Abstract
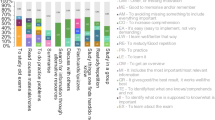
Students have conceptions about the relationship between instructional interventions and learning or, in other words, students have ‘instructional metacognitive knowledge’. In this study, the efficiency of instructional interventions has been investigated as a specific object of students' instructional metacognitive knowledge. By means of a survey, conceptions about the efficiency of various instructional interventions of 488 freshmen in educational sciences and psychology have been investigated. Two research questions directed this exploratory study: (1) How do students assess the efficiency of instructional interventions; and (2) Do differences in gender, educational background, and/or subject of study affect evaluations of the efficiency of instructional interventions. Results show that respondents regard regular instructional interventions at the university directed toward, or supporting, surface-level processing and reproduction to be highly efficient. The use of technology is conceived as inefficient by these students. The limited number of differences between groups of students also suggests students' conceptions to be both consistent and robust.
The study illustrates the need to investigate instructional metacognitive knowledge as distinct from other forms of metacognitive knowledge, and raises questions about the major components and structure of instructional metacognitive knowledge and individual differences in it. The findings suggest the need for the elaboration of a framework to describe instructional interventions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, P.A. and Dochy, F.J.R.C. (1995). ‘Conceptions of knowledge and beliefs: A comparison across varying cultural and educational communities’, American Educational Research Journal 32, 413–442.
Alexander, P.A., Murphy, P.K., Huan, J. and Murphy, P.A. (1996). How Students and Teachers in Singapore and the United States Conceptualize Knowledge and Beliefs: Positioning Learning within Epistemological Frameworks. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New York, April 1996.
Alexander, P.A., Schallert, D.L. and Hare, V.C. (1991). ‘Coming to terms: How researchers in learning and literacy talk about knowledge’, Review of Educational Research 61, 315–343.
Berry, J. and Sahlberg, P. (1996). ‘Investigating pupils’ ideas of learning’, Learning and Instruction 6, 19–36.
Broder, J.M. and Dorfman, J.H. (1994). ‘Determinants of teaching quality: What’s important to students?’, Research in Higher Education 35(2), 235–249.
Brown, A.L. (1978). ‘Metacognitive development and reading’, In Spiro, R.J., Bruce, B.C. and Brewer, G.W.F. (eds.), Theoretical Issues in Reading Comprehension. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Calfee, R. (1981). ‘Cognitive psychology and educational practice’, Review of Research in Education 9, 3–73.
Carroll, J.B. (1963). ‘A model of school learning’, Teachers Colleges Record 64, 723–733.
Chi, M.T.H., Glaser, R. and Farr, M.J. (1988) (eds.). The Nature of Expertise. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Clark, R.E. and Salomon, G. (1986). ‘Media in teaching’, in Wittrock, M.C. (ed.), Handbook of Research on Teaching. Chicago: Rand McNally, pp. 464–478.
Cleave-Hogg. D. and Rothman, A.I. (1991). ‘Discerning views. Medical Students' perceptions of their learning environment’, Evaluation and the Health professions 14, 456–474.
Dochy, J.R.C. (1992). Assessment of Prior Knowledge as a Determinant For Future Learning. Heerlen: Onderwijstechnologisch Innovatiecentrum, Open Universiteit.
Donald, J.G. (1996). Professors’ and Students' Perceptions of Teaching and Learning Post Secondary Students' Orientation to Learning. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New York, April 1996.
Elen, J. and Lowyck, J. (in press). Metacognitive instructional knowledge: Cognitive mediation and instructional design. Journal of Structural Learning.
Elen, J., Lowyck, J. and Proost, K. (1996). ‘The design of telematic learning environments: A cognitive mediational view’, Educational Research and Evaluation 2(3), 213–230.
Ertmer, P.A., Newby, T.J. and McDougall, M. (1996). ‘Students' responses and approaches to case-based instruction: The role of reflective self-regulation’, American Educational Research Journal 33(3), 719–752.
Flavell, J.H. (1979). ‘Metacognition and cognitive monitoring: A new area of cognitive-developmental inquiry’, American Psychologist 34(10), 906–911.
Fraser, B.J., Walberg, H.J., Welch, W.W. and Hattie, J.A. (1987). Syntheses of education productivity research. International Journal of Educational Research 11, 145–252.
Kinzie, M.B., Delcourt, M.A.B. and Powers, S.M. (1994). ‘Computer technologies: attitudes and self-efficacy across undergraduate disciplines’, Research in Higher Education 35, 745–768.
Kniveton, B.H. (1996). ‘Student perceptions of assessment methods’, Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education 21(3), 229–237.
Levy, J., Wubbels, T. and Brekelmans, M. (1996). Cultural Factors in Students’ and teachers' Perceptions of the Learning Environment. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New York, April 1996.
Marton, F., Wen, Q. and Nagle, A. (in press). ‘Views on learning in different cultures. Comparing patterns in China and Uruguay’, Anales de psicologia.
McRobbie, C.J., Lucas, K.B. and Roth, W.-M. (1996). Student and Teacher Views About the Nature of Science and the Enacted Curriculum. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New York, April 1996.
Pratt, D.D. (1992). ‘Conceptions of teaching’, Adult Education Quarterly 42(4), 203–220.
Proost, K., Elen, J. and Lowyck, J. (1997). ‘Effects of gender on perceptions and preferences of TLEs’, Journal of Research on Computing in Education 29(4), 370–384.
Richey, R. (1991). ‘Adult attitudes toward alternative delivery systems and industrial training outcomes’, in Simonson, M.R. and Hargraves, C. (eds.), 13th Annual Proceedings of Selected Research Presentations at the 1991 Convention of the Association of Educational Communications and Technology. Ames: University of Iowa, College of Education, pp. 635–680.
Schnackenberg, H.L., Sullivan, H.J., Leader, L. and Jones, E.E.K. (1996). Matching Learner Preference to Preferred Amounts of Instruction. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New York, April 1996.
Schommer, M. (1994). ‘An emerging conceptualization of epistemological beliefs and their role in learning’, in Garner, R. and Alexander, P.A. (eds.), Beliefs About Text and Instruction with Text. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum, pp. 25–40.
Schott, F. (1994). ‘Efficiency as lodestar for the modelling 1.D.-research adventure’, in Lowyck, J. and Elen, J. (eds.), Modelling 1.D.-Research. Proceedings of the First Workshop of the Special Interest Group of Instructional design of EARLI. Leuven: K.U. Leuven, pp. 21–33.
Singer, E.R. (1996). ‘Espoused teaching paradigms of college faculty’, Research in Higher Education 37(6), 659–679.
Stebler, R. and Reusser, K. (1996). Purpose and Benefits of Peer Collaboration: What teachers Believe and Students Perceive. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New York, April 1996.
Vermunt, J.D.H.M. (1992). Leerstijlen en sturen van leerprocessen in het hoger onderwijs: Naar een procesgerichte instructie in zelfstandig denken. Amsterdam: Swets & Zeitlinger.
Wierstra, R.F.A. and Beerends, E.P.M. (1996). ‘Leeromgevingspercepties en leerstrategieen van eerstejaars studenten sociale wetenschappen’, Tijdschrift voor Onderwijsresearch 21(4), 306–322.
Winne, P.H. and Marx, R. (1982). ‘Students' and teachers' views on thinking processes for classroom learning’, The Elementary School Journal 82, 493–518.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elen, J., Lowyck, J. Students' views on the efficiency of instruction: An exploratory survey of the instructional metacognitive knowledge of university freshmen. Higher Education 36, 231–252 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003227502618
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003227502618