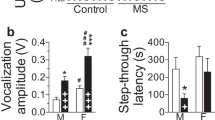
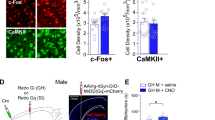
Abstract
In addition to their robust difference in trait anxiety, as illustrated by a variety of behavioral tests, HAB and LAB rats differ in their stress coping strategies, the former being more susceptible and vulnerable to stressor exposure and preferring more passive strategies. HAB rats of either gender show signs of a hyper-reactive hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis, thus resembling psychiatric patients. As shown by in situ hybridization and microdialysis in freely behaving animals, both the expression and release of vasopressin in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus are higher in HAB than in LAB rats, thus contributing to the HPA axis hyperdrive. Accordingly, in HAB animals, administration of a V1 receptor antagonist normalized the pathological outcome of the dexamethasone/corticotropin-releasing hormone test and triggered behavioral changes toward reduced anxiety and active stress coping. Pharmacological validation has revealed signs of depressive-like behavior, as HAB but not LAB rats have shown more active stress coping behavior and a normalized HPA axis after treatment with paroxetine. Of interest, this antidepressant reduced the hypothalamic overexpression of vasopressin; this novel mechanism of action is likely to contribute to paroxetine effects on both behavioral and neuroendocrine parameters. Cross-mating and cross-fostering paradigms showed that the divergent emotionality in HAB vs. LAB rats is determined genetically, rather than postnatally through maternal behavior. As the behavioral and neuroendocrine phenotyping pointed to the vasopressin gene as a candidate gene critically involved in anxiety, preliminary genetic approaches have been focused on this gene, revealing single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the promotor area of the vasopressin gene in HAB, but not LAB rats. HAB/LAB rats are thus proving to be a unique animal model to identify and characterize neurobiological, neuroendocrine, and genetic correlates of trait anxiety, and perhaps depression, in humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andreatini, R., Wolfman, C., Viola, H., Medina, J. H., Da Cunha, C., and Ribeiro, R. L. (1999). The “anxiety state” and its relation with rat models of memory and habituation. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 72:78–94.
Arborelius, L., Owens, M. J., Plotsky, P. M., and Nemeroff, C. B. (1999). The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in depression and anxiety disorders. J. Endocrinol. 160:1–12.
Beuzen, A., and Belzung, C. (1995). Link between emotional memory and anxiety states: A study by principal component analysis. Physiol. Behav. 58:111–118.
Buss, D. M. (1991). Evolutionary personality psychology. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 42:459–491.
Cahill, J., and McGaugh, J. L. (1998). Mechanism of emotional arousal and lasting memory. TINS 21:294–299.
Caldji, C., Tannenbaum, B., Sharma, S., Francis, D., Plotsky, P. M., and Meaney, M. J. (1998). Maternal care during infancy regulates the development of neural systems mediating the expression of fearfulness in the rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:5335–5340.
Castanon, N., Perez-Diaz, F., and Mormède, P. (1995). Genetic analysis of the relationships between behavioral and neuroendocrine traits in Roman high and low avoidance rat lines. Behav. Genet. 25:371–384.
Carrive, P. (2000). Conditioned fear to environmental context: Cardiovascular and behavioural components in the rat. Brain Res. 858:440–445.
Chapouthier, G., Bondoux, D., Martin, B., Desforges, C., and Launay, J.-M. (1991). Genetic differences in sensitivity to b-carboline: Evidence for the involvement of brain benzodiazepine receptors. Brain Res. 553:342–346.
Clément, Y., Proeschel, M.-F., Bondoux, D., Girard F., Launay, J.-M., and Chapouthier, G. (1997). Genetic factors regulate processes related to anxiety in mice. Brain Res. 752:127–135.
Commissaris, R. L., Harrington, G. M., and Altman, H. J. (1990). Benzodiazepine anticonflict effects in Maudsley Reactive (MR/Har) and Nonreactive (MNR/Har) rats. Psychopharmacology 100:287–292.
