Abstract
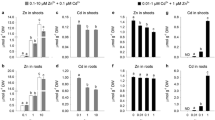
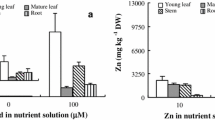
Effect of varied zinc (Zn) supply (0, 0.1, 1, 5 μM) on re-translocation of radio-labeled cadmium (109Cd) and rubidium (86Rb) from mature leaf to root and other parts of shoot was studied in 11-day-old durum wheat (Triticum durum cv. C-1252) plants grown in nutrient solution under controlled environmental conditions. Application of 109Cd and 86Rb was carried out by immersing the tips (3 cm) of mature leaf in radio-labeled solutions for 10 s at three different times over a 42 h period. Differences in Zn supply for 11 days did not affect plant growth nor did it cause visual leaf symptoms, such as necrosis and chlorosis, at either the lowest or the highest Zn supply. Only at the nil Zn supply (0 μM), shoot and root dry weights tended to decrease and increase, respectively, causing a lower shoot/root dry weight ratio. Partitioning of more dry matter to roots rather than shoots, a typical phenomena for Zn-deficient plants in nutrient solution experiments, indicated existence of a mild Zn deficiency stress at the nil-Zn treatment. Irrespective of Zn supply, plants could, on average, retranslocate 3.8% and 38% of the total absorbed 109Cd and 86Rb from the treated leaf to roots and other parts of shoots within 42 h, respectively. At nil-Zn treatment, 2.8% of the total absorbed 109Cd was re-translocated from the treated leaf, particularly into roots. The highest re-translocation of 109Cd (6.5%) was found in plants supplied with 0.1 μM Zn. Increases in Zn supply from 0.1 μM reduced 109Cd re-translocation from 6.5% to 4.3% at 1 μM Zn and 1.3% at 5 μM Zn. With the exception of the nil-Zn treatment, the proportion of re-translocated 109Cd was greater in the remainder of the shoot than in the roots. Contrary to the 109Cd results, re-translocation of 86Rb was not (at 0, 0.1 and 1 μM Zn), or only slightly (at 5 μM), affected by changing Zn supply. The results indicate an inhibitory action of increased concentrations of Zn in shoot tissues on phloem-mediated Cd transport. This effect is discussed in relation to competitive inhibition of Cd loading into phloem sap by Zn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson A and Siman G 1991 Levels of Cd and some other trace elements in soils and crops as influenced by lime and fertilizer level. Acta Agric. Scand. 41, 3–11.
Cakmak I and Marschner H 1988 Increase in membrane permeability and exudation in roots of zinc-deficient plants. J. Plant Physiol. 132, 356–361.
Cakmak I, Gulut K Y, Marschner H and Graham R D 1994 Effects of zinc and iron deficiency on phytosiderophore release in wheat genotypes differing in zinc efficiency. J. Plant Nutr. 17, 1–17.
Cakmak I, Sari N, Marschner H, Kalayci M, Yilmaz A, Eker S and Gulut K Y 1996 Dry matter production and distribution of zinc in bread and durum wheat genotypes differing in zinc efficiency. Plant Soil 180, 173–181.
Cakmak I, Ekiz H, Yilmaz A, Torun B, Koleli N, Gultekin I, Alkan A and Eker S 1997 Differential response of rye, triticale, bread and durum wheats to zinc deficiency in calcareous soils. Plant Soil 188, 1–10.
Cakmak I, Torun B, Erenoglu B, Ozturk L, Marschner H, Kalayci M, Ekiz H and Yilmaz A 1998 Morphological and physiological differences in cereals in response to zinc deficiency. Euphytica 100, 349–357.
Choudhary M, Bailey L D and Grant C A 1994 Effect of zinc on Cadmium concentration in tissue of durum wheat. Can. J. Plant Sci. 74, 549–552.
Clarke J M, Leisle D, De Pauw R M and Thiessen L L 1997 Registration of five pairs of durum wheat genetic stocks near-isogenic for cadmium concentration. Crop Sci. 37, 297.
Graham R D, Ascher J S and Hynes S C 1992 Selecting zincefficient cereal genotypes for soils of low zinc status. Plant Soil 241–250.
