Abstract
Objective
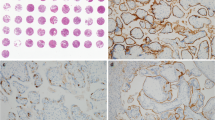
Despite emerging data on the in vitro modulatory effects of trophoblast-associated human leukocyte antigen G (HLA-G), its in vivo function needs to be determined. Immunohistochemical studies show a decrease in protein expression of trophoblast HLA-G in preeclampsia. Such a decrease in protein might be the consequence of a shift in HLA-G mRNA spliceform patterns. In an exploratory pilot study we determined trophoblast HLA-G mRNA spliceform distribution in preeclampsia.
Methods
Placental samples were collected immediately after cesarean delivery from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia or the syndrome hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count (HELLP) and uncomplicated normotensive pregnancies as controls. HLA-G mRNA spliceform distribution was analyzed using a semiquantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction procedure.
Results
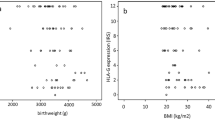
Analysis of HLA-G spliceform distribution showed a significant increase in frequency of the G5 form encoding for a soluble HLA-G molecule in preeclampsia. This increase in G5 form was not found in pregnancies complicated by HELLP.
Conclusion
The increased frequency in the expression of the HLA-G G5 spliceform may play a role in the pathophysiology of preeclampsia, in particular through a recently suggested effect of this soluble HLA-G molecule on remodeling of the spiral arteries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kilburn BA, Wang J, Duniec-Dmuchkowski ZM, Leach RE, Romero R, Armant DR. Extracellular matrix composition and hypoxia regulate the expression of HLA-G and integrins in a human trophoblast cell line. Biol Reprod 2000;62:739–47.
Moffett-King A. Natural killer cells and pregnancy. Nat Rev Immunol 2002;2:656–63.
Le Bouteiller P, Pizzato N, Barakonyi A, Solier C. HLA-G, pre-eclampsia, immunity and vascular events. J Reprod Immunol 2003;59:219–34.
Matijevic R, Johnston T. In vivo assessment of failed trophoblastic invasion of the spiral arteries in pre-eclampsia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1999;106:78–82.
Goldman-Wohl DS, Ariel I, Greenfield C, et al. Lack of human leukocyte antigen-G expression in extravillous trophoblasts is associated with pre-eclampsia. Mol Hum Reprod 2000;6:88–95.
Hara N, Fujii T, Yamashita T, Kozuma S, Okai T, Taketani Y. Altered expression of human leukocyte antigen G (HLA-G) on extravillous trophoblasts in preeclampsia: Immunohistological demonstration with anti-HLA-G specific antibody “87G” and anti- cytokeratin antibody “CAM5.2.” Am J Reprod Immunol 1996;36:349–58.
Colbern GT, Chiang MH, Main EK. Expression of the nonclas-sic histocompatibility antigen HLA-G by preeclamptic placenta. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;170:1244–50.
O’Brien M, Dausset J, Carosella ED, Moreau P. Analysis of the role of HLA-G in preeclampsia. Hum Immunol 2000;61:1126–31.
Lim KH, Zhou Y, Janatpour M, et al. Human cytotrophoblast differentiation/invasion is abnormal in pre-eclampsia. Am J Pathol 1997;151:1809–18.
van der Ven K, Skrablin S, Engels G, Krebs D. HLA-G polymorphisms and allele frequencies in Caucasians. Hum Immunol 1998;59:302–12.
Le Bouteiller P. HLA-G: On the track of immunological functions. Eur J Immunogenet 1997;24:397–408.
Paul P, Cabestre FA, Ibrahim EC, et al. Identification of HLA-G7 as a new splice variant of the HLA-G mRNA and expression of soluble HLA-G5, -G6, and -G7 transcripts in human transfected cells. Hum Immunol 2000;61:1138–49.
Kovats S, Main EK, Librach C, Stubblebine M, Fisher SJ, De-Mars R. A class I antigen, HLA-G, expressed in human trophoblasts. Science 1990;248:220–3.
Van Wijk IJ, Griffioen S, Tjoa ML, et al. HLA-G expression in trophoblast cells circulating in maternal peripheral blood during early pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:991–7.
Riteau B, Rouas-Freiss N, Menier C, Paul P, Dausset J, Carosella ED. HLA-G2, -G3, and -G4 isoforms expressed as nonmature cell surface glycoproteins inhibit NK and antigen-specific CTL cytolysis. J Immunol 2001;166:5018–26.
Le Bouteiller P, Legrand-Abravanel F, Solier C. Soluble HLA-G1 at the materno-foetal interface—a review. Placenta 2003;24(Suppl A):S10–S15.
Fuzzi B, Rizzo R, Criscuoli L, et al. HLA-G expression in early embryos is a fundamental prerequisite for the obtainment of pregnancy. Eur J Immunol 2002; 1273201.
Lachmeijer AM, Arngrimsson R, Bastiaans EJ, et al. A genomewide scan for preeclampsia in the Netherlands. Eur J Hum Genet 2001;9:758–64.
Zusterzeel PL, Peters WH, De Bruyn MA, Knapen MF, Merkus HM, Steegers EA. Glutathione S-transferase isoenzymes in de-cidua and placenta of preeclamptic pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol 1999;94:1033–8.
Davey DA, MacGillivray I. The classification and definition of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1988;158:892–8.
Moreau P, Carosella E, Gluckman E, et al. Alternative transcripts of the MHC of the non-classical class I HLA-G gene in the trophoblast during the first pregnancy trimester and in the placenta at term. C R Acad Sci III 1995;318:837–42.
Onno M, Guillaudeux T, Amiot L, et al. The HLA-G gene is expressed at a low mRNA level in different human cells and tissues. Hum Immunol 1994;41:79–86.
Starzyk KA, Salafia CM, Pezzullo JC, et al. Quantitative differences in arterial morphometry define the placental bed in preeclampsia. Hum Pathol 1997;28:353–8.
Grummer R, Donner A, Winterhager E. Characteristic growth of human choriocarcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Placenta 1999;20:547–53.
Rebmann V, Pfeiffer K, Passier M, et al. Detection of soluble HLA-G molecules in plasma and amniotic fluid. Tissue Antigens 1999;53:14–22.
Hunt JS, Jadhav L, Chu W, Geraghty DE, Ober C. Soluble HLA-G circulates in maternal blood during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;183:682–8.
Terrone DA, Panehart BK, May WL, Moore A, Magann EF, Martin JNJ. Leukocytosis is proportional to HELLP syndrome severity: Evidence for an inflammatory form of preeclampsia. South Med J 2000;93:768–71.
Lee N, Malacko AR, Ishitani A, et al. The membrane-bound and soluble forms of HLA-G bind identical sets of endogenous peptides but differ with respect to TAP association. Immunity 1995;3:591–600.
Hiby SE, King A, Sharkey A, Loke YW. Molecular studies of trophoblast HLA-G: Polymorphism, isoforms, imprinting and expression in preimplantation embryo. Tissue Antigens 1999;53:1–13.
Hannke-Lohmann A, Pildner VS, Dehne K, et al. Downregulation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in the placentas of women with preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 2000;96:582–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by “Zorg Onderzoek Nederland” (grant no. 2810063).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emmer, P.M., Joosten, I., Schut, M.H. et al. Shift in Expression of HLA-G mRNA Spliceforms in Pregnancies Complicated by Preeclampsia. Reprod. Sci. 11, 220–226 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsgi.2003.10.011
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsgi.2003.10.011