Crabbe, J. C., Wahlsten, D., and Dudek, B. C. (1999). Genetics of mouse behavior: Interactions with laboratory environment. Science 284:1670–1672.
Driscoll, P., and Bättig, K. (1982). Behavioral, emotional and neurochemical profiles of rats selected for extreme differences in active, two-way avoidance performance. In Liebich, I. (ed.), Genetics of the Brain, Elsevier Biomed, Amsterdam, pp. 95–123.
Engelmann, M., Wotjak, C. T., and Landgraf, R. (1995). Social discrimination procedure: An alternative method to investigate juvenile recognition abilities in rats. Physiol. Behav. 58:351–321.
Engelmann, M., Wotjak, C. T., Neumann, I., Ludwig, M., and Landgraf, R. (1996). Behavioral consequences of intracerebral vasopressin and oxytocin: Focus on learning and memory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 20:341–358.
Fernandez-Teruel, A., Escorihuela, R. M., Tobena, A., and Driscoll, P. (1991). Stress and putative endogenous ligands for benzodiazepine receptors: The importance of characteristics of the aversive situation and of differential emotionality in experimental animals. Experientia 47:1051–1056.
Gold, P. W., and Chrousos, G. P. (2002). Organization of the stress system and its dysregulation in melancholic and atypical depression: High vs low CRH/NE states. Mol. Psychiat. 7: 254–275.
Green, S., and Hodges, H. (1991). Animal models of anxiety. In Willner, P. (ed.), Behavioural Models in Psychopharmacology, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp. 21–49.
Griebel, G. (1995). 5-Hydroxytryptamine-interacting drugs in animal models of anxiety disorders: More than 30 years of research. Pharmacol. Therap. 65:319–395.
Griebel, G., Simiand, J., Serradeil-LeGal, C., Wagnon, J., Pascal, M., Scatton, B., Maffrand, J.-P., and Soubrie, P. (2002). Anxiolyticand antidepressant-like effects of the non-peptide vasopressin V1b receptor antagonist, SSR 149415, suggest an innovative approach for the treatment of stress-related disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:6370–6375.
Henniger, M. S. H., Ohl, F., Hölter, S. M., Weißenbacher, P., Toschi, N., Lörscher, P., Wigger, A., Spanagel, R., and Landgraf, R. (2000). Unconditioned anxiety and social behaviour in two rat lines selectively bred for high and low anxiety-related behaviour. Behav. Brain Res. 111:153–163.
Henniger, M. S. H., Spanagel, R., Wigger, A., Landgraf, R., and Hölter, S. M. (2002). Alcohol self-administration in two rat lines selectively bred for extremes in anxiety-related behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 26:729–736.
Hermann, B., Landgraf, R., Keck, M. E., Wigger, A., Morrow, A. L., Ströhle, A., Holsboer, F., and Rupprecht, R. (2000). Pharmacological characterisation of cortical g-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptors in two Wistar rat lines selectively bred for high and low anxiety-related behaviour. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 1:137–143.
Hess, J., Lesser, D., and Landgraf, R. (1992). Vasopressin and oxytocin in brain areas of rats selectively bred for differences in behavioral performance. Brain Res. 569:106–111.
Hogg, S. (1996). A review of the validity and variability of the elevated plus-maze as an animal model of anxiety. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 54:21–30.
Keck, M. E., Welt, T., Post, A., Müller, M. B., Toschi, N., Wigger, A., Landgraf, R., Holsboer, F., and Engelmann, M. (2001a). Neuroendocrine and behavioral effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in a psychopathological animal model are suggestive of antidepressant-like effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:337–349.
Keck, M. E., Welt, T., Wigger, A., Renner, U., Engelmann, M., Holsboer, F., and Landgraf, R. (2001b). The anxiolytic effect of the CRH1 receptor antagonist R121919 depends on trait emotionality in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 13:373–380.
