Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to review the literature on school screening and its reported effectiveness.
Summary of Background Data
There is no worldwide consensus concerning the mandating of school screening for scoliosis. This remains a controversial issue.
Methods
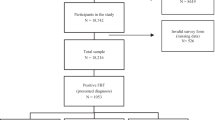
The following databases were employed: Medline, Premedline, CINAHL, CENTRAL, AMED, Embase, SCOPUS, Ovid nursing, and Web of Science. These data were generated from the Forward Bend Test, the angle of trunk rotation and Moire topography. The first and second authors each independently screened titles and abstracts for potential studies. Fulltext papers of potential studies were also independently read by the first two authors to identify studies to be included based on strict inclusion/exclusion criteria. A heterogeneity test was performed by testing for the significance of the between-study variance. Publication bias was examined by a funnel plot.
Results
We found 20 studies that met our inclusion criteria. The pooled estimate of prevalence of scoliosis curves in the population was 1.1% for curves greater than 10°, and 0.2% for curves greater than 20°. The pooled referral rate to radiography during the screening process was 6.6%. The pooled positive predictive values for detecting curves >10° and >20° were 32.3% and 6.5% respectively. Analysis of data demonstrated significant heterogeneity between studies but was not suggestive of the presence of publication bias.
Conclusions
We support the implementation of scoliosis screening as a means of detecting curves at an early treatable stage. The current available evidence in the literature for routine scoliosis screening is low to moderate. Challenges exist to the school scoliosis screening including a high referral rate to radiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asher MA, Burton DC. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: natural history and long term treatment effects. Scoliosis 2006;1:2.
Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JC, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet 2008;371:1527–37.
Parent S, Newton PO, Wenger DR. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: etiology, anatomy, natural history, and bracing. Instr Course Lect 2005;54:529–36.
Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Spratt KF, et al. Health and function of patients with untreated idiopathic scoliosis—a 50-year natural history study. JAMA 2003;289:559–67.
Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Wright JG, et al. Effects of bracing in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. N Engl J Med 2013;369:1512–21.
Lange JE, Steen H, Brox JI. Long-term results after Boston brace treatment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis 2009;4:17.
Karachalios T, Sofianos J, Roidis N, et al. Ten-year follow-up evaluation of a school screening program for scoliosis. Is the forward-bending test an accurate diagnostic criterion for the screening of scoliosis? Spine 1999;24:2318–24.
Yawn BP, Yawn RA. The estimated cost of school scoliosis screening. Spine 2000;25:2387–91.
Bunge EM, Juttmann RE, Van Biezen FC, et al; For the Netherlands Evaluation Study for Screening for Scoliosis (NESCIO) group. Estimating the effectiveness of screening for scoliosis: a case-control study. Pediatrics 2008;121:9–14.
Korfage IJ, Juttmann RE, Das BV, et al. Idiopathic scoliosis in adolescents; an inventory into the possibilities of studying the efficacy of screening and treatment. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 2002;146:1228–33.
Bunnell WP. Selective screening for scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005;434:40–5.
Richards BS, Vitale MG. Screening for idiopathic scoliosis in adolescents. An information statement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;90:195–8.
Montgomery F, Willner S. Screening for idiopathic scoliosis: comparison of 90 cases shows less surgery by early diagnosis. Acta Orthop Scand 1993;64:456–8.
US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: policy statement. JAMA 1993;269:2664–6.
US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: review article. JAMA 1993;269:2667–72.
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for idiopathic scoliosis in adolescents: recommendation statement, http://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/3rduspstf/scoliosis/scoliors.htm; 2004.
Adobor RD, Riise RB, Sorensen R, et al. Scoliosis detection, patient characteristics, referral patterns and treatment in the absence of a screening program in Norway. Scoliosis 2012;7:18.
Ali FM, Edgar M. Detection of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Acta Orthop Belg 2006;72:184–6.
Beausejour M, Roy-Beaudry M, Goulet L, et al. Patient characteristics at the initial visit to a scoliosis clinic: a cross-sectional study in a community without school screening. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:1349–54.
Labelle H, Richards SB, De Kleuver M, et al. Screening for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: an information statement by the scoliosis research society international task force. Scoliosis 2013;8:17.
Goldbloom RB. Screening for idiopathic adolescent scoliosis. In: Canadian Task Force on the Periodic Health Examination: Canadian guide to clinical preventative healthcare. Ottawa, Ontario, Canada: Health Canada; 1994. p. 346–54.
British Orthopaedic Association and British Scoliosis Society. School screening for scoliosis. Br Med J 1983;287:963–4.
