Abstract
Objective
The current study sought to investigate the influence of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) on the function of the amino acid transport system A in trophoblasts.
Methods
BeWo choriocarcinoma cells were exposed to recombinant human IL-1β in serum-free medium. Cells incubated with serum-free medium in the absence of IL-1β were used as control. System A activity was determined in control and treated cells by measuring the uptake of α-(methylamino)isobutyric acid. The results obtained were confirmed by measuring system A activity in placental brush border membrane vesicles isolated from pregnant rats injected with IL-1β.
Results
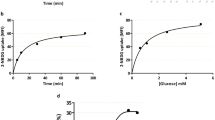
Treatment of BeWo cells with IL-1β resulted in a time- and dose- dependent inhibition of system A. Treatment with IL-1β also inhibited the uptake of arginine, and glutamate but had no significant effect on the uptake of leucine, tryptophan, and ascorbate. The inhibition of system A activity by IL-1β was abolished in the presence of IL-1β receptor antagonist. The inhibitory effect was associated with a decrease in the maximal velocity of the transport system with no effect on the substrate affinity. Steady-state levels of both SNAT1 and SNAT2 mRNA were reduced by IL-1β treatment as evidenced by semiquantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis. In rat placental brush border membrane vesicles isolated from IL-1β-treated pregnant rats, system A activity was found to be decreased by approximately 40% compared to activity in control membrane vesicles.
Conclusions
IL-1β decreases SNAT1 and SNAT2 mRNA levels in trophoblasts, which is associated with a decrease in system A—mediated transport activity at the functional level. These findings may have important consequences under both physiologic conditions and pathologic conditions during pregnancy that are associated with elevated levels ofIL-1β.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jansson T. Amino acid transporters in the human placental. Pediatr Res 2001;49:141–147.
Smith CH, Moe AJ, Ganapathy V. Nutrient transport pathways across the epithelium of the placenta. Annu Rev Nutr 1992;12:183–206.
Kuruvilla AG, D’Souza SW, Glazier JD, et al. Altered activity of the system A amino acid transporter in microvillous membrane vesicles from placentas of macrosomic babies born to diabetic women. J Clin Invest 1994;94:689–695.
Godfrey KM, Matthews N, Glazier J, et al. Neutral amino acid uptake by the microvillous plasma membrane of the human placenta is inversely related to fetal size at birth in normal pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998;83:3320–3326.
Dicke JM, Henderson GI. Placental amino acid uptake in normal and complicated pregnancies. Am J Med Sci 1988;295:223–227.
Glazier JD, Cetin I, Perugino G, et al. Association between the activity of the system A amino acid transporter in the microvillous plasma membrane of the human placenta and severity of fetal compromise in intrauterine growth restriction. Pediatr Res 1997;42:514–519.
Harrington B, Glazier J, D’Souza S, Sibley C. System A amino acid transporter activity in human placental microvillous membrane vesicles in relation to various arthropometric measurements in appropriate and small for gestational age babies. Pediatr Res 1999;45:810–814.
Mahendran D, Donnai P, Glazier JD, et al. Amino acid (system A) transporter activity in microvillous membrane vesicles from the placentas of appropriate and small for gestational age babies. Pediatr Res 1993;34:661–665.
Ganapathy V, Inoue K, Prasad PD, Ganapathy ME. Cellular uptake of amino acids: systems and regulation. In: Cynober LA, ed. Metabolic and therapeutic aspects of amino acids in clinical nutrition. 2nd ed. New York: CRC Press, 2003:63–78.
Mackenzie B, Hediger MA.SLC11 family of H+-coupled metalion transporters NRAMP1 and DMT1. Pflugers Arch 2004;447:571–579.
Jones CR, Srinivas SR, Devoe LD, Ganapathy V, Prasad PD. Inhibition of system A amino acid transport activity by ethanol in BeWo choriocarcinoma cells. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;187:209–216.
Shotwell MA, Kilberg MS, Oxender DL. The regulation of neutral amino acid transport in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1983;737:267–284.
Kilberg MS, Stevens BR, Novak DA. Recent advances in mammalian amino acid transport. Annu Rev Nutr 1993;13:137–165.
McGivan JD, Astor-Anglada M. Regulatory and molecular aspects of mammalian amino acid transport. Biochem J 1994;299:321–334.