Keck, M. E., Welt, T., Müller, M. B., Uhr, M., Ohl, F., Wigger, A., Toschi, N., Holsboer, F., and Landgraf, R. (2002a). Downregulation of hypothalamic vasopressinergic hyperdrive is involved in clinically relevant behavioral and neuroendocrine antidepressant drug effects. Neuropsychopharmacology (in press).
Keck, M. E., Wigger, A., Welt, T., Müller, M. B., Gesing, A., Reul, J. H. M. H., Holsboer, F., Landgraf, R., and Neumann, I. D. (2002b). Vasopressin mediates the response of the combined dexamethasone/CRH test in hyper-anxious rats: Implications for pathogenesis of affective disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 26:94–105.
Kendler, K. S. (1996). Major depression and generalised anxiety disorder: Same genes, (partly) different environments—revisited. Br. J. Psychiatry 168(Suppl. 30):68–75.
Koolhaas, J. M., Korte, S. M., De Boer, S. F., Van Der Vegt, B. J., Van Reenen, C. G., Hopster, H., De Jong, I. C., Ruis, M. A., and Blokhuis, H. J. (1999). Coping styles in animals: Current status in behavior and stress-physiology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 23:925–935.
Lader, M. (1991). Animal models of anxiety: A clinical perspective. In Willner, P. (ed.), Behavioural Models in Psychopharmacology, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK pp. 76–88.
Lancel, M., Müller-Preuss, P., Wigger, A., Landgraf, R., and Holsboer, F. (2002). The CRH1 receptor antagonist R121919 attenuates stress-elicited sleep disturbances in rats, particularly in those with high trait anxiety. J. Psychiatr. Res. (in press)
Landgraf, R. (1995). Intracerebrally released vasopressin and oxytocin: Measurement, mechanism and behavioral consequences. J. Neuroendocrinol. 7:243–253.
Landgraf, R. (2001). Neuropeptides and anxiety-related behavior. Endocr. J. 48:517–533.
Landgraf, R., Gerstberger, R., Montkowsky, A., Probst, J. C., Wotjak, C. T., Holsboer, T., and Engelmann, M. (1995). V1 vasopressin receptor antisense oligodeoxynucleotide into septum reduces vasopressin binding, social discrimination abilities, and anxietyrelated behavior in rat. J. Neurosci. 15:4250–4258.
Landgraf, R., Wigger, A., Holsboer, F., and Neumann, I. D. (1999). Hyper-reactive hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis in rats bred for high anxiety-related behaviour. J. Neuroendocrinol. 11:405–407.
Liebsch, G., Landgraf, R., Gerstberger, R., Probst, J. C., Wotjak, C. T., Engelmann, M., Holsboer, F., and Montkowski, A. (1995). Chronic infusion of CRH1-receptor antisense oligodeoxynucleotide into the central nucleus of the amygdala reduced anxiety-related behavior in socially defeated rats. Reg. Pept. 59:229–239.
Liebsch, G., Wotjak, C. T., Landgraf, R., and Engelmann, M. (1996). Septal vasopressin modulates anxiety-related behaviour in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 217:101–104.
Liebsch, G., Linthorst, A. C. E., Neumann, I. D., Reul, J. M. H. M., Holsboer, F., and Landgraf, R. (1998a). Behavioral, physiological, and neuroendocrine stress responses and differential sensitivity to diazepam in two Wistar rat lines selectively bred for high-and low-anxiety-related behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 19:381–396.
Liebsch, G., Montkowski, A., Holsboer, F., and Landgraf, R. (1998b). Behavioural profiles of two Wistar rat lines selectively bred for high or low anxiety-related behaviour. Behav. Brain Res. 94:301–310.
Liebsch, G., Landgraf, R., Engelmann, M., Lörscher, P., and Holsboer, F. (1999). Differential behavioural effects of chronic infusion of CRH1 and CRH2 receptor antisense oligonucleotides into the rat brain. J. Psychiatr. Res. 33:153–163.
Lucki, I. (1997). The forced swimming test as a model for core and component behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs. Behav. Pharmacol. 8:523–532.
