Abstract
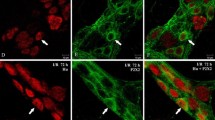
We evaluated the neurotrophic effect of the neurokinin SP in the induced megacolon and the cell proliferation of the colonic epithelium after treatment. Colon segments of Wistar rats were chemically denervated by topical application of 2 mM benzalconium chloride and animals were daily injected intraperitoneally with SP (70 μg/kg body wt) for 15 days. Control rats received either SP or were denervated and treated with saline. Neuronal profiles of the myenteric plexus were studied by immunohistochemistry to motor protein myosin V and cell proliferation by PCNA immunolabeling. Denervation induced a significant reduction in the number of neurons and an enlargement of the surviving perikarya (from 263.7 μm2 in the control-saline group to 468.9 μm2 in the denervated groups). The total area occupied by neurons was maintained in the denarvated SP group but was significantly smaller in the denervated-saline group. The proliferative index was significantly higher in the denervated groups, of which the SP-treated group showed the highest index. These results suggest that SP may have a neurotrophic effect for the neurons of the myenteric plexus chemically denervated and that this denervation stimulates cell proliferation, especially after SP administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howard ER, Nixon HH: Internal anal sphincter. Observations on development and mechanism of inhibitory responses in premature infants and children with Hirschprung's disease. Arch Dis Child 43:569-578, 1968
Köberle F: Enteromegaly and cardiomegaly in Chagas' disease. Gut 4:399-405, 1963
Tarleton RL: Parasite persistence in the aetiology of Chagas disease. Int J Parasitol 31:550-554, 2001
Oliveira JSM, Llorach-Veludo MAS, Sales-Neto VN: Megacolon in rats. Digestion 45:166-171, 1990
Saffrey MJ, Burnstock G: Growth-factors and the development and plasticity of the enteric nervous system. J Autonom Nerv Syst 49:183-196, 1994
Pernow B: Substance P. Pharmacol Rev 35:85-141, 1983
Ziche M, Morbidelli L, Pacini M, Geppetti P, Alessandri G, Maggi CA: Substance P stimulates neovascularization in vivo and proliferation of cultured endothelial cells. Microvasc Res 40:264-278, 1990
Reid TW, Murphy CJ, Iwahashi CK, Foster BA, Mannis MJ: Stimulation of epithelial cell growth by the neural peptide substance P. J Cell Biochem 52:476-485, 1993
Tanaka T, Danno K, Ikai K, Imamura S: Effects of substance P and substance K on the growth of cultured keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 90:399-401, 1988
Bolner T, Beesley PW, Thorndyke MC: Pattern of substance P-and cholecytokinin-like immunoreactivity during regeneration of the neural complex in the ascidian Ciana intestinalis. J Comp Neurol 22:572-580, 1992
Pare M, Descarries L, Quirion R: Up-regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine-2 and neurokinin-1, receptors associated with serotonin/substance P hyperinnervation in the rat inferior olive. Neuroscience 51:97-107, 1992
Espreafico EM, Cheney RE, Matteoli M, Nascimento AAC, de Camilli PV, Larson RE, Mooseker MS: Primary structure and cellular localization of chicken brain myosin-V (p 190), an unconventional myosin with calmodulin light chains. J Cell Biol 119:1541-1557, 1992
Sakata K, Luneida T, Furuta T, Sato A: Seletive destruction of intestinal nervous elements by local application of benzalkonium solution in the rat. Experientia 35:1611-1613, 1979
Hasenöhrl RU, Jentjens O, De Souza Silva MA, Tomaz C, Huston JP: Anxiolytic-like action of neurokinin substance P administered systemically or into the nucleus basalis magnocellularis region. Eur J Pharmacol 354:123-133, 1998
Drengk AC, Kajiwara JK, Garcia SB, Carmo VS, Larson RE, Zucoloto S, Espreafico EM: Immunolocalization of myosin-V in the enteric nervous system of the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst 78:109-112, 2000
McLean IW, Nakane PK: Periodate—lysine—paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixative for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 22:1077-1083, 1974
Maskens AP: Histogenesis of colon glands during postnatal growth. Acta Anat 100:17-26, 1978
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ: Biometry. New York, Freeman and Company, 1995
Fox DA, Epstein ML, Bass P: Surfactants selectively ablate enteric neurons of the rat jejunum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:538-544, 1983
See NA, Epstein LE, Schultz E, Pienkowski TP, Bass P: Hyperplasia of jejunal smooth muscle in the myenterically denervated rat. Cell Tissue Res 253:609-617, 1988
See NA, Epstein LE, Dahl JL, Bass P: The myenteric plexus regulates cell growth in rat jejunum. J Autonom Nerv Syst 31:219-230, 1990
Zucoloto S, Diaz JA, Oliveira JSM, Muccilo G, Sales-Neto V, Kajiwara JK: Effect of chemical ablation of myenteric neurones on intestinal cell proliferation. Cell Tissue Kinet 21:213-219, 1988
