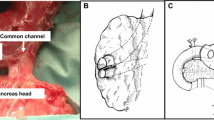
Abstract
Duodenal adenocarcinoma remains the leading cause of cancer death in familial adenomatous polyposis patients following colectomy. Stratification based on Spigelman’s criteria provides a means for determining therapy. Spigelman stage IV patients have been selected for pancreas-sparing duodenectomy. Twentyone patients underwent resection between 1992 and 2004, with a mean age of 58 ±11 years. The mean time from colectomy to duodenectomy was 27 ±13 years. Invasive cancer was found in the distal duodenum in one patient. Operative time averaged 327 ±61 minutes with a mean blood loss of 503 ± 266 ml. There was no mortality, and eight patients (38%) had 14 complications: six (29%) with delayed gastric emptying, four (19%) with biliary/pancreatic anastomotic leak, one with pancreatitis, and one with wound infection. There were two reoperations: one for delayed gastric emptying and one for an early biliary leak. Mean length of stay was 15 ±10 days. Two late complications occurred: a stomal ulcer and an intestinal obstruction at 48 and 24 months, respectively. Mean follow-up was 79 months (range, 3–152 months). Two patients developed polyps in the advanced jejunal limb and were endoscopically treated. Pancreassparing duodenectomy represents a definitive treatment for advanced duodenal polyposis and can obviate the need for pancreaticoduodenectomy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Groves CJ, Saunders BP, Spigelman AD, Phillips RKS. Duodenal cancer in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP): results of a 10 year prospective study. Gut 2002; 50:636–641.
Spigelman AD, Williams CB, Talbot IC, et al. Upper gastrointestinal cancer in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet 1989;2:783–785.
Bulow S, Bjork J, Christensen IJ, Fausa O, Jarvinen H, Moesgaard F, et al. Duodenal adenomatosis in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut 2004;53:381–386.
de Vos tot Nederveen Cappel WH, Jarvinen HJ, Bjork J, Berk T, Griffioen G, Vasen HFA. Worldwide survey among polypsis registrites of surgical management of severe duodenal adenomatosis in familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg 2003;90:705–710.
Alarcon FJ, Burke CA, Church JM, van Stolk RU. Familial adenomatous polyposis: efficacy of endoscopic and surgical treatment for advanced duodenal adenomas. Dis Colon Rectum 1999;42:1553–1556.
Penna C, Bataille N, Balladur P, Tiret E, Parc R. Surgical treatment of severe duodenal polyposis in familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg 1998;85:665–668.
Norton ID, Geller A, Petersen BT, Sorbi D, Gostout CJ. Endoscopic surveillance and ablative therapy for periampullary adenomas. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:101–106.
Iwama T, Tomita H, Kawachi Y, et al. Indications of local excision of ampullary lesions associated with familial adenomatous polyposis. J Am Coll Surg 1994;179:462–464.
Chung RS, Church JM, VanStolk R. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy: Indications, surgical technique, and results. Surgery 1995;117:254–259.
Kalady MF, Clary BM, Tyler DS, Pappas TN. Pancreaspreserving duodenctomy in the management of duodenal familial adenomatous polyposis. J Gastrointest Surg 2002;6:82–87.
Sarmiento JM, Thompson GB, Nagorney DM, Donohue JH, Farnell MB. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy for duodenal polyposis. Arch Surg 2002;137:557–563.
Burke CA, Beck GJ, Church JM, van Stolk RU. The natural history of untreated duodenal and ampullary adenomas in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis followed in an endoscopic surveillance program. Gastrointest Endosc 1999;49:358–364.
Sohn TA, Lillemoe KD, Cameron JL, et al. Adenocarcinoma of the duodenum: factors influencing long-term survival. J Gastrointest Surg 1998;2:79–87.
Baradi H, Walsh RM, Henderson JM, Vogt D, Popovich M. Postoperative jejunal feeding and outcome of pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Gastrointest Surg 2004;8:428–433.
Gallagher MC, Shankar A, Groves CJ, Russell RCG, Phillips RKS. Pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy for advanced duodenal disease in familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg 2004;91:1157–1164.
Yeo C, Cameron J, Sohn T, Lillemoe K, et al. Six hundred fifty consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies in the 1990’s: pathology, complications, and outcomes. Ann Surg 1997;226:248–260.
Balcom J, Rattner D, Warshaw A, Chang Y, Fernandez C. Ten-year experience with 733 pancreatic resections: changing indications, older patients, and decreasing length of hospitalization. Arch Surg 2001;136:391–398.
Melvin WS, Buekers KS, Muscarella P, Johnson JA, Schirmer WJ, Ellison EC. Outcome analysis of long-term survivors following pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Gastrointest Surg 1998;2:72–78.
Conlon KC, Labow D, Leung D, et al. Prospective randomized clinical trial of the value of intraperitoneal drainage after pancreatic resection. Ann Surg 2001;234:487–494.
Hosotani R, Doi R, Imarmura M. Duct-to-mucosa pancreaticojejunostomy reduces the risk of pancreatic leakage after pancreatoduodenectomy. W J Surg 2002;26:99–104.
Hamanaka Y, Nishihara K, Hamasaki T, et al. Pancreatic juice output after pancreatoduodenectomy in relation to pancreatic consistency, duct size, and leakage. Surgery 1996;119:281–287.
Suzuki Y, Fujino Y, Tanioka Y, et al. Selection of pancreaticojejunostomy techniques according to pancreatic texture and duct size. Arch Surg 2002;137:1044–1047.
Murakami Y, Uemura K, Sasaki M, et al. Duodenal cancer arising from the remaining duodenum after pyloruspreserving pancreatoduodenectomy for ampullary cancer in familial adenomatous polyposis. J Gastrointest Surg 2005;9:389–392.
Maher MM, Yeo CJ, Lillemoe KD, Roberts JR, Cameron JL. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy for infra-ampullary duodenal pathology. Am J Surg 1996;171:62–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackey, R., Walsh, R.M., Chung, R. et al. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy is effective management for familial adenomatous polyposis. J Gastrointest Surg 9, 1088–1093 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gassur.2005.07.021
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gassur.2005.07.021