McGaugh, J. L., Cahill, L., and Roosendaal, B. (1996). Involvement of the amygdala in memory storage: Interaction with other brain systems. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 93:13508–13514.
Neumann, I. D., Wigger, A., Liebsch, G., Holsboer, F., and Landgraf, R. (1998). Increased basal activity of the hypothalamo-pituitaryadrenal axis during pregnancy in rats bred for high anxietyrelated behaviour. Psychoneuroendocrinology 23:449–463.
Nijsen, M. J. M. A., Croiset, G., Diamant, M., Stam, R., Delsing, D., de Wied, D., and Wiegant, V. M. (1998). Conditioned fearinduced tachycardia in the rat: Vagal involvement. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 350:211–222.
Ohl, F., Roedel, A., Storch, C., Holsboer, F., and Landgraf, R. (2002). Cognitive performance in rats differing in their inborn anxiety. Behav. Neurosci. 116:464–471.
Ohl, F., Toschi, N., Wigger, A., Henniger, M. S. H., and Landgraf, R. (2001). Dimensions of emotionality in a rat model of trait anxiety. Behav. Neurosci. 115:429–436.
Ohta, R., Matsumoto, A., Nagao, T., and Mizutani, M. (1998). Comparative study of behavioral development between high and low shuttlebox avoidance rats. Physiol. Behav. 63:545–551.
Opp, M. (1995). Corticotropin-releasing hormone involvement in stressor-induced alterations in sleep and in the regulation of waking. Adv. Neuroimmunol. 5:127–143.
Overstreet, D. H., Rezvani, A. H., and Janowski, D. S. (1992). Maudsley Reactive and Nonreactive rats differ only in some tasks reflecting emotionality. Physiol. Behav. 52:149–152.
Palanza, P. (2001). Animal models of anxiety and depression: How are females different? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 25:219–233.
Paterson, A., Whiting, P. J., Gray, J. A., Flint, J., and Dawson, G. R. (2001). Lack of consistent behavioural effects of Maudsley Reactive and Non-reactive rats in a number of animal tests of anxiety and activity. Psychopharmacology 154:336–342.
Plomin, R. (1990). The role of inheritance in behavior. Science 248:183–188.
Ramos, A., Berton, O., Mormède, P., and Chaouloff, F. (1997). A multiple-test study of anxiety-related behaviors in six inbred rat strains. Behav. Brain Res. 85:57–69.
Rausch, J. L., Mac Hobby, H., Shendarkar, N., Johnson, M. E., and Li, J. (2001). Fluvoxamine treatment of mixed anxiety and depression: Evidence for serotonergically mediated anxiolysis. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 21:139–142.
Ressler, K. J., and Nemeroff, C. B. (2000). Role of serotonergic and noradrenergic systems in the pathophysiology of depression and anxiety disorders. Depress. Anxiety 12(Suppl. 1):2–19.
Rodgers, R. J., Cao, B. J., Dalvi, A., and Holmes, A. (1997). Animal models of anxiety: An ethological perspective. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 30:289–304.
Rogan, M. T., and LeDoux, J. E. (1996). Emotion: Systems, cells, synaptic plasticity. Cell 85:469–475.
Roozendaal, B., Wiersma, A., Driscoll, P., Koolhaas, J. M., and Bohus, B. (1992). Vasopressinergic modulation of stress responses in the central amygdala of the Roman high-avoidance and low-avoidance rat. Brain Res. 596:35–40.
Rowe, W. B., Spreekmeester, E., Meaney, M. J., Qiron, R., and Rochford, J. (1998). Reactivity to novelty in cognitively impaired and cognitively unimpaired aged and young rats. Neuroscience 83:669–680.
Ruis, M. A., te Brake, J. H., Buwalda, B., de Boer, S. F., Meerlo, P., Korte, S. M., Blokhuis, H. J., and Koolhaas, J. M. (1999). Housing familiar male wildtype rats together reduces the long-term adverse behavioural and physiological effects of social defeat. Psychoneuroendocrinology 24:285–300.