Zucoloto S, Deus DA, Martins AA, Muglia VF, Kajiwara JK, Garcia SB: The relationship between myenteric neuronal denervation, smooth muscle thickening and epithelial cell proliferation in the rat colon. Res Exp Med 197:117-124, 1997
Ramalho FS, Ramalho LNZ, Zucoloto S, Santos GC, Kajiwara JK: Myenteric neuron number after acute and chronic denervation of the proximal jejunum induced by benzalkonium chloride. Neurosc Lett 163:74-76, 1993
Cracco C, Filogamo G: Neuronal and non-neuronal plasticity in the rat following myenteric denervation. Adv Exp Med Biol 429:159-169, 1997
Parr EJ, Sharkey KA: Multiple mechanisms contribute to myenteric plexus ablation induced by benzalconium chloride in the guinea-pig ileum. Cell Tissue Res 289:253-264, 1997
Furness JB, Costa M: The Enteric Nervous System. New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1987
White SR: A comparison of the effects of serotonin, substance P and thyrotropin-releasing hormone on excitability of rat spinal motoneurons in vivo. Brain Res 335:63-70, 1985
Nicoll A: The action of thyrotropin-releasing hormone, substance P and related peptides on frog spinal motoneurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 207:217-224, 1978
Van Den Bergh P, De Beukelaer M, Deconink N: Effect of muscle denervation on the expression of substance P in the ventral raphe-spinal pathway of the rat. Brain Res 707:206-212, 1996
Hadzijahic N, Renehan WE, Ma CK, Zhang X, Fogel R: Myenteric plexus destruction alters morphology of rat intestine. Gastroenterology. 105:1017-1028, 1993
Holle GE: Changes in the structure and regeneration mode of the rat small intestinal mucosa following benzalkonium chloride treatment. Gastroenterology. 101:1264-1273, 1991
Hernandes L, Zucoloto S, Alvares EP: Effect of myenteric denervation on intestinal epithelium proliferation and migration of suckling and weanling rats. Cell Prolif 33:127-138, 2000
Maskens AP, Dujardin-Loits RM: Kinetics of tissue proliferation in colorectal mucosa during post-natal growth. Cell Tissue Kinet 14:467-477, 1981
Park HS, Goodlad RA, Ahnen DJ, Winnet A, Sasieni P, Lee CY, Wright NA: Effects of epidermal growth factor and dimethylhydrazine on crypt size, cell proliferation, and crypt fission in the rat colon. Cell proliferation and crypt fission are controlled independently. Am J Pathol 151:843-852, 1997
Cooke HJ: Neurobiology of the intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology 90:1057-1081, 1986
Sternini C, Su D, Gamp PD, Bunnet NW: Cellular sites of expression of the neurokinin-1 receptor in the rat gastrointestinal-tract. J Comp Neurol 358:531-540, 1995
Southwell BR, Furness JB: Immunohistochemical demonstration of the tachykinin receptor on muscle and epithelia in guinea pig intestine. Gastroenterology 120:1140-1151, 2001
Vannucchi MG, Faussone-Pellegrini MS: NK-1, NK-2 and NK-3 tachykinin receptor localization and tachykinin distribution in the ileum of the mouse. Anat Embryol 202:247-255, 2000
Pothoulakis C, Castagliuolo I, Leeman SE, Wang CC, Li H, Hoffman BJ, Mezey E: Substance P receptor expression in intestinal epithelium in clostridium difficile toxin A enteritis in rats. Am J Physiol 275:G68-G75, 1998
Harrison NK, Dawes KE, Know OJ, Barnes PJ, Laurent GJ, Chung KF: Effects of neuropeptides on human lung fibroblast proliferation and chemotaxis. Am J Physiol 268:L278-L283, 1995
Smith MJ, Globus M, Verthamany-Globus S: Nerve extracts and substance P activate the phosphatidylinositol signaling pathway and mitogenesis in newt forelimb regenerates. Developmental Biol 167:239-251, 1995
Castagluolo I, Valenick L, Liu J, Pothoulakis C: Epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation mediates substance P-induced mitogenic responses in U-373 MG cells. J Biol Chem 275:26545-26550, 2000
Burbach GJ, Kim KH, Zyvoni AS, Kim A, Aranda J, Wright S, Naik SM, Caughman W, Ansel JC, Armstrong CA: The neurosecretory tachykinins substance P and neurokinin A directly induce keratinocyte nerve growth factor. J Invest Dermatol 117:1075-1082, 2001
Watanabe T, Kubota Y, Muto T: Substance P containing nerve fibers in ulcerative colitis. In J Colorectal Dis 13:61-67, 1998
Forsgren S, Höckerfelt U, Norrgård ö, Henriksson R, Franzén L: Pronounced substance P innervation in irradiation-induced enteropathy—a study on human colon. Regul Pept 88:1-13, 2000
Maifrino LBM, Liberti EA, de Souza RR: Vasoactive-intestinal-peptide-and substance-P-immunoreactive nerve fibres in the myenteric plexus of mouse colon during the chronic phase of Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Ann Trop Med Paras 93:49-56, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buttow, N.C., Zucoloto, S., Espreafico, E.M. et al. Substance P Enhances Neuronal Area and Epithelial Cell Proliferation After Colon Denervation in Rats. Dig Dis Sci 48, 2069–2076 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026103311800
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026103311800