Adobor RD, Rimeslatten S, Steen H, et al. School screening and point prevalence of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in 4000 Norwegian children aged 12 years. Scoliosis 2011;6:23.
Alsharbati MM, Alchalabi TS, Rummani SF. School screening for scoliosis in Baghdad. Saudi Med J 1993;14:298–302.
Ascani E, Salsano V, Giglio G. The incidence and early detection of spinal deformities. A study based on the screening of 16,104 schoolchildren. Ital J Orthop Traumatol 1977;3:111–7.
Corea JR, Magbool GM, Alarfaj A, et al. School screening for scoliosis in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J 1993;14:209–12.
Goldberg CJ, Dowling FE, Fogarty EE, et al. School scoliosis screening and the United States Preventative Task Force—an examination of long-term results. Spine 1995;20:1368–74.
Gore DR, Passehl R, Sepic S, et al. Scoliosis screening. Results of a community project. Paediatrics 1981;67:196–200.
Grivas TB, Koukos K, Koukou UI, et al. The incidence of idiopathic scoliosis in Greece. Stud Health Technol Inform 2002;91:71–5.
Grivas TB, Dangas S, Samelis P, et al. Lateral spinal profile in school-screening referrals with and without late onset idiopathic scoliosis 10°–20°. Stud Health Technol Inform 2002;91:25–31.
Koukourakis I, Giaourakis G, Kouvidis G, et al. Screening school children for scoliosis on the Island of Crete. J Spinal Disord 1997;10:527–31.
Liston C. An evaluation of school screening for scoliosis in Western Australia. Aust J Physiother 1981;27:37–43.
Lonstein JE. Screening for spinal deformities in Minnesota schools. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1977;126:33–42.
Lonstein JE, Bjorklund S, Wanninger MH, Nelson RP. Voluntary school screening for scoliosis in Minnesota. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1982;64:481–8.
Morais T, Bernier M, Turcotte F. Age- and sex-specific prevalence of scoliosis and the value of school screening programs. Am J Public Health 1985;75:1377–80.
Nussinovitch M, Finkelstein Y, Amir J, et al. Adolescent screening for orthopaedic problems in high school. Public Health 2002;116:30–2.
Pruijs JE, Van der Meer R, Hageman MA, et al. The benefits of school screening for scoliosis in the central part of the Netherlands. Eur Spine J 1996;5:374–9.
Randall FM, Denton TE. Scoliosis screening: a school survey. Ala J Med Sci 1983;20:395–6.
Ugras AA, Yilmaz M, Sungur I, et al. Prevalence of scoliosis and cost-effectiveness of screening in schools in Turkey. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 2010;23:45–8.
Velezis MJ, Sturm PF, Cobey J. Scoliosis screening revisited: findings from the District of Columbia. J Pediatr Orthop 2002;22:788–91.
Willner S. Development of trunk asymmetries and structural scoliosis in prepuberal school children in Malmö: follow-up study of children 10–14 years of age. J Pediatr Orthop 1984;4:452–5.
Wong HK, Hui JHP, Rajan U, et al. Idiopathic scoliosis in Singapore schoolchildren. A prevalence study 15 years into the screening program. Spine 2005;30:1188–96.
Yawn BP, Yawn RA, Hodge D. A population based study of school scoliosis screening. JAMA 1999;282:1427–32.
Pin LH, Mo LY, Lin L, et al. Early diagnosis of scoliosis based on school-screening. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1985;67–A:1202–5.
Smyrnis PN, Valavanis J, Alexopoulos A, et al. School screening for scoliosis in Athens. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1979;61–B:215–7.
Gurr JF. A school screening program that works. Can Nurse 1977;73:24–9.
Ohtsuka Y, Yamagata M, Arai S, et al. School scoliosis screening for scoliosis by the Chiba University Medical School Screening Program. Results of 1.24 million students over an 8-year period. Spine 1988;13:1251–7.
Sabarin J, Bakri R, Buang SN, et al. School scoliosis screening programme—a systematic review. Med J Malaysia 2010;65:4.
Bunnell WP. An objective criterion for scoliosis screening. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1984;66A:1381–7.
Pruijs JE, Keessen W, Van der Meer R, et al. School screening for scoliosis: the value of quantitative measurement. Eur Spine J 1995;4:226–30.
Lonstein JE, Winter RB. The Milwaukee brace for the treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1994;76A:1207–21.
Montgomery F, Willner S. The natural history of idiopathic scoliosis. A study if the incidence of treatment. Spine 1988;13:401–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altaf, F., Drinkwater, J., Phan, K. et al. Systematic Review of School Scoliosis Screening. Spine Deform 5, 303–309 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspd.2017.03.009
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspd.2017.03.009