identification of the Japanese Odonata. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pls. 72 + figs. 105 + 140 pp (in Japanese).
Kobe Marine Meteorological Observatory, 1991–1996. Monthly report of meteorological observations. Kobe (in Japanese).
Kondoh, S., 1993. How to breed small larvae of dragonflies by using zoea of Brine Shrimp as their food. Gracile 50: 1–3. (in Japanese).
Kurata, M., 1971. Life history of Gomphus melaenops. Tombo 14: 6–11 (in Japanese).
Müller, O., 1995. Ökologiche Untersuchungen an Gomphiden (Odonata: Gomphidae) unter besonderer Berücksichtigung ihrer Larvenstadien. Dissertation Dr.rer.nat., Humboldt-Universität of Berlin.
Norling, U., 1976. Seasonal regulation in Leucorrhinia dubia (Vander Linden) (Anisoptera: Libellulidae). Odonatologica 5: 245–263.
Norling, U., 1984a. Life history patterns in the northern expansion of dragonflies. Adv. Odonatol. 2: 127–156.
Norling, U., 1984b. Life cycle and larval photoperiodic responses of Coenagrion hastulatum (Charpentier) in two climatically different areas (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae). Odonatologica 13: 429–449.
Norling, U., 1984c. Photoperiodic control of larval development in Leucorrhinia dubia (Vander Linden): A comparison between populations from northern and southern Sweden (Anisoptera: Libellulidae). Odonatologica 13: 529–550.
Schütte, C., P. Schridde & F. Suhling, 1998. Life histroy patterns of Onychogomphus uncatus (Charpentier). (Anisoptera: Gomphidae). Odonatologica 27: 71–86.
Suhling, F., 1995. Temporal patterns of emergence of the riverine dragonfly Onychogomphus uncatus (Odonata: Gomphidae). Hydrobiologia 302: 113–118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoki, T. Larval development, emergence and seasonal regulation in Asiagomphus pryeri (Selys) (Odonata: Gomphidae). Hydrobiologia 394, 179–192 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003626011117
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003626011117