Abstract
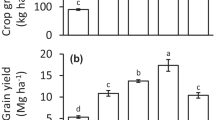
The suitability of sesbania (Sesbania rostrata) as green manure for lowland rice was evaluated in the Inland Valley Swamp (IVS) of Sierra Leone, and attempts were made to identify appropriate methods of its management in combination with urea. Sesbania — rice intercropping and sesbania — rice rotation treatments were compared with 60 kg N ha−1 applied in two splits and 30 kg N ha−1 as basal or top dressed to rice grown in the two cropping systems. The 15N isotope dilution technique was used to quantify N uptake from the green manure and urea and its utilization by rice. Rotating 40–50 days old sesbania two days prior to transplanting and top dressing with 30 kg N ha−1 as urea at nine weeks after transplanting gave highest rice grain yield (121% over the control without sesbania and urea). However intercropping sesbania with rice tended to increase N uptake and N fertilizer utilization more than the rotation treatments. The higher grain yield of rice in rotation despite lower N uptake than intercropping shows that other effects than only N explain the beneficial effect of sesbania on rice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacon PE (1990) Effect of stubble and N fertilization management on N availability and uptake under successive rice (Oryza sativa L.) crops. Plant and soil 121: 11-19
Baggie I and Bah AR (1993) Problem soils in Sierra Leone and potential management practices for rice production. Paper presented at the initial problem soils task force meeting 16-19 February 1993. WARDA, Bouake, Côte d'Ivoire
Becker M, Ladha JK and Ottow JC (1988) Stem-nodulating legumes as green manure for lowland rice. Philipp J Crop Science 13(3): 121-127
Becker M, Ladha JK and Ottow JC (1990) Growth and N2 fixation of two stem-nodulation legumes and their effect as green manure on lowland rice. Soil Biol Biochem 22: 1109-1119
Biwas TK (1988) Nitrogen dynamics and Nitrogen-15 balance in lowland rice as affected by green manure and urea application. PhD Thesis, Indian Agric Research Institute, New Delhi, India
Bouldin DR (1988) Effect of green manure on soil organic matter content and Nitrogen availability. Paper presented at the symposium on sustainable Agriculture, 25-29 May 1987, International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, Philippines
Channel RQ and Lynch JM (1984) Possible adverse effects of decomposing crop residues on plant growth. In organic matter and Rice, pp 455-475. International Rice Research Institute, P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines
Chou CH and Chiou SJ (1979) Auto-intoxification mechanism of oryza sativa, II. Effect of culture treatments on the chemical nature of paddy soil and rice productivity. J Chem Ecol 5: 839-859
De Datta SK and Buresh RJ (1989) Integrated nitrogen management in irrigated rice. Adv Soil Sci 10: 143-169
Diekmann KH (1991) Nitrogen transformation processes involving 15N labelled Sesbania and Aeschynomene afraspera green manure in lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.). PhD Thesis Justus Liebig University, Germany
Dreyfus B, Rinaudo G and Dommergues Y (1985) Observation on the use of Sesbania rostrata as green manure in paddy fields. MIRCEN J 1: 111-121
Fiedler R and Proksch G (1975) The determination of nitrogen-15 by emission and mass spectrometry in biochemical analysis. A Review: Anal Chim Acta 78: 1-62
Flinn JC and De Datta SK (1994) Trends in irrigated rice yield under intensive cropping at Philippines Research Station. Field Crop Res 9: 1-15
Fried M and Middelboe V (1977) Measurement of amount of nitrogen fixed by a legume crop. Plant and Soil 47: 713-715
George T, Ladha JK, Buresh RJ and Garrity DP (1992) Managing native and legume-fixed nitrogen in lowland rice-based cropping systems. Plant and soil 141: 69-91
Hess PR (1984) Potential of organic materials for soil improvement. In: Organic matter and rice. pp. 35-44. International Rice Research Institute. P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines
Jiao Bin (1983) Utilization of green manure for raising soil fertility in China. Soil Sci 135: 65-69
Ladha JK, Miyan S and Garcia M (1989) Sesbania rostrata as a green manure for lowland rice: growth, N-fixation, Azorhizobium sp. inoculation and effects on succeeding crop yields and nitrogen balance. Biol Fertil soils 7: 191-197
Ladha JK, Pareek RP and Becker M (1992) Stem-nodulating legume-Rhizobium symbiosis and its agronomic use in lowland rice. Adv Soil Sci 20: 149-192
Meelu OP and Morris RA (1987) Green manure management in rice-based cropping systems. Paper presented at the symposium on sustainable Agriculture, 25-29
Morris RA, Meelu OP and Furoc RE (1985) Green manuring for rice. Paper presented at the Biological Nitrogen Fixation Project Advisory Group Meeting, 18-21 November 1995, International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, Laguna, Philippines
Morris RA, Fouroc RE and Dizon MA (1986) Rice responses to a short duration green manure, II. N recovery and utilization. Agron J 78: 413-416
Page AL, Miller RH and Keeney DR (1982) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part II, second edition. ASA and SSA, Wisconsin, USA, 1159 pp
Pareek RP, Ladha JK and Watanabe I (1990) Estimating N2 fixation by Sesbania rostrata and S. cannabina (Syn. S. acuelata) in lowland rice soil by the 15N dilution method. Biol Fertil Soils 10: 77-88
Rinaudo G, Alazard D and Moudiongui M (1988) Stem-nodulating legumes and green manure for rice in West Africa. In sustainable Agriculture. Green Manure rice farming, pp 98-109. International Rice Research Institute, P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines
SAS Institute Inc (1990) SAS Users' Guide. Statistical Analysis System Institute Inc, Cary, North Carolina, USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bar, A.R., Baggie, I. & Sanginga, N. The use of Sesbania (Sesbania rostrata) and urea in lowland rice production in Sierra Leone. Agroforestry Systems 48, 111–118 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006345920266
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006345920266