Chard T. Cytokines in implantation. Hum Reprod Update 1995;1:385–396.
Paulesu L. Cytokines in mammalian reproduction and speculation about their possible involvement in nonmammalian viviparity. Microsc Res Tech 1997;38:188–194.
Bowen JM, Chamley L, Keelan JA, Mitchell MD. Cytokines of the placenta and extra-placental membranes: Roles and regulation during human pregnancy and parturition. Placenta 2002;23:257–273.
Bowen JM, Chamley L, Mitchell MD, Keelan JA. Cytokines of the placenta and extra-placental membranes: Biosynthesis, secretion and roles in establishment of pregnancy in women. Placenta 2002;23:239–256.
Hillier SL, Witkin, SS, Krohn MA, et al. The relationship of amniotic fluid cytokines and preterm delivery, amniotic fluid infection, histologic chorioamnionitis, and chorioamnioninfection. Obstet Gynecol 1993;81:941–948.
Menon R, Swan KF, Lyden TW, Rose NS, Fortunato SJ. Expression of inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6) in amniochorionic membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:493–500.
Arntzen KJ, Kjollesdal AM, Halgunset J, Vatten L, Austgulen R. TNF, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8 and soluble TNF receptors in relation to chorioamnionitis and premature labor. J Perinat Med 1998;26:17–26.
Dinarello CA, Savage N. Interleukin-1 and its receptor. Crit Rev Immunol 1989;9:1–20.
Kekuda R, Leibach FH, Furesz TC, Smith CH, Ganapathy V. Polarized distribution of interleukin-1 receptors and their role in regulation of serotonin transporter in placenta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2000;292:1032–1041.
Ikoma Y, Nomura S, Ito T, et al. Interleukin-1beta stimulates placental leucine aminopeptidase/oxytocinase expression in BeWo choriocarcinoma cells. Mol Hum Reprod 2003;9:103–110.
Bergstrom S. Infection-related morbidities in the mother, fetus and neonate. J Nutr 2003;133:1656S–1660S.
von Dadelszen P, Magee LA. Could an infectious trigger explain the differential maternal response to the shared placental pathology of preeclampsia and normotensive intrauterine growth restriction? Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2002;81:642–648.
Resnik R. Intrauterine growth restriction. Obstet Gynecol 2002;99:490–496.
Seki H, Zosmer A, Elder MG, Sullivan MH. The regulation of progesterone and hCG production from placental cells by interleukin-1beta. Biochim Biophys Acta 1997;1336:342–348.
Nuamah MA, Yura S, Sagawa N, et al. Significant increase in maternal plasma leptin concentration in induced delivery: A possible contribution of pro-inflammatory cytokines to placental leptin secretion. Endocr J 2004;51:177–187.
Mohan A, Asselin J, Sargent IL, Groome NP, Muttukrishna S. Effect of cytokine and growth factors on the secretion of inhibit inhibin A, Activin A and follistatin by term placental villous trophoblasts in culture. Eur J Endocrinol 2001;145:505–511.
Ganapathy V, Prasad PD, Leibach FH. Use of human placenta in studies of monoamine transporters. Methods Enzymol 1998;296:278–290.
Prasad PD, Leibach FH, Mahesh VB, Ganapathy V. Specific interaction of 5-(N-methyl-N-isobutyl)amiloride with the organic cation-proton antiporter in human placental brush-border membrane vesicles. Transport and binding. J Biol Chem 1992;267:23632–23639.
Ramamoorthy S, Ramamoorthy JD, Prasad PD, et al. Regulation of the human serotonin transporter by interleukin-1 beta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1995;216:560–567.
Feneant-Thibault M, Galera P, Maccario J. et al. Interleukin-1 beta-induced changes in the kinetic constants of L-proline uptake in human skin fibroblasts. Biochem J 1991;276:57–62.
Le Maire V, Solito E, Russo-Marie F, et al. System A neutral amino acid transporter regulation by interleukin-1beta in human osteoarthritic synovial cells: evidence for involvement of prostaglandin E(2) as a second messenger. J Cell Physiol 2000;183:65–73.
Le Maire V, Herrivann A, Le Marechal H, Ekindjian OG, Aussel C. IL-1 modifies system A transport activity in human rheumatoid synovial cells. Cell Biol Int 1997;21:455–460.
