Abstract
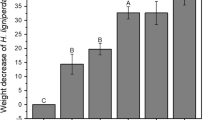
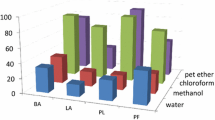
Extracts of five plants, namely Argemone mexicana, Artemisia absinthium, Cassia occidentalis, Cymbopogon citratus and Siegesbeckia orientalis were tested for their antifeedant and insecticidal effects on third-instar larvae of the cabbage webworm, Crocidolomia binotalis, which is presently one of the most important pests of cruciferous crops in Mauritius. All the five plant species investigated showed significant antifeedant properties, with A. mexicana showing the highest control potential of the five plant species studied against C. binotalis.
Résumé
Les effets antifeedant et insecticides de cinq plantes, a savoir de Argemone mexicana, Artemisia absinthium, Cassia occidentalis, Cymbopogon citratus et Siegesbeckia orientalis furent teste sur la troisieme instar de larvae de Crocidolomia binotalis, qui represente de nos jours un des plus grand fleau de nos plantes cruciferes a Maurice. Lors cette etudes, on a detecte des proprietes antifeedant importantes chez les cinq plantes examines, plus particulierement chez le Argemone mexicana qui a temoigne d’une plus grande activite. Les resultats de cette etude demontrent bien le potential inestimable des proprietes insecticides de ces cinq plantes sur le C. binotalis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S., Grainge, M., Hylin, J. W., Mitchell, W. C. and Litsinger, J. A. (1983) Some promising plant species for use as pest control agents under traditional farming systems. Proc. 2nd Int. Neem Conf., Rauischholz-hausen, pp. 565–580.
Facknath, S. (1990) Pesticide utilization in Mauritius and its environmental implications. Proc. Seminar on Environmental Management, Waste Disposal and Risk Assessment in Mauritius. University of Mauritius, July 1990.
Fagoonee, I. (1981) Behavioural response of Crocidolomia binotalis to neem. Proc. 1st Neem Conf., Rottach-Egern, pp. 109–120.
Fagoonee, I. and Lauge, G. (1981) Noxious effects of neem extracts on Crocidolomia binotalis. Phytoparasitica 9, 111–118.
Finney, D. J. (1971) Probit Analysis. 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, London.
Grainge, M., Ahmed, S., Mitchell, W. C. and Hylin, J. W. (1984) Plant species reportedly possessing pest control properties — A database. EWC/UH Database. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA.
Jacobson, M. (1958) USDA Agric. Handbk. 154, Washington, DC.
Jacobson, M. (1975) USDA Agric. Handbk. 461, Washington, DC.
Msonthi, J.D. (1981) A survey of traditional medicinal plants of Malawi. Resource Document, African Natural Product Programme. Commonwealth Secretariat, UK.
Sharaby, A. (1988) Anti-insect properties of the essential oil in lemon grass, Cymbopogon citratus against the lesser cotton leafworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hbn). Insect Sci. Applic. 9, 77–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Facknath, S., Kawol, D. Antifeedant and Insecticidal Effects of Some Plant Extracts on the Cabbage Webworm, Crocidolomia Binotalis. Int J Trop Insect Sci 14, 571–574 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1017/S174275840001794X
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S174275840001794X