Abstract
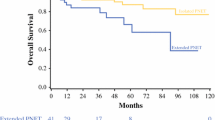
Well-differentiated islet cell tumors can be associated with aggressive biology, resulting in early metastases to the liver. This study was carried out to determine whether survival for patients with malignant islet cell tumors and synchronous liver metastases is affected by complete surgical resection. Thirty-one patients with synchronous liver metastases from islet cell cancer underwent surgical exploration with the intent for complete tumor resection, and all patients underwent resection of the pancreatic primary. The patients were divided into two groups, those with resectable versus unresectable liver metastases. Twenty-six of 31 (84%) patients underwent complete resection of both the primary tumor and all liver metastases, and 5 (16%) patients underwent only complete resection of the pancreatic primary without liver resection. To extirpate the primary tumor, a pancreaticoduodenectomy was performed in 11 of the 26 (42%) completely resected patients and in 4 of the 5 (80%) incompletely resected patients, P = NS. The remainder of the patients underwent distal pancreatectomy. There were no statistical differences in primary tumor size, lymph node metastases, or adjuvant treatments between patients with resected and unresected liver metastases. The median overall survival for the completely resected group was 78 months, longer than the 17 months for the group with unresectable liver metastases (P = 0.06). Complete tumor resection (or the tumor biology that allows such complete resection) affords a survival advantage to patients with metastatic islet cell tumors of the pancreas. Patterns of liver metastases from islet cell tumors, specifically multiple bilobar metastases that are not amenable to resection and/or ablation, predict a poor outcome despite resection of the primary pancreatic tumor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phan GQ, Yeo CJ, Hruban RH, Lillemoe KD, Pitt HA, Cameron JL. Surgical experience with pancreatic and peripancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: review of 125 patients. J GASTROINTEST SURG 1998;2(5):472–482.
Moertel CG, Lefkopoulo M, Lipsitz S, Hahn RG, Klaassen D. Streptozocin-doxorubicin, streptozocin-fluorouracil or chlorozotocin in the treatment of advanced islet-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1992;326(8):519–523.
Steele G Jr., Bleday R, Mayer RJ, Lindblad A, Petrelli N, Weaver D. A prospective evaluation of hepatic resection for colorectal carcinoma metastases to the liver: Gastrointestinal Tumor Study Group Protocol 6584. J Clin Oncol 1991;9(7):1105–1112.
Wagman LD, Kemeny MM, Leong L, Terz JJ, Hill LR, Beatty JD, Kokal WA, Riihimaki DU. A prospective, randomized evaluation of the treatment of colorectal cancer metastatic to the liver. J Clin Oncol 1990;8(11):1885–1893.
Chamberlain RS, Canes D, Brown KT, Saltz L, Jarnagin W, Fong Y, Blumgart LH. Hepatic neuroendocrine metastases: does intervention alter outcomes? J Am Coll Surg 2000; 190(4):432–445.
Chen H, Hardacre JM, Uzar A, Cameron JL, Choti MA. Isolated liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors: does resection prolong survival? J Am Coll Surg 1998;187(1):88–92.
Grazi GL, Cescon M, Pierangeli F, Ercolani G, Gardini A, Cavallari A, Mazziotti A. Highly aggressive policy of hepatic resections for neuroendocrine liver metastases. Hepatogastroenterology 2000;47(32):481–486.
McEntee GP, Nagorney DM, Kvols LK, Moertel CG, Grant CS. Cytoreductive hepatic surgery for neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery 1990;108(6):1091–1096.
Norton JA, Warren RS, Kelly MG, Zuraek MB, Jensen RT. Aggressive surgery for metastatic liver neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery 2003;134(6):1057–1063.
Que FG, Nagorney Dm, Batts KP, Linz LJ, Kvols LK. Hepatic resection for metastatic neuroendocrine carcinomas. Am J Surg 1995;169(1):36–42.
Ahlman H, Wangberg B, Jansson S, Friman S, Olausson M, Tylen U, Nilsson O. Interventional treatment of gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumours. Digestion 2000;62(Suppl). 1:59-l:68.
Anthuber M, Jauch KW, Briegel J, Groh J, Schildberg FW. Results of liver transplantation for gastroenteropancreatic tumor metastases. World J Surg 1996;20(1):73–76.
