Abstract
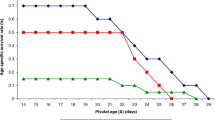
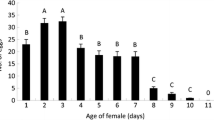
Oomyzus sokolowskii (Kurdjumov) is a gregarious larval-pupal parasitoid of the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella (L.). The objective of this study was to investigate the interactions between host and parasitoid by examining the effects of biotic factors such as gregariousness, host origin and stages, and female parasitoid age on the parasitism rate, developmental time, the number of offspring and the offspring sex ratio of O. sokolowskii under laboratory conditions. The percentage of parasitism and the number of parasitoids increased with the number of O. sokolowskii females. Oomyzus sokolowskii preferred fourth larval instars over other larval stages. The parasitism rate and the progeny production of O. sokolowskii decreased with parasitoid age; however, the developmental time and the sex ratio of the offspring were not significantly different. Our results confirm previous findings on larval preferences of O. sokolowskii. The study also confirmed the importance of geographical origin of the host on the performance of O. sokolowskii.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amalin D. M., Peña J. E. and Duncan R. E. (2005) Effects of host age, female parasitoid age, and host plant on parasitism of Ceratogramma etiennei (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Florida Entomologist 88, 77–82.
Andow D. A., Ragsdale D. W. and Nyvall R. F. (eds) (1997) Ecological Interactions and Biological Control. Westview Press, Boulder, CO. 334 pp.
Aruna A. S. and Manjunath D. (2010) Reproductive performance of Nesolynx thymus (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) as influenced by host (Musca domestica) size. BioControl 55, 245–252.
Arvanitakis L., Bonal F., Bordat A., Kirk A. A. and Bordat D. (2002) Biological and molecular variability within seven populations of Plutella xylostella (L.) from Benin, pp. 135–137. In Improving Biocontrol of Plutella xylostella (edited by A. A. Kirk and D. Bordat). Proceedings of the International Symposium on Improving Biocontrol of Plutella xylostella, Montpellier, France. 21–24 October 2002. CIRAD, Montpellier.
Bai B., Luck R. F., Forster L., Stephens B. and Janssen J. M. (1992) The effect of host size on quality attributes of the egg parasitoid, Trichogramma pretiosum. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 64, 37–48.
Chen R. X., Zhang F., Huangfu W. G., Yao H. Y., Zhou J. B. and Kuhlmann U. (2008) Reproductive attributes of the eulophid Oomyzus sokolowskii, a biological control agent of diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Biocontrol Science and Technology 18, 753–765.
Chown S. L., Jumbam K. R., Sorensen J. G. and Terblanche J. S. (2009) Phenotypic variance, plasticity and heritability estimates of critical thermal limits depend on methodological context. Functional Ecology 23, 133–140.
Edwards R. L. (1954) The effect of diet on egg maturation and resorption in Mormoniella vitripennis (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science 95, 459–468.
Ferreira S. W. J., Barros R. and Torres J. B. (2003) Exigencias termicas e estimativa do nhmero de geracoes de Oomyzus sokolowskii (Kurdjumov) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), para regioes produtoras de cruciferas em Pernambuco. Neotropical Entomology 32, 407–411.
Fidgen J. G., Eveleigh E. S. and Quiring D. T. (2000) Influence of host size on oviposition behaviour and fitness of Elachertus cacoeciae attacking a low-density population of spruce budworm Choristoneura fumiferana larvae. Ecological Entomology 25, 156–164.
Giron D. and Casas J. (2003) Mothers reduce egg provisioning with age. Ecology Letters 6, 273–277.
Godfray H. C. J. (1994) Parasitoids: Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ. 473 pp.
Grzywacz D., Rossbach A., Rauf A., Russell D. A., Srinivasan R. and Shelton A. M. (2010) Current control methods for diamondback moth and other brassica insect pests and the prospects for improved management with lepidopteran-resistant Bt vegetable brassicas in Asia and Africa. Crop Protection 29, 68–79.
Gu H., Wang Q. and Dorn S. (2003) Superparasitism in Cotesia glomerata: response of host and consequences for parasitoids. Ecological Entomology 28, 422–431.
