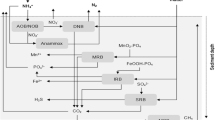
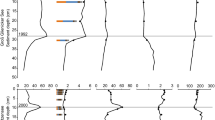
Abstract
In a laboratory experiment, different ironsalts (FeCl2, FeCl3, FeSO4) andFe2O3 were added to a phosphateenriched silty loam sediment in order to studytheir effect on phosphate mobilisation.Phosphate concentrations in sediment pore waterwere not reduced by the addition ofFe2O3. Addition of both ironchlorides, however, resulted in a strongdecrease of phosphate levels in sediment porewater. A similar but less pronounced effect wascaused by the addition of iron as iron(II)sulphate. Sulphate appears to counteract theimmobilisation of phosphate brought about byiron(II). Phosphate release from the sedimentappeared to be determined by the iron/phosphateratio in the sediment pore water. The additionof Fe2O3 barely affected thephosphate release from the sediment whereas theaddition of iron salts was effective inpreventing phosphate release. Increased amountsof iron added to the sediment resulted in adecreased phosphate release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baccini P (1985) Phosphate interactions at the sediment-water interface. In: Stumm W. (Ed.) Chemical Processes in Lakes (pp 189-224). Wiley, NY, U.S.A.
Beltman B,Rouwenhorst TG,van Kerkhoven MB,van der Krift T &Verhoeven JTA (2000) Internal eutrophication in peat soils through competition between chloride and sulphate with phosphate for binding sites. Biogeochem. 50: 183-194
Bjork S (1988) Redevelopment of lake ecosystems. A case study approach. Ambio 17: 90-98
Boers PCM (1991) The release of phosphorus from lake sediments. Ph.D. Thesis. Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Boström B,Jansson M &Forsberg C (1982) Phosphorus release from lake sediments. Arch. Hydrobiol. 18: 5-59
Caraco NF,Cole JJ &Likens GE (1989) Evidence for sulphate controlled phosphorus release from sediments of aquatic systems. Nature 341: 316-318
Cullen P &Forsberg C (1988) Experiences with reducing point sources of phosphorus to lakes. Hydrobiologia 170: 321-336
Curtis PC (1989) Effects of hydrogen ion and sulphate on the phosphorus cycle of a Precambium Shield lake. Nature 337: 156-158
Davison W (1993) Iron and mangenese in lakes. Earth Sc. Rev. 34: 119-163
Giblin AE,Likens GE,White D &Howarth RW (1990) Sulfur storage and alkalinity generation in New England lake sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 35: 852-869
Grasshoff K &Johannsen H (1977) A new sensitive method for the determination of ammonium in sea water. Wat. Res. 2: 516.
Henriksen A (1965) An automated method for determining low level concentrations of phosphate in fresh and saline waters. Analyst 90: 29-34
Lamers LPM,Tomassen HBM &Roelofs JGM (1998) Sulphate induced eutrophication and phytotoxicity in freshwater wetlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32: 199-205
Lamers LPM,Ten Dolle GE,van den Berg STG,van Delft SPJ &Roelofs JGM (2001) Differential responses of freshwater wetland soils to sulphate pollution. Biogeochem. (in press)
Mortimer CH (1941) The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes. J. Ecol. 29: 280-329
O'Brien J (1962) Automatic analysis of chlorides in sewage wastes. Engineering 33: 670-672
Ponnamperuma FN (1972) The chemistry of submerged soils. Adv. Agron. 24: 29-96
Portielje R &Lijklema L (1999) Estimation of sediment-water exchange of solutes in lake Veluwe, The Netherlands. Wat. Res. 33: 279-285
Redschaw CJ,Mason CR,Hayes CR &Roberts RD (1990) Factors influencing phosphate exchange across the sediment-water interface in eutrophic reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 192: 233-245
Roden EE &Edmonds JW (1997) Phosphate mobilization in iron-rich anaerobic sediments: microbial Fe(III) oxide reduction versus iron-sulfide formation. Arch. Hydrobiol. 139: 347-378
Roelofs JGM (1991) Inlet of alkaline river water into peaty lowlands: effects on water quality and Stratiotes aloides L. stands. Aquat. Bot. 39: 267-293
Roelofs JGM,Bobbink R,Brouwer E & de Graaf MCC (1996) Restoration ecology of aquatic and terrestrial vegetation on non-calcareous sandy soils in The Netherlands. Acta Bot. Neerl. 45: 517-541
Schindler DW,Turner MA &Stainton MP (1986) Natural resources of acid neutralizing capacity in low alkalinity lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33: 1637-1640
Smolders AJP &Roelofs JGM (1993) Sulphate-mediated iron limitation and eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems. Aquat. Bot. 46: 247-253
Smolders AJP &Roelofs JGM (1995) Internal eutrophication, iron limitation and sulphide accumulation due to the inlet of river Rhine water in peaty shallow waters in the Netherlands. Arch. Hydrobiol. 133: 349-365
Smolders AJP,Nijboer RC &Roelofs JGM (1995) Prevention of sulphide accumulation and phosphate mobilization by the addition of iron(II) chloride to a reduced sediment: an enclosure experiment. Freshw. Biol. 34: 559-568
Sperber JL (1958) Release of phosphate from soil and minerals by hydrogen sulphide. Nature 181: 934
Technicon Auto Analyser Methodology (1981) Industrial Method 635-81 W. Technicon, NY, U.S.A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smolders, A., Lamers, L., Moonen, M. et al. Controlling phosphate release from phosphate-enriched sediments by adding various iron compounds. Biogeochemistry 54, 219–228 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010660401527
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010660401527