Abstract
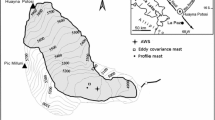
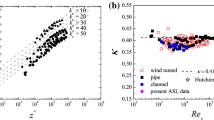
Profile and eddy-correlation (heights of 4 and 10 m) measurements performed on the Pasterze glacier (Austria) are used to study the characteristics of the stable boundary layer under conditions of katabatic and large-scale forcing. We consider cases where large-scale forcing results in a downslope (or following) ambient wind. The analysis of averaged spectra and cospectra reveals low frequency perturbations that have a large influence on the variances of temperature and horizontal wind components and also alter the cospectra of momentum and sensible heat flux. Only the spectrum of the vertical wind speed is comparable to universal spectra. The low frequency perturbations occur as brief intermittent events and result in downward entrainment of ambient air thereby producing enhanced downward sensible heat fluxes and downward as well as upward momentum fluxes with various magnitudes and timescales. After the variances were high pass filtered, the normalised standard deviations of wind speed and temperature compare favourably to findings in the literature within the range 0>z/L>0.5. For larger z/L they deviate as a result of an increased influence from low frequency perturbations and thus non-stationarity. In line with this, the turbulent kinetic energy budget (at 4 m height) indicates that production (shear) is in balance with destruction (buoyancy and dissipation) within the range 0>z/L>0.3. Non-dimensional gradients of wind speed within the range 0>z/L>0.3 have a slope of about 3.5. The scatter for the dimensionless temperature gradient is quite large, and the slope is comparable to that for wind speed gradients. For z/L>0.3 the imbalance in the turbulent kinetic energy budget grows and non-dimensional gradients for wind speed and temperature deviate considerably from accepted values as a result of increased non-stationarity. Average roughness lengths for momentum and sensible heat flux derived from wind speed and temperature profiles are respectively 1 × 10-3 m and 6 × 10-5 m, consistent with the literature. The ratio (z0h/z0m) compares to those predicted by surface renewal models. A variation of this ratio with the roughness Reynolds number is not indicated by our data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreas, E.: 1987, 'A Theory for the Scalar Roughness and the Scalar Coefficients over Snow and Ice', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 38, 159-184.
Bintanja, R. and Van den Broeke, M. R.: 1995, 'Momentum and Scalar Transfer Coefficients over Aerodynamically Smooth Antarctic Surfaces', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 74, 89-111.
Busch, N.: 1969, 'Waves and Turbulence', Radio Sci. 4, 1377-1379.
Caughey, S. J.: 1977, 'Boundary-Layer Turbulence Spectra in Stable Conditions', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 11, 3-14.
Caughey, S. J. and Readings, C. J.: 1975, 'An Observation of Waves and Turbulence in the Earth's Boundary Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 9, 279-296.
Chiba, O. and Kobayashi, S.: 1986, 'A Study of the Structure of Low-Level Katabatic Winds at Mizuho Station, East Antarctica', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 37, 343-355.
Einaudi, F. and Finnigan, J. J.: 1981, 'The Interaction Between an Internal Gravity Wave and the Planetary Boundary Layer. Part I: The Linear Analysis', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 107, 793- 806.
Finnigan, J. J. and Einaudi, F.: 1981, 'The Interaction Between an Internal Gravity Wave and the Planetary Boundary Layer. Part II: Effect of the Wave on the Turbulence Structure', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 107, 793-806.
Garratt, J. R.: 1992, The Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, MA, 316 pp.
Greuell, W., Knap, W. H., and Smeets, P. C.: 1997, 'Elevational Changes inMeteorological Variables Along a Mid-Latitude Glacier During Summer', J. Geo. Phys. Rev., submitted.
Hicks, B. B. and Martin, H. C.: 1972, 'Atmospheric Turbulent Fluxes over Snow', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2, 496-502.
Högström, U.: 1988, 'Non-Dimensional Wind and Temperature Profiles in the Atmospheric Surface Layer: A Re-Evaluation', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 42, 55-78.
Högström, U.: 1990, 'Analysis of Turbulence Structure in the Surface Layer with a Modified Similarity Formulation for Near Neutral Conditions', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 47, 1949-1972.
Inoue, J.: 1989a, 'Surface Drag over the Snow Surface of the Antarctic Plateau. 1. Factors Controlling Surface Drag over the Katabatic Wind Region', J. Geophys. Res. 94(D II), 2207-2217.
Inoue, J.: 1989b, 'Surface Drag over the Snow Surface of the Antarctic Plateau. 2. Seasonal Change of Surface Drag in the Katabatic Wind Region', J. Geophys. Res. 94(D II), 2219-2224.
Jacobs, A. and McNaughton, K.: 1994, 'The Excess Temperature of a Rigid Fast-Response Thermometer and its Effects on Measured Heat Flux', J. Atmos. Oceanic Techn. 11, 680-686.
