Abstract
Objective
In humans, the factors that govern the switch from myometrial quiescence to coordinated contractions at the initiation of labor are not well defined. Recent studies have highlighted a role for the coactivator, CREB binding protein (CBP), in the human myometrium during pregnancy and labor through its ability to acetylate histones. In the present study, the expression of CBP and its related coactivator, p300, were examined.
Methods
Levels and interactions of CBP and its paralogue p300 were determined by Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and coimmunoprecipitation experiments using myometrial biopsy samples from nonpregnant (NP), pregnant nonlaboring (P), and spontaneously laboring (SL) women.
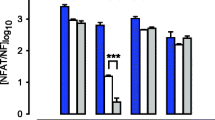
Results
Levels of CBP were seen to increase in term P myometrial samples but were then greatly reduced in SL myometrium. In contrast, levels of p300 remained uniform between NP, P, and SL tissues. These observations were confirmed by immunhistochemical analyses. Immunoprecipitation experiments highlighted that CBP was able to interact with CREB, CREM, ATE-2, and p300 in P lower segment myometrium.
Conclusion
Recent evidence suggests that competition for CBP plays an important role in regulating gene expression during cell growth. Consequently our data suggest that the increase in myometrial CBP levels during pregnancy may occur to meet this increase in CBP demand. Moreover, from coimmunoprecipitation experiments, this increase in CBP expression would be expected to facilitate the transactivation potential of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent transcription factors CREB, CREM, and ATF-2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lumley J. Defining the problem: The epidemiology of preterm birth. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 2003;110(Suppl 20):3–7.
López-Bernal A, Watson SP, Phaneuf S, Europe GN. Biochemistry and physiology of preterm labour and delivery. Baillieres Clin Obstet Gynaecol 1993;7:523–52.
Europe-Finner GN, Phaneuf S, Watson SP, López-Bernal A. Identification and expression of G-proteins in human myometrium: Up-regulation of Gαs in pregnancy. Endocrinology 1993;132:2484–90.
Bailey J, Sparey C, Phillips RJ, et al. Expression of CREB, CREM and ATF2 cyclic AMP dependent transcription factors in the human myometrium during pregnancy and labour. Mol Hum Reprod 2000;6:648–60.
Europe-Finner GN, Phaneuf S, Tolkovsky AM, Watson SP, López-Bernal A. Down regulation of Gαs in human myometrium in term and preterm labour: A mechanism for parturition. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994;79:1835–9.
MacDougall MWJ, Europe GN, Robson SC. Human myometrial quiescence and activation during gestation and parturition involve dramatic changes in expression and activity of particulate type II (RIIα) protein kinase A holoenzyme. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003;88:2194–205.
Sparey C, Robson SC, Bailey J, Lyall F, Europe GN. The differential expression of myometrial connexin-43, cyclooxyge-nases 1 & 2 and Gas proteins in the upper and lower segments of the human uterus during pregnancy and labour. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:1705–10.
Goodman RH, Smolik S. CBP/p300 in cell growth, transformation and development. Genes Dev 2000;14:1553–77.
Perkins ND, Felzien LK, Betts JC, Leung K, Beach DH, Nabel GJ. Regulation of NF-KB by cyclin-dependent kinases associated with the p300 coactivator. Science 1997;275:523–7.
Sheppard K-A, Rose DW, Haque ZK, et al. Transcriptional activation by NF-KB requires multiple coactivators. Mol Cell Biol 1999;19:6367–78.
Webster GA, Perkins ND. Transcriptional cross talk between NF-KB and p53. Mol Cell Biol 1999;19:3485–95.
Chrivia JC, Kwok RP, Lamb N, Hagiwara M, Montminy MR, Goodman RH. Phosphorylated CREB binds specifically to the nuclear protein CBP. Nature 1993;365:855–9.
De Cesare D, Fimia GM, Sassone-Corsi P. Signalling routes to CREM and CREB: Plasticity in transcriptional activation. Trends Biochem Sci 1999;24:281–5.
Sano Y, Tokitou F, Dai P, Maekawa T, Yamamoto T, Ishii S. CBP alleviates the intramolecular inhibition of ATF-2 function. J Biol Chem 1998;273:29098–105.
Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature 1996;384:641–3.
Ogryzko W, Schütz RL, Russanova V, Howard BH, Nakatani Y. The transcriptional co-activators p300 and CBP are histone acetyltransferases. Cell 1996;87:953–9.
Shaywitz AJ, Greenberg ME. CREB: A stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Ann Rev Biochem 1999;68:821–61.
Condon JC, Jeyasuria P, Faust JM, Wilson JW, Mendelson CR. A decline in the levels of progesterone receptor coactivators in the pregnant uterus at term may antagonize progesterone receptor function and contribute to the initiation of parturition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003;100:9518–23.
Phaneuf S, Europe GN, Varney M, Mackenzie IE, Watson SP, López-Bernal A. Oxytocin-stimulated phosphoino-sitide hydrolysis in human myometrial cells: Involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive and -insensitive G-proteins. J Endocrinol 1993;136:497–509.
Petrij F, Giles RH, Dauwerse HG, et al. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome caused by mutations in the transcriptional co-activator CBP. Nature 1995;376:348–51.
Tanaka Y, Naruse I, Maekawa T, Masuya H, Shiroishi T, Ishii S. Abnormal skeletal patterning in embryos lacking a single cbp allele: A partial similarity with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94:10215–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A.A.L. and N.R.C. contributed equally to this work.
The authors are grateful to Drs Alison Tyson-Capper, Kate Gilmore, Robert Philips, Jarrod Bailey, Gendie Lash, and Judith Bulmer for technical assistance and for critically reading the manuscript. This work was funded by the NHS (A.A.L. as part of Sub-Speciality Training) and University of Newcastle-upon-Tyne (N.R.C). G.N.E.F. is funded by grants from Action Medical Research and the Wellcome Trust.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, A.A., Chapman, N.R., Innes, B. et al. Expression and Interaction of the Transcriptional Coregulators, CBP/p300, in the Human Myometrium During Pregnancy and Labor. Reprod. Sci. 12, 92–97 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsgi.2004.10.012
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsgi.2004.10.012