Abstract
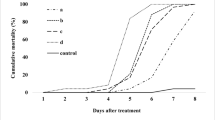
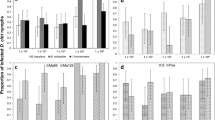
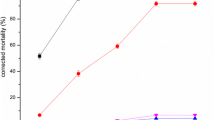
Infectivity of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae against workers of the arboreal termite Odontotermes sp. was assayed under laboratory conditions. Test isolates were collected from different sources, including soil from varied locations and insect hosts from the orders Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Hemiptera and Orthoptera. All the 23 isolates tested and the standard (ARSEF 7413) were pathogenic to the workers of Odontotermes sp. at a concentration of 107 conidia/ml, with mean mortality ranging from 57.5 to 100%. Two of the isolates (Ma2, Ma13) and the standard caused 100% mortality in the termite species. A detailed bioassay was subsequently conducted with the five most promising isolates, namely Ma1, Ma2, Ma13, Ma16 and Ma17, at concentrations ranging from 104 to 107 conidia/ml. The lethal concentrations (LC50) of these isolates ranged from 0.01 to 0.46 × 105 conidia/ml. The average survival time (AST) for the termites treated with the most virulent isolate (Ma2) varied from 4.2 to 5.7 days across the four spore loads, while AST with the standard isolate ranged from 5.3 to 6.3 days. Two of the isolates, Ma2 and Ma13, were found to be significantly more pathogenic to Odontotermes sp. workers than all the others, including the standard.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott W. S. (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. Journal of Economic Entomology 18, 265–267.
Almedia J. E. M., Alves S. B. and Pereia R. M. (1997) Selection of Beauveria spp. isolates for control of the termite Heterotermes tenuis (Hagen, 1858). Journal of Applied Entomology 121, 539–543.
Bao L. L. and Yendol W. G. (1971) Infection of the eastern subterranean termite, Reticulitermes flavipes (Kollar) with the fungus Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuill. Entomophaga 16, 343–352.
Changjin D., Jiamin Z., Hai H. Wugwo C. and Yuanyang H. (2009) Pathogenicity of a new China variety of Metarhizium anisopliae var. dcjhyium to subterranean termite Odontotermes formosans. Microbiological Research 164, 27–35.
Creffield J. W. (1996) Wood-destroying insects, Wood Borers and Termites. CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood. 44 pp.
Delante K. M., Grace J. K. and Tome C. H. M. (1995) Potential use of pathogenic fungi in baits to control the Formosan subterranean termite (Isopt., Rhinitermitidae). Journal of Applied Entomology 119, 429–433.
Ferron P. (1981) Pest control by the fungi Beauveria and Metarhizium, pp. 465–482. In Microbial Control of Pest and Plant Diseases (edited by H. D. Burges). Academic Press, New York.
Finney D. J. (1971) Probit Analysis. Cambridge University Press. 333 pp.
Goettel M. S. (1992) Fungal agents for biocontrol, pp. 122–132. In Biological Control of Locust and Grasshoppers (edited by C. J. Lomer and C. Prior). CAB International, Oxon.
Gunner H. B., Kane J. and Duan H. (1994) Biological Control of Termites. PCT Patent Application W094/04034.
Houping L. I. U., Margaret S., Bruce L. P. and Michael B. (2002) Pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes), and other entomopathogenic fungi against Lygus lineolaris (Hemiptera: Miridae). Journal of Economic Entomology 95, 675–681.
Jones W. E., Grace J. K. and Tamashiro M. (1996) Virulence of seven isolates of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae to Coptotermes formosanus (Isoptera, Rhinotermitidae). Environmental Entomology 25, 481–487.
Khan K. (1991) Mycopathogens for biological control of Odontotermes brunneus (Hagen). Journal of Biological Control 5, 32–35.
Latch G. C. M. (1965) Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschnikoff) Sorokin strains in New Zealand and their possible use for controlling pasture-inhabiting insects. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research 8, 384–396.
Latch G. C. M. (1976) Studies on the susceptibility of Oryctes rhinoceros to some entomogenous fungi. Entomophaga 21, 31–38.
McCoy C. W., Samson R. A. and Boucias D. G. (1988) Entomogenous fungi, pp. 151–236. In CRC Handbook of Natural Pesticides (edited by C. M. Ignoffo). CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, Florida.
Milner R. J. and Staples J. A. (1996) Biological control of termites - results and experiments within a CSIRO project in Australia. Biocontrol Science and Technology 6, 3–9.
Milner R. J., Staples J. A. and Lutton G. G. (1998) The selection of an isolate of the Hyphomycete fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae for control of termites in Australia. Biological Control 3, 240–247.
Poprawski T. J., Marchal M. and Robert P. H. (1985) Comparative susceptibility of Otiorhynchus sulcatus and Sitona lineatus (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) early stage to five entomopathogenic Hyphomycetes. Environmental Entomology 14, 247–253.
Rath A. C. (2000) The use of entomopathogenic fungi for control of termites. Biocontrol Science and Technology 10, 563–581.
Remadevi O. K., Sivaramakrishnan V. R. and Sarma C. R. (1998) Control of arboreal termites on Santalum album Linn. in plantations, pp. 196–199. Sandal and its Products. Proceedings of an International Seminar held at Bangalore, India on 19–20 December 1997, Canberra ACIAR Proceedings No. 84.
Soares G. G., Marchal M. J. and Ferron P. (1983) Susceptibility of Otiorhynchus sulcatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) larvae to Metarhizium anisopliae and Metarhizium flavoviridae (Deuteromycotina, Hyphomycetes) at two different temperatures. Environmental Entomology 12, 1886–1890.
Watson J. A. L. and Gay F. J. (1991) Isoptera, pp. 330–347. In Insects of Australia (edited by I. D. Naumanni). Melbourne University Press, Melbourne.
Wiseman S. and Eggleton P. (1994) The Termiticide Market. Agrow Report DS88. PJB Publications, Richmond.
Yendol W. G. and Paschke J. D. (1965) Pathology of an entomophthora infection in the eastern subterranean termite Reticulitermes flavipes (Kollar). Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 7, 414–422.
Zoberi M. H. and Grace J. K. (1990) Isolation of the pathogen Beauveria bassiana from Reticulitermes flavipes (Isoptera, Rhinotermitidae). Sociobiology 16, 289–296.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balachander, M., Remadevi, O.K., Sasidharan, T.O. et al. Infectivity of Metarhizium anisopliae (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) isolates to the arboreal termite Odontotermes sp. (Isoptera: Termitidae). Int J Trop Insect Sci 29, 202–207 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758409990294
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758409990294