Abstract
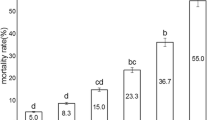
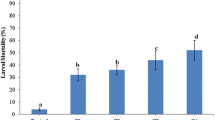
The effectiveness of Bacillus thuringiensis var. galleriae HD-129 against the moths and egg masses of the cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis, has been demonstrated in laboratory experiments. The longevity and egg production were significantly affected when the moths were fed on a sucrose diet containing 17.2 × 103 IU of the tested formulation/mg or higher rates. At lower concentrations (4.4–8.7 × 103 IU/mg), the females gave normal egg production, but the longevity was adversely affected. Investigations show that a formulation with spores alone affects the egg production and hatching, while a formulation with active crystals alone had no effect on egg production. Sprays of B. thuringiensis combined with sucrose on flowering cotton plants seem to affect the biology of the moths released on it. Egg masses sprayed with B. thuringiensis hatched normally, but the survival of the hatched larvae was reduced when treatment was made shortly before egg hatching. Based on the results obtained, B. thuringiensis showed a promising effect in the control of the moth S. littoralis as well as an ovicide larvicide agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah M. (1969) The joint action of microbial insecticides in the cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.). Bull. ent. Soc. Egypt, Econ. Ser. 3, 209–217.
Afify A., Abdel Samei M. and Merdan A. (1968) Isolation and pathogenicity of 3 varieties of Bacillus associated with diseased cotton worms in Egypt. Proc. Egypt. Acad. Sci. 21, 87–89.
Afify A. and Merdan A. (1969) On tracing the response of some Egyptian cotton worms in different larval ages to Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner. Z. angew. Ent. 63, 263–267.
Ali A. S. and Watson T. F. (1982) Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki on tobacco budworm adult and egg stages. J. econ. Ent. 75, 596–598.
Govindarajan R., Jayaraj S. and Narayanan K. (1975) Observations on the nature of resistance in Spodoptera litura (F.) to infection by Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner. Ind. J. exp. Biol. 13, 548–550.
Moore I. and Navon A. (1973) Studies on the susceptibility of the cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) to various strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. Phytoparasitica 1, 23–32.
Potter M. F., Jensen M. and Watson T. (1983) Influence of sweet bait Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki combinations on adult tobacco budworm. J. econ. Ent. 75, 1157–1160.
Salama H. S. (1970) Rearing the corn borer Ostrinia nubi-lalis Hubn. on a semiartificial diet. Z. angew. Ent. 65, 216–218.
Salama H. S. (1983) Cotton pest management in Egypt. Crop Prot. 2, 183–191.
Salama H. S., Foda M. S. and El-Sharaby A. (1981) Potency of spore ´-endotoxin complexes of Bacillus thuringiensis against some cotton pests. Z. angew. Ent. 91, 388–398.
Salama H. S. and Foda M. S. (1982) A strain of Bacillus thuringiensis var. entomocidus with high potential activity on Spodoptera littoralis. J. Invertebr. Path. 39, 110–111.
Salama H. S., Foda M. S., Zaki F. and Khalafallah A. (1983a) Persistence of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner spores in cotton cultivations. Z. angew. Ent. 95, 321–326.
Salama H. S., Azmy N. and Sharaby A. (1983b) Gustation in the moth Spodoptera littoralis. Zool. Jb. Physiol. 88, 165–178.
Salama H. S., Rizk A. and Sharaby A. (1983c) Chemical stimuli in flowers and leaves of cotton that affect moth behaviour of Spodoptera littoralis. Entomologia gen. In press.
Salama H. S., Foda M. and Sharaby A. (1984) Role of feeding stimulants on the potency of B. thuringiensis vs cotton pests. J. Invertebr. Path. In press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salama, H.S. Control of Spodoptera littoralis Through moth and Eggs Treatment with Bacillus thuringiensis. Int J Trop Insect Sci 6, 49–53 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400002666
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400002666