Abstract
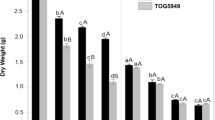
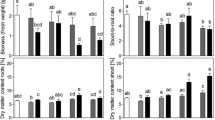
Atriplex nummularia plants are able to grow well in the absence of significant amounts of Na+. Medium levels of salinity (100 mM NaCl or KCl) did not cause substantial inhibition of growth but increasing concentrations of salt induced a progressive decline in length and weight of the plants. This inhibition was significantly higher in KCl grown plants than in NaCl grown plants. In addition, although it has been proposed that both K+ and Na+ are involved in the osmotic adjustment of plants in response to high soil salinity, we show that Na+ ions contribute more efficiently than K+ ions to perform this function. Our results also indicate that most of the osmotic adjustment of the plant was due to the accumulation of inorganic ions. The strong inhibition of Rb+ transport caused by internal sodium suggests that this cation could be efficiently used by the plant and, as a consequence, the transport of other monovalent cations is down-regulated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almagro A, Prista C, Castro S, Quintas C, Madeira-Lopes A, Ramos J and Loureiro-Dias M C 2000 Effects of salts on Debaryomyces hansenii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae under stress conditions. Internl. J. Food Microbiol. 56, 191–197.
Ashby W C and Beadle N C W 1957 Salinity factors in the growth of Australian saltbushes. Ecology 38, 344–352.
Aslam Z, Jeschke W D, Barrett-Lennard E-G, Setter T L, Watkin E and Greenway H 1986 Effects of external NaCl on the growth of Atriplex amnicola and the ion relations and carbohydrate status of leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 9, 571–580.
Benlloch M, Moreno I and Rodríguez-Navarro A 1989 Two modes of rubidium uptake in sunflower plants. Plant Physiol. 90, 939–942.
Bohnert H J, Nelson D E and Jensen R G 1995 Adaptation to environmental stresses. Plant Cell 7, 1099–1111.
Chatterton N J and McKell C M 1969 Atriplex polycarpa. I. Germination and growth as affected by sodium chloride in water cultures. Agronomy J. 61, 451–453.
Egan T and Ungar I A 1998 Effect of different salts of sodium and potassium on the growth of Atriplex prostrata (Chenopodiaceae). J. Plant Nutrition 21, 2193–2205.
Flowers T J, Troke P F and Yeo A R 1977 The mechanism of salt tolerance in halophytes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 28, 89–121.
Glenn E P and O'Leary J W 1984 Relationship between salt accumulation and water content of dicotyledonous halophytes. Plant Cell Environ. 7, 253–261.
Glenn E P, Pfister R, Brown J J Thompson T L and O'Leary J W 1996 Na+ and K+ accumulation and salt tolerance of Atriplex canescens (Chenopodiaceae) genotypes. Am. J. Bot. 83, 997–1005.
Gorham J 1995 Mechanisms of salt tolerance in halophytes. In Halophytes and biosaline agriculture. Eds. R Choukr-Allah, C V Malcolm and A Hamdy. pp. 31–53. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, USA.
Greenway H and Munns R 1980 Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 31, 149–190.
Hamada A, Shono M, Xia T, Ohta M, Hayashi Y, Tanaka A and Hayakawa T 2001 Isolation and characterization of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from the halophyte Atriplex gmelini. Plant Mol. Biol. 46, 35–42.
Khan M A, Ungar I A and Showalter A M 2000 Effects of salinity on growth, water relations and ion accumulation of the subtropical perennial halophyte, Atriplex griffithii var. stocksii. Ann. Bot. 85, 225–232.
Matoh T, Watanabe J and Takahashi E 1986 Effects of sodium and potassium salts on the growth of a halophyte Atriplex gmelini. Soil Sci. Plant Nutrit. 32, 451–459.
McKell C M 1994 Salinity tolerance in Atriplex species: Fodder shrubs of arid lands. In Handbook of plant and crop stress. Ed. P Pessarakli. pp. 497–503 Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, USA.
Prista C, Almagro A, Loureiro-Dias M C and Ramos J 1997 Physiological basis for the high salt tolerance of Debaryomyces hansenii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 4005–4009.
Quintero J M, Molina R, Fournier J M, Benlloch M and Ramos J 2001 Glucose-induced activation of rubidium transport and water flux in sunflower root systems. J. Experim. Bot. 52, 99–104.
Reimann C 1992 Sodium exclusion by Chenopodium species. J. Experim. Bot. 43, 503–510.
Serrano R and Rodríguez-Navarro A 2001 Ion homeostasis during salt stress in plants. Curr. Opin. Cell Bio. 13, 399–404.
Thomé-Ortiz P E, Peña A and Ramírez J 1998 Monovalent cation fluxes and physiological changes of Debaryomyces hansenii grown at high concentrations of KCl and NaCl. Yeast 14, 1355–1371.
Wyn Jones R G and Storey R 1981 Betaines. In Physiology and biochemistry of drought resistance in plants. Eds. L G Paleg and D Aspinall. pp. 171–204 Academic Press, Sydney.
Zid E and Boukharis M 1977 Quelques aspects de la tolerance de l'Atriplex halimus L. au chlourure de sodium. Oecologia Plantarum 12, 351–362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramos, J., López, M.J. & Benlloch, M. Effect of NaCl and KCl salts on the growth and solute accumulation of the halophyte Atriplex nummularia . Plant and Soil 259, 163–168 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLSO.0000020953.50331.a5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLSO.0000020953.50331.a5