Abstract
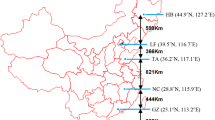
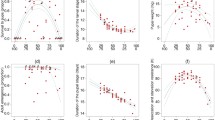
The southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella, has expanded its range during this century so that it is now distributed between about 18 and 38°N latitude in Mexico and the United States. The species survives from year to year by entering a facultative larval diapause, and over most of its range it is bivoltine or trivoltine. Fully grown pre-diapausing larvae prepare an overwintering cell in the stalk crown of their host plant, typically maize, and then ecdyse from a spotted to a pigment-free morph at the onset of diapause. Southwestern corn borers originally obtained from southcentral Mexico (19°N latitude) and the United States (33-38°N latitude) were reared on an artificial diet under standardized conditions to compare several of their life history traits. Information is presented about voltinism, photoperiodic responses, growth and reproduction, larval behaviour and ecdyses, and the diapause-associated protein in an attempt to evaluate characteristics that have enabled the species to disperse from a tropical to a temperate region.
Résumé
L’aire de répartition du foreur du maïs, Diatraea grandiosella, s’est beaucoup élargie au cours de ce siècle, à tel point qu’elle s’étend maintenant entre 18°N et 38°N de latitude, au Mexique et aux Etats-Unis. L’espèce se maintient d’une année à l’autre grâce à une diapause facultative larvaire, et elle est bivoltine ou trivoltine sur la majeure partie de son aire de répartition. Les larves prédiapausantes complètement développées tissent un cocon à la base de la tige de leur plante-hôte, en général le maïs, puis muent, passant de la forme tâchetée à la forme immaculée, au début de la diapause. Des larves de D. grandiosella provenant du centre sud du Mexique (19°N latitude) et des Etats-Unis (33°N à 38°N de latitude) ont été élevées sur un milieu artificiel en conditions contrôlées, pour comparer quelques unes des particularités de leur cycle. Sont étudiés ici le voltinisme, les réponses photopériodiques, le développement et la reproduction, le comportement larvaire et les mues, et la protéine de diapause, en vue d’apprécier les caractéristiques qui ont permis à cette espèce de se répandre d’une région tropicale à une région tempérée.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarca M., Iturbe A. C. and Caceres S. F. (1958) The sugarcane borers in Mexico. An attempt to control them through parasites. Proc. 10th Int. Congr. Ent. pp. 827–834.
Brown J. J. (1980) Haemolymph protein reserves of diapausing and nondiapausing codling moth larvae, Cydia pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J. Insect Physiol. 26, 487–491.
Brown J. J. and Chippendale G. M. (1978) Juvenile hormone and a protein associated with the larval diapause of the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella. Insect Biochem. 8, 359–367.
Chippendale G. M. (1978) Behavior associated with the larval diapause of the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella: probable involvement of the juvenile hormone. Ann. Ent. Soc. Am. 71, 901–905.
Chippendale G. M. (1979) The southwestern corn borer: case history of an invading insect. Univ. Missouri-Columbia Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Bull. no. 1031.
Chippendale G. M. and Cassatt K. L. (1985) Case history of the southwestern corn borer. II. Annotated bibliography, 1977 to 1985. Misc. Publ. Ent. Soc. Am. no. 60, pp. 1–30.
Chippendale G. M. and Reddy A. S. (1974) Diapause of the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella: low temperature mortality and geographical distribution. Environ. Ent. 3, 233–238.
Chippendale G. M. and Yin C.-M. (1976) Endocrine interactions controlling the larval diapause of the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella. J. Insect Physiol. 22, 989–995.
Danthanarayana W. (1976) Environmentally cued size variation in the light-brown apple moth, Epiphyas postvittana (Walk.) (Tortricidae), and its adaptive value in dispersal. Oecologia 26, 121–132.
Davis E. G., Horton J. R., Gable C. H., Walter E. V., Blanchard R. A. and Heinrich C. (1933) The south-western corn borer. USDA Tech. Bull. no. 388.
Davis F. M. (1973) Calco Oil Red N-1700 for marking adults and eggs of the southwestern corn borer. Ann. Ent. Soc. Am. 66, 1167–1168.
Denlinger D. L. (1986) Dormancy in tropic insects. A. Rev. Ent. 31, 239–264.
Dillwith J. W. and Chippendale G. M. (1984) Purification and properties of a protein that accumulates in the fat body of pre-diapausing larvae of the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella. Insect Biochem. 14, 369–381.