Joffre, S.: 1982, 'Momentum and Heat Transfers in the Surface Layer over a Frozen Sea', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 24, 211-229.
Kaimal, J., Wyngaard, J., Izumi, Y., and Coté, O.: 1972, 'Spectral Characteristics of Surface Layer Turbulence', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 98, 653-689.
King, J.: 1990, 'Some Measurements of Turbulence over an Antarctic Ice Shelf', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 116, 379-400.
King, J. and Anderson, P.: 1994, 'Heat andWater Vapour Fluxes and Scalar Roughness Lengths over an Antarctic Ice Shelf', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 69, 101-121.
Kobayashi, S., Ishikawa, N., Ohata, T., Kawaguchi, S., and Chiba, O.: 1994, 'Some Characteristics of an Atmospheric Boundary Layer on the Sloped Ice Sheet at Mizuho Station, East Antarctica', IAHS Publ. 223, 41-52.
Kondo, J. and Yamazawa, H.: 1986, 'Bulk Transfer Coefficient over a Snow Surface', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 34, 123-135.
Mahrt, L.: 1985, 'Vertical Structure and Turbulence in the Very Stable Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 42, 2333-2349.
Martin, S.: 1975, 'Wind Regimes and Heat Exchange on Glacier de Saint-Sorlin', J. Glaciol. 14(70), 91-105.
McBean, G. and Elliott, J.: 1975, 'The Vertical Transports of Kinetic Energy by Turbulence and Pressure in the Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 753-766.
Moore, C.: 1986, 'Frequency Response Corrections for Eddy Correlation's Systems', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 37, 17-35.
Morris, E.: 1989, 'Review Paper: Turbulent transfer over Snow and Ice', J. Hydrol. 105, 205-223.
Munro, D.: 1989, 'Surface Roughness and Bulk Heat Transfer on a Glacier: Comparison with Eddy Correlation', J. Glaciol. 35(121), 344-348.
Munro, D. and Davies, J.: 1978, 'On Fitting the Log-Linear Model to Wind Speed and Temperature Profiles over a Melting Glacier', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 15, 423-437.
Nai-Ping, L., Neff, W., and Kaimal, J.: 1983, 'Wave and Turbulence Structure in a Disturbed Nocturnal Inversion', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 26, 141-155.
Nieuwstadt, F.: 1984, 'The Turbulence Structure of the Stable, Nocturnal Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 2202-2216.
Oerlemans, J.: 1994, 'Quantifying Global Warming from the Retreat of Glaciers', Science 264, 243-245.
Ohmura, A., Konzelmann, T., Rotach, M., Forrer, J., Wild, M., Abe-Ouchi, A., and Toritani, H.: 1994, 'Energy Balance for the Greenland Ice Sheet by Observations and Model Computation', IAHS Publ. 223, 85-94.
Poulos, G.: 1996, The Interaction of Katabatic Winds and Mountain Waves, Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado State University, Ft. Collins, CO, U.S.A., 300 pp.
Schotanus, P., Nieuwstadt, F., and de Bruin, H.: 1983, 'Temperature Measurement with a Sonic Anemometer and its Application to Heat and Moisture Fluxes', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 26, 81-93.
Stewart, R.: 1969, 'Turbulence and Waves in a Stratified Atmosphere', Radio Sci. 4, 1269-1278.
Thorpe, M., Banke, E., and Smith, S.: 1973, 'Eddy-Correlation Measurements of Evaporation and Sensible-Heat Flux over Arctic Sea Ice', J. Geophys. Res. 78, 3573-3584.
Van Asselt, C., Jacobs, A., Van Boxel, J., and Jansen, A.: 1991, 'A Rigid Fast-Response Thermometer for Atmospheric Research', Meas. Sci. Technol. 2, 26-31.
Van den Broeke, M. R.: 1996, The Atmospheric Boundary Layer over Ice Sheets and Glaciers, Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University, The Netherlands, 178 pp.
Van den Broeke, M. R.: 1997, 'Structure and Diurnal variation of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer over a Mid-Latitude Glacier in Summer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 83, 183-205.
Webb, E. K.: 1970, 'Profile Relationships: The Log-Linear Range, and Extension to Strong Stability', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 96, 67-90.
Wyngaard, J. C. and Coté, O. R.: 1971, 'The Budgets of Turbulent Kinetic Energy and Temperature Variance in the Atmospheric Surface Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 190-201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smeets, C.J.P.P., Duynkerke, P.G. & Vugts, H.F. Turbulence Characteristics of the Stable Boundary Layer Over a Mid-Latitude Glacier. Part I: A Combination of Katabatic and Large-Scale Forcing. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 87, 117–145 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000860406093
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000860406093