Harvey J. A., Bezemer T. M., Elzinga J. A. and Strand M. R. (2004) Development of the solitary endoparasitoid Microplitis demolitor: host quality does not increase with host age and size. Ecological Entomology 29, 35–43.
Hirashima Y., Miura K., Miura T. and Matsuda S. (1990) Studies on the biological control of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus). 5. Functional responses of the egg parasitoids, Trichogramma chilonis and Trichogramma ostriniae, to host densities. Science Bulletin of the Faculty of Agriculture-Kyushu University, Japan 44, 89–93.
Islam K. S. and Copland M. J. W. (1997) Host preference and progeny sex ratio in a solitary koinobiont mealybug endoparasitoid, Anagyrus pseudococci (Girault), in response to its host stage. Biocontrol Science and Technology 7, 449–456.
Keasar T., Segoli M., Bakar R., Steinberg S. and Giron D. (2006) Costs and consequences of superparasitism in the polyembryonic parasitoid Copidosoma koehleri (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae). Ecological Entomology 31, 277–283.
Kirk A. A., Mercadier G., Bordat D., Delvare G., Pichon A., Arvanitakis L., Goudegnon A. E. and Rincon C. (2004) Variability in Plutella and its natural enemies: implications for biological control, pp. 71–77. In The Management of Diamondback Moth and Other Crucifer Pests (edited by N. M. Endersby and P. M. Ridland). Proceedings of the Fourth International Workshop, Melbourne, Australia, 26–29 November 2001. Department of Natural Resources and Environment, Melbourne.
Li S. Y., Sirois G., Lee D. L., Maurice C. and Henderson D. E. (1993) Effects of female mating status and age on fecundity, longevity and sex ratio in Trichogramma minutum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Journal ofthe Entomological Society ofBritish Columbia 90, 61–66.
Lim G. S. (1992) Integrated pest management of diamondback moth: practical realities, pp. 565–576. In Management of Diamondback Moth and Other Crucifer Pests (edited by N. S. Talekar). Proceedings of the Second International Workshop, Tainan, Taiwan, 10–14 December 1990. Asian Vegetable Research and Development Centre (AVRDC), Tainan.
Liu S. S. Wang X. G., Guo S. J., He J. H. and Song H. M. (1997) A survey of insect parasitoids of Plutella xylostella and the seasonal abundance of the major parasitoids in Hangzhou, China, pp. 61–66. In Management of Diamondback Moth and Other Crucifer Pests (edited by A. Sivapragasam, W. H. Loke, A. K. Hussan and G. S. Lim). Proceedings of the Third International Workshop, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 29 October–1 November 1996. Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute (MARDI), Kuala Lumpur.
Martinez-Castillo M., Leyva J. L., Cibrian-Tovar J. and Bujanos-Muboz R. (2002) Parasitoid diversity and impact on populations of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.) on Brassica crops in central Mexico. BioControl 47, 23–31.
Medeiros R. S., Ramalho F. S., Lemos W. P. and Zanuncio J. C. (2000) Age-dependent fecundity and life-fertility tables for Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas) (Het., Pentatomidae). Journal of Applied Entomology 124, 319–324.
Nakamura A. and Noda T. (2002) Effects of host age and size on clutch size and sex ratio of Oomyzus sokolowskii (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), a larval-pupal parasitoid of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae). Applied Entomology and Zoology 37, 319–322.
Persad A. B. and Hoy M. A. (2003) Manipulation of female parasitoid age enhances laboratory culture of Lysiphlebus testaceipes (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) reared on Toxoptera citricida (Homoptera: Aphididae). Florida Entomologist 86, 429–436.
Pichon A., Bordat D., Bordat A., Arvanitakis L. and Tertois C. (2004) Biological and genetic differences between populations of diamondback moth from different geographic regions, pp. 79–86. In The Management ofDiamondback Moth and Other Crucifer Pests (edited by N. M. Endersby and P. M. Ridland). Proceedings of the Fourth International Workshop, Melbourne, Australia, 26–29 November 2001. Department of Natural Resources and Environment, Melbourne.
Rajapakse R. H. S. (1992) Effect of host age, parasitoid age, and temperature on interspecific competition between Chelonus insularis Cresso, Cotesia marginiventris Cresson and Microplitis manilae Ashmead. Insect Science and Its Application 13, 87–94.
