Abstract
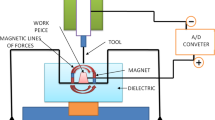
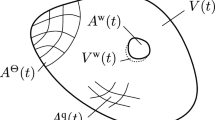
The effect of thermal-fluid properties are considered in the numerical simulation of the tool shape for a given workpiece shape in electrochemical machining. An embedding method is used for this inverse problem. A bubbly two-phase, one-dimensional flow model and a one-phase, two-dimensional flow model are applied to predict the fluid field of the electrolyte, respectively. Results show that the void fraction is the most important factor in determining the electrolyte conductivity and the shape of the workpiece. The proper machining conditions and numerical parameters are important to obtain a good solution. The relative error can be reduced under 0.002.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. L. Krylov, Soviet Phys. Doklady 13 (1968) 15.
[2] P. Lawrence, Ph. D. Thesis, Leicester University, UK (1997).
D. E. Collett, R. C. Hewson-Brown and D. W. Windle, J. Eng. Math. 4 (1970) 29.
V. K Jain and P. C. Pandey, Precision Eng. 2 (1980) 195.
[5] M. B. Nanayakkare, Ph. D. Thesis, University of Strath-clyde, UK (1977).
V. K. Jain and P. C. Pandey, Int. J. Mach, Tool Des. Res. 22 (1982) 341.
H. Tipton, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Machine Tool Research, Brimingham, UK, Sept. (1964), p. 509.
K. Kawafune, T. Mikoshiba, K. Noto and K. Hirata, CIRP Ann. 15 (1967) 65/1-65/13.
F. Hopenfeld and R. R. Cole, J. Eng. Indust., ASME Trans. 88 (1966) 455.
J. F. Thorpe and R. D. Zerkle, Int. J. Math. Tool Des. and Res. 9(1969) 131.
J. F. Thorpe and R. D. Zerkle, 'Fundamentals of Electro-chemical Machining', edited by C. L. Faust (Princeton, NJ, 1971), p. 1.
V. K. Jain, P. G. Yogindra and S. Murugan, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manufact. 27(1) (1987) 113.
L. W. Hourng and C. S. Chang, J. Appl. Electrochem. 23 (1983) 316.
L. W. Hourng and C. S. Chang, J. Appl. Electrochem. 24 (1994) 1170.
S. Das and A. K. Mitra, Int. J. Num. Methods Eng. 35 (1992) 1045.
A. A. Lacey, J. Inst. Math. Appl. 34 (1985) 259.
R. Hunt, J. Comp. Phys. 65 (1986) 448.
R. Hunt, Int. J. Num. Methods Eng. 29 (1990) 1177.
A. W. Bush and G. S. Marshall, 'Flow Modelling in Industrial Processes' (Ellis Horwood, 1989), p. 164.
J. P. Thompson, F. C. Thames and C. W. Mastin, J. Comput. Phys. 24 (1977) 274.
J. Hopenfeld and R. R. Cole, J. Eng. Indust. Aug. (1969) 755.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, C.S., Hourng, L.W. & Chung, C.T. Tool design in electrochemical machining considering the effect of thermal-fluid properties. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry 29, 321–330 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003425016532
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003425016532