Salomé, N., Viltart, O., Darnaudéry, M., Salchner, P., Singewald, N., Landgraf, R., Sequeira, H., and Wigger A. (2002). Reliability of high and low anxiety-related behaviour: Influence of laboratory environment and multifactorial analysis. Behav. Brain Res. (in press).
Silva, R. H., and Frussa-Filho, R. (2000). The plus-maze discriminative avoidance task: A model to study memory-anxiety interactions—effects of chlordiazepoxide and caffeine. J. Neurosci. Meth. 102:117–125.
Spanagel, R., Montkowski, A., Allingham, K., Stöhr, T., Shoaib, M., Holsboer, F., and Landgraf, R. (1995). Anxiety: A potential predictor of vulnerability to the initiation of ethanol self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 122:369–373.
Stahl, S. M. (1997). Mixed depression and anxiety: Serotonin 1A receptors as a common pharmacologic link. J. Clin. Psychiatry 58(Suppl. 8):20–26.
Steimer, T., la Fleur, S., and Schulz, P. E. (1997). Neuroendocrine correlates of emotional reactivity and coping in male rats from the Roman high (RHA/Verh)-and low (RLA/Verh)-avoidance lines. Behav. Genet. 27:503–512.
Takahashi, L. K. (2001). Role of CRF1 and CRF2 receptors in fear and anxiety. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 25:627–636.
Timpl, P., Spanagel, R., Sillaber, I., Kresse, A., Reul, J. M. H. M., Stalla, G. K., Blanquet, V., Steckler, T., Holsboer, F., and Wurst, W. (1998). Mice lacking a functional corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 show impaired stress response and reduced anxiety under basal and alcohol withdrawal conditions. Nature Genet. 19:162–166.
Tornatzky, W., and Miczek, K. A. (1994). Behavioral and autonomic responses to intermittent social stress: Differential protection by clonidine and metoprolol. Psychopharmacology 116:346–356.
Umriukhin, A. E., Wigger, A., Singewald, N., and Landgraf, R. (2002). Hypothalamic and hippocampal release of serotonin in rats bred for hyper-or hypo-anxiety. Stress (in press).
Vallée, M., Mayo, W., Dellu, F., Le Moal, M., Simon, H., and Maccari, S. (1997). Prenatal stress induces high anxiety and postnatal handling induces low anxiety in adult offspring: Correlation with stress-induced corticosterone secretion. J. Neurosci. 17:2626–2636.
Wall, P. M., and Messier, C. (2001). Methodological and conceptual issues in the use of the elevated plus-maze as a psychological measurement instrument of animal anxiety-like behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 25:275–286.
Weinstock, M. (1997). Does prenatal stress impair coping and regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 21:1–10.
Wigger, A., Loerscher, P., Weissenbacher, P., Holsboer, F., and Landgraf, R. (2001). Cross-fostering and cross-breeding of HAB and LAB rats: A genetic rat model of anxiety. Behav. Genet. 31:371–382.
Wigger, A., Sánchez, M. M., Mathys, K. C., Ebner, K., Liu, D., Kresse, A., Neumann, I. D., Holsboer, F., Plotsky, P. M., and Landgraf, R. (2002). Alterations in central neuropeptide expression, release, and receptor binding in rats bred for high anxiety: Critical role of vasopressin. Neuroscience (in press).
Wotjak, C. T., Ludwig, M., and Landgraf, R. (1994). Vasopressin facilitates its own release within the rat supraoptic nucleus in vivo. Neuroreport 5:1181–1184.
Zobel, A., Nickel, T., Künzel, H. E., Ackl, N., Sonntag, A., Ising, M., and Holsboer, F. (2000). Effects of the high-affinity corticotropinreleasing hormone receptor 1 antagonist R121919 in major depression: The first 20 patients. J. Psychiatr. Res. 34:171–181.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Landgraf, R., Wigger, A. High vs Low Anxiety-Related Behavior Rats: An Animal Model of Extremes in Trait Anxiety. Behav Genet 32, 301–314 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020258104318
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020258104318