Abstract
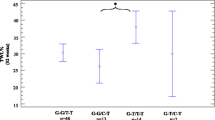
Both the gene encoding the α subunit of G stimulatory proteins (GNAS1) and the β3 subunit gene (GNB3) of G proteins are associated with obesity and/or hypertension. Moreover, the TT/TC825 polymorphism of GNB3 predicts greater weight loss than the CC825 polymorphism in obese patients (mean body mass index, 35 kg/m2) undergoing a structured nonpharmacologic weight loss program. Gastric banding enforces a low-calorie diet by diminishing the need for volitional adherence. It is unknown whether these polymorphisms predict the variable weight loss in patients after bariatric surgery. Three hundred and four severely obese patients (mean +- SEM age, 42 +- 1 years; 245 women and 59 men; mean +- SEM body mass index, 43.9 +- 0.3 kg/m2) followed prospectively for at least 3 years after surgery were genotyped for theGNB3C825T, G814A,andGNAS1T393 polymorphisms. All analyses were performed blinded to the phenotypic characteristics of the study group. Frequencies of polymorphisms were comparable to those previously published. No polymorphism studied predicted 3-year weight loss or was associated with high blood pressure in severely obese patients after gastric banding. Multivariate analysis of potentially confounding factors such as reoperation rate or use of sibutramine or orlistat revealed similar results (P > 0.1). Regardless of the mechanism(s) involved for these discordant findings, GNB3 C825T, G814A, and GNAS1 T393C polymorphisms do not seem to be reliable predictors of long-term weight loss.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comuzzie AG, Allison DB. The search for human obesity genes. Science 1998;280:1374–1377.
World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. Geneva, Switzerland: 1998, World Health Organization, WHO/NUT/NCD/98.1.
Nestle M. The ironic politics of obesity. Science 2003;299:781.
Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001; 285:2486-2497.
Klein S, Wadden T, Sugerman HJ. AGA technical review on obesity. Gastroenterology 2002;123:882–932.
Kral JG. Surgical treatment of obesity. In Bray GA, Bouchard C, James WPT, eds. Handbook of Obesity. New York: Marcel Dekker, 1998, pp 977–993.
Steffen R, Biertho L, Ricklin Th, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: A five-year prospective study. Obes Surg 2003;13:404–411.
Hauner H, Meier M, Jockel KH, et al. Prediction of successful weight reduction under sibutramine therapy through genotyping of the G-protein beta3 subunit gene (GNBS) C825T polymorphism. Pharmacogenetics 2003;13:453–459.
Frey U, Hauner H, Bachmann H, et al. Der G-Protein alpha s (GNAS1)T393C-Polymorphismus als Prädiktor für erfolgreiche Gewichtsreduktion und kardiovaskuläre Nebenwirkungen unter Therapie mit Sibutramin. Aktuel Ernaer 2003;28:311–347.
Rosskopf D, Manthey I, Habich C, et al. Identification and characterization of G beta 3s2, a novel splice variant of the G-protein beta 3 subunit. Biochem J 2003;371(Pt 1):223–232.
Siffert W. Cardiovascular pharmacogenetics: On the way toward individually tailored drug therapy. Kidney Int Suppl 2003;84:S168-S171.
Zill P, Baghai TC, Zwanzger P, et al. Evidence for an association between a G-protein beta3-gene variant with depression and response to antidepressant treatment. Neuroreport 2000; 11:1893–1897.
Schafers RF, Nurnberger J, Rutz A, et al. Haemodynamic characterization of young normotensive men carrying the 825T-allele of the G-protein beta3 subunit. Pharmacogenetics 2001;11:461–470.
Zeltner R, Delles C, Schneider M, et al. G-protein beta(3) subunit gene (GNB3) 825T allele is associated with enhanced renal perfusion in early hypertension. Hypertension 2001; 37:882–886.
Dobrev D, Wettwer E, Himmel HM, et al. G-protein beta(3)-subunit 825T allele is associated with enhanced human atrial inward rectifier potassium currents. Circulation 2000;102:692–697.
Hauner H, Rohrig K, Siffert W. Effects of the G-protein beta3 subunit 825T allele on adipogenesis and lipolysis in cultured human preadipocytes and adipocytes. Horm Metab Res 2002; 34:475–480.
Ryden M, Faulds G, Hoffstedt J, et al. Effect of the (C825T) Gbeta(3) polymorphism on adrenoceptor-mediated lipolysis in human fat cells. Diabetes 2002;51:1601–1608.
Lindemann M, Virchow S, Ramann F, et al. The G protein beta3 subunit 825T allele is a genetic marker for enhanced T cell response. FEBS Lett 2001;495:82–86.
Morrison AC, Doris PA, Folsom AR, et al. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. G-protein beta3 subunit and alpha-adducin polymorphisms and risk of subclinical and clinical stroke. Stroke 2001;32:822–829.
