Abstract
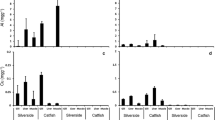
The toxicity of the Reconquista River water at Cascallares, a relatively low polluted point, was determined by means of bioassays with juvenile Cyprinus carpio as a test organism. During the summer of 1995–1996, three 30 days-long in situ caged fish tests were conducted. Changes in the activities of branchial (Na+,K+)- and Mg++-ATPases and brain AchE offish were studied. The chemical profile of the river water showed that heavymetals and phenols were the main pollutants. Gill ATPases activities were altered, while brain AchE activity resulted inhibited in one of the assays. (Na+,K+)-dependent activity was inhibited approximately 20% as compared with controls; in two assays Mg++-ATPase activity was stimulated. The condition factor of caged fish did not differ from controls.Since the protein content of gills was slightly altered, the detected changes in the enzyme activity should not be linked to alterations in the protein synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.P.H.A.: 1992, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th ed., APHA, AWWA, WEF. Washington, DC.
Bocquené, G. Galgani, F. and Walker C. H.: 1997, Les cholinesterases, biomarqueurs de neurotoxicité, in: Lagadia, L. Caquet, T. Amirad, J-C. and Ramade, F. (eds.), Biomarqueurs en écotoxicologie, Masson, Paris. 208–240.
Bourdou, A. and Ribeyre, F.: 1997, Environ. Health Persp. 105, 21–35.
Castañé, P. M., Topalián, M. L., Rovedatti, M. G. and Salibián, A.: 1998a, Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 26, 1206–1208.
Castañé, P. M., Loez, C. R., Olguín, H. F., Puig, A., Rovedatti, M. G., Topalián, M. L. and Salibián, A.: 1998b, Rev. Internat. Contamin. Amb. 14, 69–77.
de la Torre, F. R., Ferrari, L. and Salibián, A.: 1996, Acta Toxicol. Argent. 4, 56.
de la Torre, F. R., Demichelis, S. O., Ferrari, L. and Salibián, A.: 1997a, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 58, 558–565.
de la Torre, F. R., Ferrari, L. and Salibián, A.: 1997b, Evaluación ecotoxicológica del agua del río Reconquista: cambios en la actividad de enzimas marcadoras de peces mantenidos in situ. Proc. Internat. Congr. Water, (Argentina), I. 34.
de la Torre, F. R., Salibián, A. and Ferrari, L.: 1999, Environ.Toxicol. 14, 313–319.
Di Giulio, R. T., Benson,W. H., Sanders, B.M. and Van Veld, P. D.: 1995, Biochemical mechanisms: metabolism, adaptation and toxicity, in: Rand (ed): Fundamentals of Aquatic toxicology. Effects, environmental fate and risk assessment, Washington DC, 523–560.
Ellman, G. L., Courtney, K. D., Andreas, V. Jr. and Feathersone, R. M.: 1961, Biochem. Pharmacol. 7, 88–95.
Erickson, R. J., Benoit, D. A., Mattson, V. R., Nelson, Jr. H. P. and Leonard, E. N.: 1996, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 181–193.
Espina, S., Salibián, A., Rosas, C., Sanchez, A. and Alcaraz, G.: 1995, Acta Toxicol. Argentina 3, 8–10.
Ferrari, L., Demichelis, S. O., García, M. E., de la Torre, F. R. and Salibián, A.: 1997, Environ. Toxicol. Wat. Qual. 12, 117–121.
Fiske, C. H. and Subbarow, Y.: 1925, J. Biol. Chem. 66, 375–400.
García, M. E., Demichelis, S. O.; de la Torre, F. R. and Ferrari, L.: 1998, Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 26, 1216–1218.
Gill, T. S., Tewari, H. and Pande, J.: 1991, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 100, 501–505.
Glynn, A. W.: 1996, Aquatic Toxicol. 35, 47–58.
Hanke, W., Guth, G., Bubel, H. and Müller, R.: 1983, Ecotoxicol. Environm. Saf. 7, 229–241.
Hollis, L., Muench, L. and Playle, R. C.: 1997, J. Fish. Biol. 50, 703–720.
Kakuta, I. and Murachi, S.: 1997, Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 12, 1–9.
Loez, C. R. and Salibián, A.: 1990, Rev. Hydrobiol. Trop. 23, 283–296.
Loez, C. R., Salibián, A. and Topalián, M.L.: 1998, Rev. Sci. Eau 11, 315–332.
Lowry, O. H., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. and Randall, R. J.: 1951, J.Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Martínez, J. E. and Salibián, A.: 1995a, Spatial and temporal distribution of Coliform group in the Reconquista river. Abstr. XXVI Internat. Congr. Theor. Appl. Limnology, 295.
Martínez, J. E. and Salibián, A.: 1995b, Fecal pollution of surface water in an urban river. Proc. 7th Internat. Symp. Toxicity Assess. ISTA7 (Chile), 75.
Neubecker, T. A. and Allen, H. E.: 1983, Water Res. 17, 1–14.
OECD: 1992, Guideline for testing of chemicals N° 210. Fish, early life stage toxicity test 1/18-18/18.
Pan American Health Association (PAHA): 1987, Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality-Vol. 2. Health Criteria and other Supporting Information.
Salánki, J.: 1989, Acta Biol. Hungarica 40, 295–328.
Simkiss, K.: 1996, Ecotoxicants at the cell-membrane barrier, in: Newman, M. C. and Jagoe, C. H. (eds): Ecotoxicology: a hierarchical treatment, Boca Raton, FL. 59–83.
Theodorakis, C. W., D'surney, S. J., Bickham, J. W., Lyne, T. B., Bradley, B. P., Hawkins, W. E., Farkas, W. L., McCarthy, J. F. and Shugart, L. R.: 1992, Ecotoxicology 1, 45–73.
Topalián, M. L., Rovedatti, M. G., Castañé, P. M. and Salibián, A. (a): Pollution in a lowland river system. A case study: the Reconquista river (Buenos Aires, Argentina). Water Air Soil Poll. In press.
Topalián, M. L., Castañé, P. M., Rovedatti, M. G. and Salibián, A. (b): Principal component analysis of dissolved heavy metals in water of the Reconquista River ( Buenos Aires, Argentina): Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. In press.
Van der Putte, I., Lubbers, J. and Kolar, Z.: 1981a, Aquat. Toxicol. 1, 3–18.
Van der Putte, I., Brinkhorst, M. A. and Koeman, Z.: 1981b, Aquat. Toxicol. 1, 129–142.
Verrengia-Guerrero, N. and Kesten, E. M.: 1994, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 52, 254–260.
Walker, C. H., Hopkin, S. P., Silby R.M. and Peakall DB.; 1997, Principles of Ecotoxicology, Taylor and Francis, London. 321 pp.
Watson, T. A. and Beamish, F. W. H.: 1980, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 66C, 77–82.
Watson, C. F. and Benson, W. H.: 1987, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 14, 252–259.
Wendelaar Bonga S. E.: 1997, Physiol. Revs. 77, 591–625.
Zar, J. H.: 1996, Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice-Hall N.J., 662 pp.
Zaugg, W. S.: 1982, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 39, 215–217.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de la Torre, F.R., Ferrari, L. & Salibián, A. Long-term in situ Toxicity Bioassays of the Reconquista River (Argentina) Water with Cyprinus carpio as Sentinel Organism. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 121, 205–215 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005243521758
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005243521758