Abstract
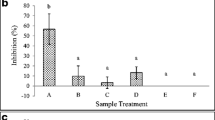
The presence of biofertilizers can affect the life and movement of subterranean organisms in the soil. In the current study, the effect of three biofertilizers (Unigrow, Rhizogold and Rhizogold Plus) alone and in combination with diatomaceous earth (DE) and insecticides on mortality and movement of subterranean termites, Coptotermes heimi (Wasmann), was investigated under laboratory conditions. The mortality of termites in soil mixed with biofertilizers was low as compared to the control treatment, which led to significant mortality. Length of galleries formed by termites with the addition of Unigrow in the soil was significantly higher as compared to the other two biofertilizers and control treatments. Mortality increased in the presence of insecticides and DE in the soil substrate. Unigrow mixed soil having chlorfenapyr had maximum mortality and minimum gallery length followed by Rhizogold and Rhizogold Plus. The addition of DE and insecticide further enhances mortality, and we recommend that some toxic elements should be incorporated in biofertilizers to control subterranean termites.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Bengtsson J., Ahnström J. and Weibull A.-C. (2005) The effects of organic agriculture on biodiversity and abundance: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Ecology 42, 261–269.
Chen J.-H. (2006) The combined use of chemical and organic fertilizers and/or biofertilizer for crop growth and soil fertility, pp. 1–11. In International Workshop on Sustained Management of the Soil-Rhizosphere System for Efficient Crop Production and Fertilizer Use, 16-20 October 2006. Land Development Department, Bangkok, Thailand.
Ebeling W. and Forbes C. F. (1988) Sand barriers for subterranean termite control. IPM Practitioner 10(5), 1–6.
Geisseler D. and Scow K. M. (2014) Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms - A review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 75, 54–63.
Grace J. K. and Yamamoto R. T. (1993) Diatomaceous earth is not a barrier to formosan subterranean termites (Isoptera: Termitidae). Sociobiology 23, 25–30.
Hirose E., Neves P. M. O. J., Zequi J. A. C., Martins L. H., Peralta C. H. and Alcides Moino Jr. (2001) Effect of biofertilizers and neem oil on the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. and Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch.) Sorok. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology 44, 419–423.
Jiang M., Wang X., Liusui Y., Sun X., Zhao C. and Liu H. (2015) Diversity and abundance of soil animals as influenced by long-term fertilization in grey desert soil, China. Sustainability 7, 10837–10853.
Mando A. and Brussard L. (1999) Contribution of termites to the breakdown of straw under Sahelian conditions. Biology and Fertility of Soils 29, 332–334.
Megali L., Glauser G. and Rasmann S. (2014) Fertilization with beneficial microorganisms decreases tomato defenses against insect pests. Agronomy for Sustainable Development 34, 649–656.
Osaka N., Nagai K., Mizuno S., Sakka M. and Sakka K. (2011) Development of an anaerobic hydrogen and methane fermentation system for kitchen waste biomass utilization, pp. 447–454. In Proceedings of the World Renewable Energy Congress. 8–13 May 2011, Linköping, Sweden. Available at: https://doi.org/www.ep.liu.se/ecp/057/vol1/060/ecp57vol1_060.pdf.
Sop T. K., Kagambega F. W., Bellefontaine R., Schmiedel U. and Thiombiano A. (2011) Effects of organic amendment on early growth performance of Jatropha curcas L. on a severely degraded site in the sub-Sahel of Burkina Faso. Agroforestry Systems 86, 387–399.
Wang S., Chen H. Y. H., Tan Y., Fan H. and Ruan H. (2016) Fertilizer regime impacts on abundance and diversity of soil fauna across a poplar plantation chronosequence in coastal eastern China. Scientific Reports 6, Article number: 20816.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, S., Hassan, B. & Farooq, M.U. Effect of biofertilizers and diatomaceous earth on life and movement of subterranean termites under laboratory conditions. Int J Trop Insect Sci 38, 348–352 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758418000103
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758418000103