Riddick E. W. (2003) Factors affecting progeny production of Anaphes iole. Biocontrol 48, 177–189.
Roux O., Gevrey M., Arvanitakis L., Gers C., Bordat D. and Legal L. (2007) ISSR-PCR: tool for discrimination and genetic structure analysis of Plutella xylostella populations native to different geographical areas. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 43, 240–250.
Sarfraz M., Dosdall L. M. and Keddie B. A. (2006) Diamondback moth-host plant interactions: implications for pest management. Crop Protection 25, 625–639.
Shelly T., Rendon P., Hernandez E., Salgado S., McInnis D., Villalobos E. and Liedo P. (2003) Effects of diet, ginger root oil, and elevation on the mating competitiveness of male Mediterranean fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) from a mass-reared, genetic sexing strain in Guatemala. Journal of Economic Entomology 96, 1132–1141.
Shelton A. M. (2004) Management of the diamondback moth: Deja vu all over again?, pp. 3–8. In The Management of Diamondback Moth and Other Crucifer Pests (edited by N. M. Endersby and P. M. Ridland). Proceedings of the Fourth International Workshop, Melbourne, Australia, 26–29 November 2001. Department of Natural Resources and Environment, Melbourne.
Silva-Torres C. S. A. and Matthews R. W. (2003) Development of Melittobia australica Girault and Melittobia digitata Dahms (Parker) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) parasitizing Neobellieria bullata (Parker) (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) puparia. Neotropical Entomology 32, 645–651.
Silva-Torres C. S. A., Barros R. and Torres J. B. (2009a) Effect of age, photoperiod and host availability on the parasitism behavior of Oomyzus sokolowskii Kurdjumov (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Neotropical Entomology 38, 512–519.
Silva-Torres C. S. A., Filho I. T. R., Torres J. B. and Barros R. (2009b) Superparasitism and host size effects in Oomyzus sokolowskii, a parasitoid of diamondback moth. Entomologia Experimentalis etApplicata 133, 65–73.
Sivinski J., Jeronimo F. and Holler T. (2000) Development of aerial releases of Diachasmimorpha tryoni (Cameron) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) a parasitoid that attacks the Mediterranean fruit fly, Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann) (Diptera: Tephritidae) in the Guatemalan highlands. Biocontrol Science and Technology 10, 15–25.
Sivinski J., Aluja M., Pinero J. and Qjeda M. (2004) Novel analysis of spatial and temporal patterns of resource use in a group of tephritid flies of the genus Anastrepha. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 97, 504–512.
STATVIEW (1996) StatView Version 4.55 for Windows. Abacus Concepts, Inc., Berkeley, CA.
Talekar N. S. and Hu W. J. (1996) Characteristics of parasitism of Plutella xylostella (Lep., Plutellidae) by Oomyzus sokolowskii (Hym., Eulophidae). Entomophaga 41, 45–52.
van Loon J. J. A., Wang C. Z., Nielsen J. K., Gols R. and Qiu Y. T. (2002) Flavonoids from cabbage are feeding stimulants for diamondback moth larvae additional to glucosinolates: chemoreception and behaviour. Entomologia Experimental et Applicata 104, 27–34.
Wang X., Liu S., Gao S. and Lin W. (1999) Effect of host stages and temperature on population parameters of Oomyzus sokolowskii, a larval-pupal parasitoid of Plutella xylostella. BioControl 44, 391–402.
Yamada Y. Y. and Miyamoto K. (1998) Pay off from self and conspecific superparasitism in a dryinid parasitoid, Haplogonatopus atratus. Oikos 81, 209–216.
Zaviezo T. and Mills N. (2000) Factors influencing the evolution in clutch size in a gregarious insect parasitoid. Journal of Animal Ecology 61, 1047–1057.
Zhou L., Huang J. and Xu H. (2011) Monitoring resistance of field populations of diamondback moth Plutella xylostella L. (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae) to five insecticides in South China: a ten-year case study. Crop Protection 30, 272–278.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sow, G., Arvanitakis, L., Niassy, S. et al. Performance of the parasitoid Oomyzus sokolowskii (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) on its host Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) under laboratory conditions. Int J Trop Insect Sci 33, 38–45 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758412000422
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758412000422