Poch E, Gonzalez D, Gomez-Angelats E, et al. G-Protein beta(3) subunit gene variant and left ventricular hypertrophy in essential hypertension. Hypertension 2000;35:214–218.
Siffert W, Forster P, Jöckel K-H, et al. Worldwide ethnic distribution of the G protein γ3 subunit 825T allele and its association with obesity in Caucasian, Chinese, and Black African individuals. J Am Soc Nephrol 1999;10:1021–1030.
Gutersohn A, Naber C, Muller N, et al. G-protein beta3 825TT genotype and post-pregnancy weight retention. Lancet 2000;51:1601–1608.
Hocher B, Slowinski T, Stolze T, et al. Association of maternal G protein beta3 subunit 825T allele with low birthweight. Lancet 2000;355:1241–1242.
Beige J, Engeli S, Ringel J, et al. Donor G protein beta3 subunit 825TT genotype is associated with reduced kidney allograft survival. J Am Soc Nephrol 1999;10:1717–1721.
Kato N, Sugiyama T, Morita H, et al. G-protein b3 subunit variant and essential hypertension in Japanese. Hypertension 1998;32:935–938.
Larson N, Hutchinson R, Boerwinkle E. Lack of association of 3 functional gene variants with hypertension in African Americans. Hypertension 2000;35:1297–1300.
Snapir A, Heinonen P, Tuomainen TP, et al. G-protein b3 subunit C825T polymorphism: No association with risk for hypertension and obesity. J Hypertens 2001;19:2149–2155.
Benjafield AV, Lin RCY, Dalziel B, et al. G-protein b3 subunit gene splice variant in obesity and overweight. Int J Obes 2001;25:777–780.
Rosskopf D, Busch S, Manthey I, et al. G protein b3 gene: Structure, promoter, and additional polymorphisms. Hypertension 2000;36:33–41.
Sokel RR, Rolf FJ. Biometry. New York: WH Freeman and Co, 1981, p 765.
Branson R, Potoczna N, Kral JG, et al. Binge eating as a major phenotype of melanocortin 4 receptor gene mutations. N Engl J Med 2003;348:1096–1103.
Hauri P, Steffen R, Ricklin T, et al. Treatment of morbid obesity with the Swedish Adjustable Gastric Band (SAGB): Complication rate during a 12-month follow-up period. Surgery 2000;127:484–488.
Wiesner W, Weber M, Hauser RS, et al. Anterior versus posterior slippage: Two different types of eccentric pouch dilatation in patients with adjustable gastric banding. Dig Surg 2001;18:182–186.
James WP, Astrup A, Finer N, et al. Effect of sibutramine on weight maintenance after weight loss: A randomised trial. Lancet 2000;356:2119–2125.
Zoss I, Piec G, Horber FF. Impact of orlistat therapy on weight reduction in morbidly obese patients after implantation of the Swedish Adjustable Gastric Band. Obes Surg 2002;12:113–117.
Steffen R, Horber F, Hauri P. Swedish Adjustable Gastric Band (SAGB)-distal gastric bypass: A new variant of an old technique in the treatment of superobesty and failed band restriction. Obes Surg 1999;9:171–176.
Gagner M, Steffen R, Biertho L, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding with duodenal switch for morbid obesity: Technique and preliminary results. Obes Surg 2003;13:444–449.
Hellmich N. Obesity on track as No. 1 killer. USA Today. Available at: http://www.usatoday.com/news/health/2004-03-09-obesity_x.htm. Accessed September 12, 2004.
O’Brien PE, Dixon JB. Lap-band: Outcomes and results. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 2003;13:265–270.
Kral JG, Branson R, Piec G, et al. Melanocortin-4 receptor gene variants affect results of gastric banding. J GASTROINTEST SURG 2004;126(Suppl 2):A774.
Kral JG, Lentes K-U, Horber FF. Binge eating as a phenotype of melanocortin 4 receptor gene mutations. N Engl J Med 2003;349:606–609; author reply 606-609.
Davy KP, Hall JE. Obesity and hypertension: Two epidemics or one? Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2004;286:R803-R813.
Siffert W, Rosskopf D, Erbel R. Genetic polymorphism of the G-protein beta3 subunit, obesity and essential hypertension. Herz 2000;25:26–33.
Stevens VJ, Obarzanek E, Cook NR, et al. Long-term weight loss and changes in blood pressure: Results of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention, phase II. Ann Intern Med 2001; 134:1–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Potoczna, N., Wertli, M., Steffen, R. et al. G protein polymorphisms do not predict weight loss and improvement of hypertension in severely obese patients. J Gastrointest Surg 8, 862–868 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gassur.2004.08.004
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gassur.2004.08.004