Abstract
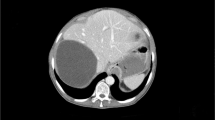
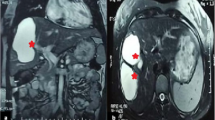
Obstruction of a major hepatic vein, or major portal vein, or biliary tree branch causes atrophy of the related hepatic region, and frequently, hypertrophy in the remaining liver—the atrophy-hypertrophy complex (AHC). Whether hydatid cysts can causeAHCis controversial. The records of 370 patients who underwent surgery for hepatic hydatid disease between August 1993 and July 2002 were evaluated retrospectively. Excluding six patients with previous interventions on the liver, AHC had been recorded in the operative notes of 16 patients (4.4%); for all patients, a cyst located in the right hemiliver had caused atrophy of the right hemiliver and compensatory hypertrophy of the left hemiliver. The computed tomography images of seven patients were suitable for volumetric analysis. The median (range) right and left hemiliver volumes were 334 (0-686) ml and 1084 (663-1339) ml, respectively. The median (range) cyst volume was 392 (70–1363) ml. AHC due to Echinococcus granulosus was confirmed by objective volumetric analysis. The presence of AHC should alert the surgeon to two implications. First, pericystectomy may be hazardous due to association with major vascular and biliary structures. Second, in patients with AHC, the hepatoduodenal ligament rotates around its axis; this should be considered to avoid vascular injury if a common bile duct exploration is to be performed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hueston JT. The production of liver lobe atrophy by hydatid cysts. Br J Surg 1953;41:427–431.
Schweizer W, Duda P, Tanner S, et al. Experimental atrophy/ hypertrophy complex (AHC) of the liver: Portal vein, but not bile duct obstruction, is the main driving force for the development of AHC in the rat. J Hepatol 1995;23:71–78.
Ham JM. Lobar and segmental atrophy of the liver. World J Surg 1990;14:457–462.
Hadjis NS, Blumgart LH. Liver hyperplasia, hypertrophy and atrophy: Clinical relevance. In: Blumgart L, ed. Surgery of the Liver and Biliary Tract. New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1988, 61–71.
Hann LE, Getrajdman GI, Brown KT, et al. Hepatic lobar atrophy: Association with ipsilateral portal vein obstruction. Am J Roentgenol 1996;167:1017–1021.
Haddad MC, Birjawi GA, Khouzami RA, Khoury NJ, El-Zein YR, Al-Kutoubi AO. Unilocular hepatic echinococcal cysts: Sonography and computed tomography findings. Clin Radiol 2001;56:746–750.
Ham JM. Segmental and lobar atrophy of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1974;139:840–844.
Lorigan JG, Charnsangavej C, Carrasco CH, Richli WR, Wallace S. Atrophy with compensatory hypertrophy of the liver in hepatic neoplasms: Radiologic findings. Am J Roentgenol 1988;150:1291–1295.
Rozanes I, Acunas B, Celik L, Minareci O, Gokmen E. CT in lobar atrophy of the liver caused by alveolar echinococcosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1992;16:216–218.
Lory J, Schweizer W, Blumgart LH, Zimmermann A. The pathology of the atrophy/hypertrophy complex (AHC) of the liver. A light microscopic and immunohistochemical study. Histol Histopathol 1994;9:541–554.
Balci NC, Tunaci A, Semelka RC, et al. Hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: MRI findings. Magn Reson Imaging 2000; 18:537–541.
Yildirgan MI, Basoglu M, Atamanalp SS, et al. Intrabiliary rupture in liver hydatid cysts: Results of 20 years’ experience. Acta Chir Belg 2003;103:621–625.
Alonso CO, Moreno GE, Loinaz SC, et al. Results of 22 years of experience in radical surgical treatment of hepatic hydatid cysts. Hepatogastroenterology 2001;48:235–243.
Gonzales EM, Selas PR, Martinez B, Garcia IG, Carazo FP, Pascual MH. Results of surgical treatment of hepatic hydatidosis: Current therapeutic modifications. World J Surg 1991;15:254–263.
Demirci S, Eraslan S, Anadol E, Bozatli L. Comparison of the results of different surgical techniques in the management of hydatid cysts of the liver. World J Surg 1989;13:88–91.
Kalovidouris A, Pissiotis C, Pontifex G, Gouliamos A, Pentea S, Papavassiliou C. CT characterization of multivesicular cysts. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1986;10:428–432.
Beggs I. The radiological appearances of hydatid disease of the liver. Clin Radiol 1983;34:555–563.
Di Matteo G, Bove A, Chiarini S, et al. Hepatogastroenterology 1996;43:1562–1565.
Sayek I, Yalin R, Sanac Y. Surgical treatment of hydatid disease of the liver. Arch Surg 1980;115:847–850.
The Brisbane 2000 terminology of hepatic anatomy and resections. HPB 2000;2:333-339.
Gharbi H, Hassine W, Brauner WN, Dupoch K. Ultrasound examination of hydatic liver. Radiology 1981;139:459–463.
Mukai JK, Stack CM, Turner DA. Pictorial essay. Imaging of surgically relevant hepatic vascular and segmental anatomy. Part 1. Normal anatomy. Am J Roentgenol 1987;149:287–292.
Leelaudomlipi S, Sugawara Y, Kaneko J, Matsui Y, Ohkubo T, Makuuchi M. Volumetric analysis of liver segments in 155 living donors. Liver Transpl 2002;8:612–614.
Abdalla EK, Denys A, Chevalier P, Nemr RA, Vauthey JN. Total and segmental liver volume variations: Implications for liver surgery. Surgery 2004;135:404–410.
Takayasu K, Muramatsu Y, Shima Y, Moriyama N, Yamada T, Makuuchi M. Hepatic lobar atrophy after obstruction of the ipsilateral portal vein from hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Radiology 1986;160:389–393.
Bilge O, Ozden I, Bilsel Y, et al. The role of total pericystectomy in hepatic hydatidosis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 1997;4:212–214.
William RJ, Blumgart LH. Operative repair of bile duct injuries involving the hepatic duct confluence. Arch Surg 1999; 134:769–775.
Hadjis NS, Adam A, Gibson R, Blenkharn JI, Benjamin IS, Blumgart LH. Nonoperative approach to hilar cancer determined by the atrophy-hypertrophy complex. Am J Surg 1989;157:395–399.
Blumgart LH. Hilar and intrahepatic biliary enteric anastomosis. Surg Clin North Am 1994;74:845–863.
Czerniak A, Soreide O, Gibson RN, et al. Liver atrophy complicating benign bile duct strictures: Surgical and interventional radiologic approaches. Am J Surg 1986;152:294–300.
Alper A, Ariogul O, Emre A, Uras A, Okten A. Choledochoduodenostomy for intrabiliary rupture of hydatid cysts of liver. Br J Surg 1987;74:243–245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Istanbul University Research Fund (Project No. BYP-790/17102 005).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karabulut, K., Özden, İ., Poyanlh, A. et al. Hepatic atrophy-hypertrophy complex due to echinococcus granulosus . J Gastrointest Surg 10, 407–412 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gassur.2005.06.007
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gassur.2005.06.007