Dingle H. and Baldwin J. D. (1983) Geographic variation in life histories: a comparison of tropical and temperate milkweed bugs (Oncopeltus). In Diapause and Life History Strategies in Insects (Edited by Brown V. K. and Hodek I.), pp. 143–165. Junk Publ., The Hague, The Netherlands.
Elias L. A. (1970) Maize resistance to stalk borers in Zeadiatraea Box and Diatraea Guilding at five localities in Mexico. Ph.D. Diss. Kansas State Univ. 172 pp. Univ. Microfilms no. 70-16, 627.
Fairchild M. L., Keaster A. J. and Burkhardt C. C. (1965) The southwestern corn borer, Proc. Hybrid Corn Industry-Research Conf. 20, 111–117.
Hanway J. J. (1971) How a corn plant develops. Iowa State Univ. Special Report no. 48.
Henderson C. A., Bennett S. E. and McQueen H. F. (1966) Known distribution of the southwestern corn borer in the United States. J. Econ. Ent. 59, 360–363.
Johnson K. J. R. (1984) Identification of Eoreuma loftini (Dyar) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in Texas, 1980: forerunner for other sugarcane boring pest immigrants from Mexico? Bull. Ent. Soc. Am. 30(3), 47–52.
Kellog W. W. and Schwäre R. (1982) Society, science and climate change. Foreign Affairs 60, 1076–1109.
Kikukawa S. and Chippendale G. M. (1983) Seasonal adaptations of populations of the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella, from tropical and temperate regions. J. Insect Physiol. 29, 561–567.
Kikukawa S., Dillwith J. W. and Chippendale G. M. (1984) Characteristics of larvae of the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella, obtained from populations present in tropical and temperate regions. J. Insect Physiol. 30, 787–796.
Mahmalji M. (1985) Investigation into the costs of entering diapause and the differences among three geographical populations of the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella. Ph.D. Diss. Univ. Missouri 151 pp. Univ. Microfilms Int. no. DA 8611749.
Peferoen M., Stynen D. and de Loof A. (1982) A reexamination of the protein pattern of the hemolymph of Leptinotarsa decemlineala, with special reference to vitellogenins and diapause proteins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 72B, 345–351.
Peterson N. S. and Mitchell H. K. (1985) Heat shock proteins. In Comprehensive Insect Physiology Biochemistry and Pharmacology (Edited by Kerkut G. A. and Gilbert L. I.), Vol. 10, pp. 347–365. Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Rolston L. H. (1955) The southwestern corn borer in Arkansas. Arkansas Agric. Exp. Stn. Bull. no. 533.
Sonobe H. and Odake H. (1986) Studies on embryonic diapause in the pnd mutant of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. V. Identification of a pnd+ gene-specific protein. Roux’s Arch. Dev. Biol. 195, 229–235.
Takeda M. and Chippendale G. M. (1982) Phenological adaptations of a colonizing insect: the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella. Oecologia 53, 386–393.
Tanguay R. M. (1983) Genetic regulation during heat shock and function of heat-shock proteins: a review. Can. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 61, 387–394.
Tauber M. J., Tauber C. A. and Masaki S. (1986) Seasonal Adaptations of Insects. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Turunen S. and Chippendale G. M. (1980) Fat body protein associated with the larval diapause of the southwestern corn borer, Diatraea grandiosella: synthesis and characteristics. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 65B, 595–603.
Usua E. J. (1970) Diapause in the maize stemborer. J. Econ. Ent. 63, 1605–1610.
Wilbur D. A., Bryson H. R. and Painter R. H. (1942) A major outbreak of the southwestern corn borer in Kansas. J. Econ. Ent. 35, 938–939.
Wilbur D. A., Bryson H. R. and Painter R. H. (1950) Southwestern corn borer in Kansas. Kansas Agric. Exp. Sta. Bull. no. 339.
Yagi S. and Fukaya M. (1974) Juvenile hormone as the key factor regulating larval diapause of the rice stem borer, Chilo suppressalis. Appl. Ent. Zool. 9, 247–255.
Zepp D. B. and Keaster A. J. (1977) Effects of corn plant densities on the girdling behaviour of the southwestern corn borer. J. Econ. Ent. 70, 678–680.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chippendale, G.M., Mahmalji, M.Z. Seasonal Life History Adaptations of a Neotropical Corn Borer, Diatraea Grandiosella. Int J Trop Insect Sci 8, 501–506 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400022542
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400022542
Key Words
- Diatraea grandiosella
- distribution
- seasonal adaptations
- environmental signals
- larval growth and behaviour
- fecundity
- diapause-associated protein