Grant C A and Bailey L D 1997 Effects of phosphorus and zinc fertiliser management on cadmium accumulation in flaxseed. J. Sci. Food Agric. 73, 307–314.
Grant C A, Buckley W T, Bailey L D and Selles F 1998 Cadmium accumulation in crops. Can. J. Plant Sci. 78, 1–17.
Hart J J, Welch R M, Norvell W A, Sullivan L A and Kochian L V 1998 Characterization of cadmium binding, uptake and translocation in intact seedlings of bread and durum wheat cultivars. Plant Physiol. 116, 1413–1420.
Jones K C and Johnston A E 1989 Cadmium in cereal grain and herbage from long-term experimental plots at Rothamsted, UK. Envir. Pollut. 57, 199–216.
McKenna I M, Chaney R L and Williams F M 1993 The effect of cadmium and zinc interactions on the accumulation and tissue distribution of zinc and cadmium in lettuce and spinach. Envir. Pollut. 79, 113–120.
McLaughlin M J, Palmer L T, Tiller K G, Beech T A and Smart M K 1994 Increased soil salinity causes elevated cadmium concentrations in filed-grown potato tubers. J. Envir. Qual. 23, 1013–1018.
Meyers M W, Fricke F L, Holmgren G G S, Kubota J and Chaney R L 1982 Cadmium and lead in wheat grain and associated surface soils of major wheat production areas in the United States. Agron. Abs. 34 p.
Moraghan J T 1993. Accumulation of cadmium and selected elements in flax seed grown on a calcareous soil. Plant Soil 150, 61–68.
Oliver D P, Schultz J E, Tiller K G, Wilhelm N S, Merry R H and Cozens G D 1994 The effects of zinc fertilization on cadmium concentration in wheat grain. J. Envir. Qual. 23, 705–711.
Rauser W E and Samarakoon A B 1980 Vein loading in seedlings of Phaseolus vulgaris exposed to excess cobalt, nickel and zinc. Plant Physiol. 65, 578–583.
Rengel Z and Graham R 1995 Wheat genotypes differ in zinc efficiency when grown in the chelate-buffered nutrient solution I. Growth. Plant Soil 176, 307–316.
Rengel Z, Romheld V and Marschner H 1998 Uptake of zinc and iron by wheat genotypes differing in tolerance to zinc deficiency. J. Plant Physiol. 152, 433–438.
Richards I R, Clayton C J and Reeve A J K 1998 Effects of long-term fertilizer phosphorus application on soil and crop phosphorus and cadmium contents. J. Agric. Sci. (Cambridge) 131, 187–195.
Roberts A H C, Longhurst R D and Brown M W 1994 Cadmium status of soils, plants and grazing animals in New Zealand. N.Z. J. Agric. Res. 37, 119–129.
Wagner G J 1993 Accumulation of cadmium in crop plants and its consequences to human health. Adv. Agron. 51, 173–212.
Williams C H and David D J 1976 The accumulation in soil of cadmium residues from phosphate fertilizers and their effect on the cadmium content of plants. Soil Sci. 121, 86–93.
Welch R M, Webb M J and Loneragen J F 1982 Zinc in membrane function and its role in phosphorus toxicity. In Plant Nutrition 1982, Proceedings of the Ninth International Plant Nutrition Colloquim. Ed. A Scaife. pp 710–715. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau, UK.
Welch R M, Hart J J, Norvell W A, Sullivan L A and Kochian, L V 1999 Effects of nutrient solution zinc activity on net uptake, translocation and root export of cadmium and zinc by separated sections of intact durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var durum) seedling roots. Plant Soil 208, 243–250.
White M C and Chaney R L 1980. Zinc, Cd and Mn uptake by soybean from two Zn-and Cd-amended coastal plain soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44, 308–313.
Zenk M H 1996 Heavy metal detoxification in higher plants - a review. Gene 179, 21–30.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cakmak, I., Welch, R., Erenoglu, B. et al. Influence of varied zinc supply on re-translocation of cadmium (109Cd) and rubidium (86Rb) applied on mature leaf of durum wheat seedlings. Plant and Soil 219, 279–284 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004777631452
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004777631452