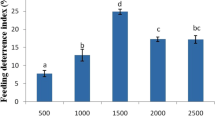
Abstract
Conessine, the steroidal alkaloid of Holarrhena untidysenterica Wall, possesses a wide range of activities against four insect species viz. Aedes aegypti, Dysdercus koenigii, Spodoptera litura and Pieris brassicae. In D. koenigii the compound inhibits the egg hatching of treated adults and nymphs. In Ae. aegypti the larval developmental periods are extended, resulting in a high mortality rate. Such effects are produced at very low dosages of 0.5 to 10ppm. Antifeedant activity is observed against larvae of S. litura and P. brassicae at concentrations of 0.005 to 0.2 % of conessine.
Résumé
La conessine, un alkaloide steroidique du Holarrhena antidysenterica Wall, possède des activités importantes contre quatre espèces d’insectes Aedes aegypti, Dysdercus koenigii, Spodoptera litura et Pieris brassicae. Dans D. koenigii la substance bloque le developpment des oeufs des adultes et chrysalides, ceci peut entrainer une mortalité très elevée. Des effets de ce genres sont produits par des doses minimes de 0,5 a 10 ppm. Une activite repulsive a èté observée a une concentration de 0,005 a 0,2% de conessine contre les larves du S. litura et P. brassicae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alford A.R. and Bentley M.D. (1986) Citrus limonoids as potential antifeedants for the spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J. econ. Entomol. 79, 35–38.
Bentley M.D., Leonard D.E. and Bushway R.J. (1984a) Solanum alkaloids as larval feeding deterrents for spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 77, 401–403.
Bentley M.D., Leonard D.E., Stoddard W.F. and Zalkow L. (1984b) Pyrrolidine alkaloids as feeding deterrents for spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 77, 393–397.
Bertho A. (1944) Pharmacological tests on extracts and alkaloids of Holarrhena antidysenterica. Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 203, 41–46.
Bhutani K.K., Raj S., Gupta D.K., Kumar S., Atal C.K. and Kaul M.K. (1984) Profile of Kurchi in India. Indian Drugs 21, 212–216.
Bhutani, K.K., Ali M., Sharma S.R., Vaid R.M. and Gupta D.K. (1988) Three new steroidal alkaloids from the bark of Holarrhena antidysenterica. Phytochemistry. 27, 925–928.
Bhutani K.K. and Vaid R.M. (1987) Nitration studies with 3 beta-Dimethylaminocon-5-enine (Conessine). J. Chem. Research (S), 282–283. J. Chem. Research (M) 2332–2351.
Blaney W.M., Simmonds M.S.J., Evans S.V. and Fellows L.E. (1984) The role of the secondary plant compound 2,5-dihydroxymethyl 3,4-dihydroxypyrrolidine as a feeding inhibitor for insects. Entomol. exp. appl. 36, 209–216.
Bowers W.S., Ohta T., Cleere J.S. and Marsella P.A. (1976) Discovery of insect anti-juvenile hormone in plants. Science 193, 542–547.
Campbell F.L. and Sullivan W.W. (1933) The relative toxicity of nicotine, anabasine, methyl anabasine, and lupinine for culicine mosquito larvae. J. econ. Ent. 26, 500–509.
Casida J.E. (1976) Prospects for new types of insecticides. In The Future for Insecticides, Needs and Prospects (Edited by Metcalf R.L. and Mckelvery Jr. J.J.) pp. 349–366, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Gombos M.A. and Gasko K. (1977) Extraction of natural antifeedants from the fruits of Amorpha fruticosa L. Acta Phytopathol. Acad. Sci. Hungaricae 12, 349–357.
Kubo I. and Klocke J.A. (1982) An insect growth inhibitor from Trichilia roka (Meliaceae). Experientia 38, 639–640.
Maradufu A., Lubega R. and Dorn F. (1978) Isolation of (5E)-Ocimenone, a mosquito larvicide from Tagetes minuta. Lloydia 41, 181–183.
Marzke F.O., Coffelt J.A. and Silhacek D.L. (1977) Impairment of reproduction of the cigarette beetle, Lasioderma serricorne (Coleoptera: Anobiidae) with the insect growth regulator, methoprene. Ent. exp. & appl. 22, 294–300.
Nakajima S. and Kawazu K. (1980) Insect development inhibitors from Coleopsis lanceolata L. Agric. Biol. Chem. 44, 1529–1533.
Ohigashi H. and Koshimizu K. (1976) Chavicol, as a larval growth inhibitor, from Viburnum japonicum Spreng. Agric. Biol. Chem. 40, 2283–2287.
Riddiford L.M. (1970) Effects of juvenile hormone on the programming of postembryonic development in eggs of the silkworm, Hyalophora cecropia. Devel. Biol. 22, 249–263.
Ross W.J. (1979) Antiamoebic agents. In Burger’s Medicinal Chemistry Part II (Edited by Wolff M.E.), pp. 415–438, John Wiley and Sons.
Sakata K., Aoki K., Chang C.F., Sakurai A., Tamura S. and Murakoshi S. (1978) Stemospironine, a new insecticidal alkaloid of Stemona japonica Miq. Isolation, structural determination and activity. Agric. Biol. Chem. 42, 457–463.
Saxena B.P., Koul O., Tikku K., Atal C.K., Suri O.P. and Suri A.K. (1979) Aristolochic acid—an insect chemosterilant from Aristolochia bracteata Retz. Indian J. exp. Biol. 17, 354–360.
Supavarn P., Knapp F.W. and Sigafus R. (1974) Biologically active plant extracts for control of mosquito larvae. Mosquito News 34, 398–402.
Waiss Jr. A.C., Chan B.G., Elliger C.A., Wiseman B.R., McMillan W.W., Widstrom N.W., Zuber M.S. and Keaster A.J. (1979) Maysin, a flavone glycoside from corn silks with antibiotic activity toward corn earworm. J. econ. Entomol. 72, 256–258.
Zebitz C.P.W. (1984) Effect of some crude and azadirachtin enriched neem (Azadirachta indica) seed kernel extracts on larvae of Aedes aegypti. Entomol. exp. appl. 35, 11–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thappa, R.K., Tikku, K., Saxena, B.P. et al. Conessine as a Larval Growth Inhibitor, Sterilant, and Antifeedant from Holarrhena antidysenterica Wall. Int J Trop Insect Sci 10, 149–155 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400010304
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400010304