Abstract
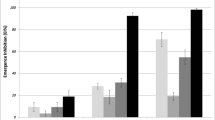
The biological effects of six insect growth regulators (IGRs) AI3-37634-C, AI3-36877-b, AI3-37603-b, AI3-36807-b, AI3-37837-a and AI3-36809-a against immature stages and adults of Aedes aegypti have been evaluated. According to IC50 values obtained (concentration to inhibit the emergence of 50% of adults), AI3-36809-a (0.02 μg/ml) proved to be the most effective compound, followed by AI3-37603-b (0.04 μg/ml), AI3-37837-a (0.11 μg/ml), AI3-36807-b (0.17 μg/ml), AI3-37634-C (0.48 μg/ml) and AI3-36877-b (1.4 μg/ml), respectively. The results showed also that the duration of the fourth instar larvae of A. aegypti was prolonged when these larvae were exposed to the effective concentrations of the above compounds.
Apart from delayed lethal action, possible effect of the compounds tested on the basal follicle numbers developed by females of A. aegypti which survived after larval treatment with IC50 of the above-mentioned compounds has been considered. Generally, the results indicate that the females treated have more follicles than the untreated ones of similar age and grown under identical conditions.
Résumé
Les effets biologiques de six régulateurs de croissance dans les insectes (IGRs) AI3-37634-C, AI3-36877-b, AI3-37603-b, AI3-36807-b, AI3-37837-a et AI3-36809-a sur les stades non mûrs et adultes de Aedes aegypti ont été évalués. D’après les valeurs de IC50 obtenues (concentration nécessaire pour inhiber l’émergence de 50% d’adultes), AI3-36809-a (0,02 g/ml), fut le composé le plus efficace, suivi par AI3-37603-b (0,04 g/ml), AI3-37837-a (0,11 g/ml), AI3-36807-b (0,17 g/ml), AI3-37634-C (0,48 g/ml) et AI3-36877-b (1,4 g/ml), respectivement. Ces résultats ont aussi montré que la durée de la 4ème phase des larves d’A. aegypti était prolongée quand ces larves étaient exposées aux concentrations efficaces de ces composés. Hormis l’action mortelle retardée, on a aussi considéré l’effet possible des composés testées sur les effectifs de base de follicules développées par les femelles de A. aegypti qui ont survécu après que les larves avaient été traitées au IC50 des composés mentionnées plus haut. En général, les résultats montrent que les femelles traitées ont plus de follicules que celles qui ne le sont pas quand elles ont le même âge et quand elles sont cultivées dans les mêmes conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaaboub I. A. (1976) Observations on the basal follicle numbers developed per female of two strains of Aedes aegypti after being fed on both hosts with different levels of microfilariae of Brugia pahangi. J. invert. Path. 28, 203–207.
Gaaboub I. A., Rawash I. A., El-Gayar F. H. and Traboulsi A. F. (1981) The delayed effects and basal follicle numbers developed by females of Culex pipiens L. emerged from treatments of larvae with partially-lethal concentrations of Altosid and Dimilin. Toxicology 19, 269–274.
Jakob W. L. and Schoof H. F. (1971) Studies with juvenile hormone type compounds against mosquito larvae. Mosquito News 31, 540–543.
Litchfield J. T. and Wilcoxon F. (1949) A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 96, 99–113.
Mulla M. S., Darwazeh H. A. and Norland R. E. (1974) Insect growth regulators: evaluation procedures and activity against mosquitoes. J. econ. Ent. 67, 329–332.
Mulla M. S. and Darwazeh H. A. (1976) The IGR Dimilin and its formulation against mosquitoes. J. econ. Ent. 69, 309–312.
Saleh M. S., Gaaboub I. A. and Kassem Sh. M. I. (1981) Larvicidal effectiveness of three controlled-release formulations of Dursban and Dimilin on Culex pipiens L. and Aedes aegypti (L.). J. agrie. Sci., Camb. 97, 87–96.
Schaefer C. H. and Wilder W. H. (1972) Insect development inhibitors: a practical evaluation as mosquito control agents. J. econ. Ent. 656, 1066–1071.
Zaghloul T. M. A. and Brown A. W. A. (1968) Effects of sublethal doses of DDT on the reproduction and susceptibility of Culex pipiens L. Bull. Wld Hlth Org. 38, 459–467.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleh, M.S. Effects of Six Insect Growth Regulators on Mosquito Larvae of Aedes Aegypti. Int J Trop Insect Sci 6, 609–611 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1017/S174275840000919X
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S174275840000919X