Abstract
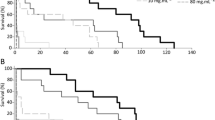
Gravid Lucilia treated topically with ivermectin (0.05 μg/g, which represented approx. 4% of the 48 hr LD50) laid fewer viable egg batches (less than 50% of controls) and more sterile ones, when compared to untreated (P = 0.019) and acetone-treated flies (P = 0.028). This effect was also seen when mature third instar larvae were dosed with 7.6 μg ivermectin/g (P = 0.0075 and 0.016 respectively); number of viable egg batches produced were only 25% of the number laid by the progeny of untreated larvae.
Dosage with fenthion stimulated an increase in the number of viable egg batches laid when incorporated in the original larval feeding medium at 0.2 μg/g liver; fewer viable egg batches were laid by the flies which developed from mature larvae treated with 7.6 μg fenthion/g. Acetone solvent alone had a mild stimulatory effect on topically dosed flies.
Résumé
Le nombre d’oeufs viables pondus par les femelles de Lucilia traitées de façon topique à l’ivermectin (0,05 μg/g, ce qui représente environ 4% de la LD50 par 48 heures), était réduit de 50% par rapport aux femelles de contrôle, avec augmentation du nombre d’oeufs stériles en comparaison avec la ponte des mouches non traitées (P = 0,019) ou traitées à l’acetone (P = 0,028). Cet effet était également observé lorsque des larves de troisième instar étaient traitées avec 7,6 μg d’ivermectin/μg (P =0,0075 et P= 0,016, respectivement); le nombre d’oeufs viables obtenus n’etait que 25% du nombre d’oeufs produits par la progénie des larves non traitées.
Le traitement par le fenthion incorporé au milieu original de nutrition larvaire (0,2 μg/g de foie) a produit une augmentation du nombre d’oeufs viables; un nombre plus faible d’oeufs viable était produit par les mouches ayont émergé de larves matures traitées avec 7,6 μg de fenthion/g. L’acetone suele avait un effet stimulant sur les mouches traitées de façon topique
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beesley W. N. (1960) Persistence of insecticide in fleece. Vet. Ret. 72, 638–640.
Campbell W. C. (1986) Ivermectin: fleas, fungi and pharmacology. Parasitology Today. 2, 75–76.
Chadd E. M. and Brady J. (1982) Sublethal insecticide effects on the probing responsiveness of tsetse flies and blowflies. Physiol. Ent. 7, 133–141.
Glancey B. M., Lofgren C. S. and Williams D. F. (1982) Avermectin B1a: Effects on the ovaries of red imported fire ant queens. J. Med. Ent. 19, 743–747.
Guillot F. S. and Wright F. C. (1984) Reduced fecundity of Psoroptes ovis (Hering) (Acari: Psoroptidae) on calves treated with ivermectin. Bull. Ent. Res. 74, 657–662.
Kumar K. and Chapman R. B. (1984) Sublethal effects of insecticides on the diamond back moth Plutella xylostella (L.) Pestic. Sci. 15, 344–352.
Langley P. A. and Roe J. M. (1984) Ivermectin as a possible control agent for the tsetse fly Glossina morsilans. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 36, 137–143.
Lofgren C. S. and Williams D. F. (1982) Avermectin B1a, a highly potent inhibitor of reproduction by queens of the red imported fire ant. J. econ. Ent. 11, 798–803.
McGarry J. W. (1986) Effects of ivermectin on metamorphosis of Lucilia sericata (Meigen 1826) following exposure to third stage larvae. Trans. R. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg. 80, 339–340.
Moriarty F. (1969) The sublethal effects of synthetic insecticides on insects. Biol. Rev. Cambridge Philos. Soc. 44, 321–357.
Spradbery J. P., Tozer R. S., Drewett N. and Lindsey M. J. (1985) The efficacy of ivermectin against larvae of the screw-worm fly (Chrysomya bezziana).Aust. Vet. J. 62, 311–314.
Tamashiro M. and Sherman M. (1955) Direct and latent toxicity of insecticides to oriental fruit fly larvae and their internal parasites. J. econ. Ent. 48, 75–79.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGarry, J.W. Effects of Low Doses of Ivermectin and Fenthion on Egg Laying by Lucilia sericata (Meigen) (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Int J Trop Insect Sci 9, 421–425 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400006445
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400006445