Arnold R, Simon B, Wied M. Treatment of neuroendocrine GEP tumours with somatostatin analogues: a review. Digestion 2000;62(Suppl). 1:84-1:91.
Eriksson BK, Larsson EG, Skogseid BM, Lofberg AM, Lorelius LE, Oberg KE. Liver embolizations of patients with malignant neuroendocrine gastrointestinal tumors. Cancer 1998;83(11):2293–2301.
Florman S, Toure B, Kim L, Gondolesi G, Roayaie S, Krieger N, Fishbein T, Emre S, Miller C, Schwartz M. Liver transplantation for neuroendocrine tumors. J GASTROINTEST SURG 2004;8(2):208–212.
Lang H, Oldhafer KJ, Weimann A, Schlitt HJ, Scheumann GF, Flemming P, Ringe B, Pichlmayr R. Liver transplantation for metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Ann Surg 1997;225(4):347–354.
Sutcliffe R, Maguire D, Ramage J, Rela M, Heaton N. Management of neuroendocrine liver metastases. Am J Surg 2004;187(1):39–46.
Dousset B, Saint-Marc O, Pitre J, Soubrane O, Houssin D, Chapuis Y. Metastatic endocrine tumors: medical treatment, surgical resection, or liver transplantation. World J Surg 1996;20(7):908–914.
Sarmiento JM, Heywood G, Rubin J, Ilstrup DM, Nagorney DM, Que FG. Surgical treatment of neuroendocrine metastases to the liver: a plea for resection to increase survival. J Am Coll Surg 2003;197(1):29–37.
Sarmiento JM, Que FG, Grant CS, Thompson GB, Farnell MB, Nagorney DM. Concurrent resections of pancreatic islet cell cancers with synchronous hepatic metastases: outcomes of an aggressive approach. Surgery 2002;132(6):976–982.
Jacobsen MB, Hanssen LE. Clinical effects of octreotide compared to placebo in patients with gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumours. Report on a double-blind, randomized trial. J Intern Med 1995;237(3):269–275.
Perry LJ, Stuart K, Stokes KR, Clouse ME. Hepatic arterial chemoembolization for metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery 1994;116(6):1111–1116.
Knechtle SJ, Kalayoglu M, D’Alessandro AM, Rikkers LF. Proceed with caution: liver transplantation for metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Ann Surg 1997;225(4):345–346.
Delcore R, Friesen SR. Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors. J Am Coll Surg 1994;178(2):187–211.
Ruszniewski P, Rougier P, Roche A, Legmann P, Sibert A, Hochlaf S, Ychou M, Mignon M. Hepatic arterial chemoembolization in patients with liver metastases of endocrine tumors. A prospective phase II study in 24 patients. Cancer 1993;71(8):2624–2630.
Hansel DE, House MG, Ashfaq R, Rahman A, Yeo CJ, Maitra A. MAGE1 is expressed by a subset of pancreatic endocrine neoplasms and associated lymph node and liver metastases. Int J Gastrointest Cancer 2003;33(2-3):141–147.
House MG, Herman JG, Guo MZ, Hooker CM, Schulick RD, Cameron JL, Hruban RH, Maitra A, Yeo CJ. Prognostic value of hMLH1 methylation and microsatellite instability in pancreatic endocrine neoplasms. Surgery 2003; 134(6):902–908.
House MG, Herman JG, Guo MZ, Hooker CM, Schulick RD, Lillemoe KD, Cameron JL, Hruban RH, Maitra A, Yeo CJ. Aberrant hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes in pancreatic endocrine neoplasms. Ann Surg 2003;238(3):423–431.
Maitra A, Hansel DE, Argani P, Ashfaq R, Rahman A, Naji A, Deng S, Geradts J, Hawthorne L, House MG, Yeo CJ. Global expression analysis of well-differentiated pancreatic endocrine neoplasms using oligonucleotide microarrays. Clin Cancer Res 2003;9(16):5988–5995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
House, M.G., Cameron, J.L., Lillemoe, K.D. et al. Differences in survival for patients with resectable versus unresectable metastases from pancreatic islet cell cancer. J Gastrointest Surg 10, 138–145 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gassur.2005.05.004
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gassur.2005.05.004