Le Maire V, Hernvann A, Vaubourdolle M, Ekindjian OG, Aussel C. Dependence of adaptative regulation for IL-1 beta action on system A activity in human synovial cells. J Cell Physiol 1996;168:721–726.
LeMaire V, Aussel C, Hernvann A, Launay JM, Ekindjian OG. Stimulation of alpha-(methylamino) isobutyric acid uptake by interleukin-1 in human synovial cells. Involvement of a cAMP dependent pathway. Eur Cytokine Netw 1994;5:449–453.
Goenner S, Cosson C, Boutron A, Legrand A, Moatti N. Interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 stimulate 2-methylaminoisobutyric acid uptake in HepG2 cells Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1997;29:667–674.
Gwosdow AR, Spencer JA, O’Connell NA, Abou-Samra AB. Interleukin-1 activates protein kinase A and stimulates adrenocorticotropic hormone release from AtT-20 cells. Endocrinology 1993;132:710–714.
Guesdon F, Freshney N, Waller RJ, Rawlinson L, Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor stimulate two novel protein kinases that phosphorylate the heat shock protein hsp27 and beta-casein. J Biol Chem 1993;266:4236–4243.
Guesdon F, Ikebe T, Stylianou E, et al. Interleukin 1-induced phosphorylation of MAD3, the major inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B of HeLa cells. Interference in signalling by the proteinase inhibitors 3,4-dichloroisocoumarin and tosylphenylalanyl chloromethylketone. Biochem J 1995;307:287–295.
Muhl H, Pfeilschifter J. Possible role of protein kinase C-epsilon isoenzyme in inhibition of interleukin 1 beta induction of nitric oxide synthase in rat renal mesangial cells. Biochem J 1994;303:607–612.
Mueller SG, Schraw WP, Richmond A. Activation of protein kinase C enhances the phosphorylation of the type B interleukin-8 receptor and stimulates in degradation in non-hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem 1995;270:10439–10448.
Seki H, Elder MG, Sullivan MH. Endothelin-1 regulates human decidual cells through both A- and B-type receptors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1995;114:111–116.
Cariappa R, Heath-Monnig E, Smith CH. Isoforms of amino acid transporters in placental syncytiotrophoblast: Plasma membrane localization and potential role in maternal/fetal transport. Placenta 2003;24:713–726.
Hatanaka T, Huang W, Ling R, et al. Evidence for the transport of neutral as well as cationic amino acids by ATA3, a novel and liver-specific subtype of amino acid transport system A. Biochim Biophys Acta 2001;1510:10–17.
Simon C, Mercader A, Gimeno MJ, Pellicer A. The interleukin-1 system and human implantation. Am J Reprod Immunol 1997;37:64–72.
Simon C, Pellicer A, Polan ML. Interleukin-1 system crosstalk between embryo and endometrium in transplantation. Hum Reprod 1995;10 Suppl 2: 43–54.
Strakova Z, Srisuparp S, Fazleabas AT. IL-1beta during in vitro decidualization in primate. J Reprod Immunol 2002;55:35–47.
LIbrach CL, Feigenbaum SL, Bass KE, et al. Interleukin-1 beta regulates human cytotrophoblast metalloproteinase activity and invasion in vitro. J Biol Chem 1994;269:17125–17131.
Shobokshi A, Shaarawy M. Maternal serum and amniotic fluid cytokines in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes with and without intrauterine infection. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2002;79:209–215.
Keelan JA, Zhou RL, Evans LW, Groome NP, Mitchell MD. Regulation of activin A, inhibin A, and follistatin production in human amnion and choriodecidual explants by inflammatory mediators. J Soc Gynecol Investig 2000;7:291–296.
Gill DJ, Low BC, Grigor MR. Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulate the cat-2 gene of the L-arginine transporter in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 1996;271:11280–11283.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
From the Departments of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and Obstetrics and Gynecology, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, Georgia.
Present address for B.T.: Department of Animal Husbandry, Faculty of Veterinary Sciences, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, 10330, Thailand.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thongsong, B., Subramanian, R.K., Ganapathy, V. et al. Inhibition of Amino Acid Transport System A by lnterleukin-1β in Trophoblasts. Reprod. Sci. 12, 495–503 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsgi.2005.06.008
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsgi.2005.06.008