Abstract
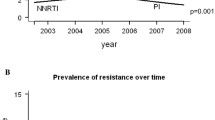
Transient decreases in the proportion of individuals newly infected with an HIV-resistant virus (primary resistance) are documented for several cities of North America, including San Francisco. Using a staged SI deterministic model, we identified three potential causes consistent with the history of the epidemic: (1) increase in risky behaviour, (2) reduction in the proportion of HIV-acutely infected individuals undergoing treatment, and (3) replacement of mono-and dual-drug therapies with triple-drug therapies. Although observed patterns resemble scenario 1 most closely, these explanations are not mutually exclusive and may have contributed synergistically to the decline. Under scenario 1 the counterintuitive situation arises where, although the proportion of primary resistance cases decreases transiently, the epidemic worsens because the actual numbers of infected individuals and of drug resistance carriers increases. Our results call for improved efforts to control the epidemic in developed nations, and highlight the usefulness of drug resistant strains as epidemiological markers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammaranond, P., Cunningham, P., Oelrichs, R., Suzuki, K., Harris, C., Leas, L., Grulich, A., Cooper, D.A., Kelleher, A.D., 2003a. Rates of transmission of antiretroviral drug resistant strains of HIV-1. J. Clin. Virol. 26, 153–161.
Ammaranond, P., Cunningham, P., Oelrichs, R., Suzuki, K., Harris, C., Leas, L., Grulich, A., Cooper, D.A., Kelleher, A.D., 2003b. No increase in protease resistance and a decrease in reverse transcriptase resistance mutations in primary HIV-1 infection: 1992–2001. AIDS 17, 264–267.
Anderson, R.M., 1989. Mathematical and statistical studies of the epidemiology of HIV. AIDS 3, 333–346.
Bacchetti, P., Moss, A.R., 1989. Incubation period of AIDS in San Francisco. Nature 338, 251–253.
Bleiber, G., Munoz, M., Ciuffi, A., Meylan, P., Telenti, A., 2001. Individual contributions of mutant protease and reverse transcriptase to viral infectivity, replication, and protein maturation of antiretroviral drug-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 75, 3291–3300.
Blower, S.M., Aschenbach, A.N., Kahn, J.O., 2003. Predicting the transmission of drug-resistant HIV: comparing theory with data. Lancet Infect. Dis. 3, 10–11.
Blower, S.M., Gershengorn, H.B., Grant, R.M., 2000. A tale of two futures: HIV and antiretroviral therapy in San Francisco. Science 287, 650–654.
Blower, S.M., Aschenbach, A.N., Gershengorn, H.B., Kahn, J.O., 2001. Predicting the unpredictable: transmission of drug-resistant HIV. Nat. Med. 7, 1016–1020.
Bonhoeffer, S., Nowak, M.A., 1997. Pre-existence and emergence of drug resistance in HIV-1 infection. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 264, 631–637.
Brenner, B.G., Routy, J.P., Petrella, M., Moisi, D., Oliveira, M., Detorio, M., Spira, B., Essabag, V., Conway, B., Lalonde, R., Sekaly, R.P., Wainberg, M.A., 2002. Persistence and fitness of multidrug-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 acquired in primary infection. J. Virol. 76, 1753–1761.
Castillo-Chavez, C., Hethcote, H.W., Andreasen, V., Levin, S.A., Liu, W.M., 1989. Epidemiological models with age structure, proportionate mixing, and cross-immunity. J. Math. Biol. 27, 233–258.
Chiesi, A., Mocroft, A., Dally, L.G., Miller, V., Katlama, C., Ledergerber, B., Pedersen, C., Phillips, A.N., Arcieri, R., Lundgren, J.D., 1999. Regional survival differences across Europe in HIV-positive people: the EuroSIDA study. AIDS 13, 2281–2288.
Cohen, J., 2002. Therapies. Confronting the limits of success. Science 296, 2320–2324.
de Mendoza, C., del Romero, J., Rodriguez, C., Corral, A., Soriano, V., 2002. Decline in the rate of genotypic resistance to antiretroviral drugs in recent HIV seroconverters in Madrid. AIDS 16, 1830–1832.
Dukers, N.H., Goudsmit, J., de Wit, J.B., Prins, M., Weverling, G.J., Coutinho, R.A., 2001. Sexual risk behaviour relates to the virological and immunological improvements during highly active antiretroviral therapy in HIV-1 infection. AIDS 15, 369–378.
Ezzell, C., 1987. AZT given the green light for clinical treatment of AIDS. Nature 326, 430.
Ghani, A.C., Ferguson, N.M., Fraser, C., Donnelly, C.A., Danner, S., Reiss, P., Lange, J., Goudsmit, J., Anderson, R.M., De Wolf, F., 2002. Viral replication under combination antiretroviral therapy: a comparison of four different regimens. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 30, 167–176.
Gonzales, M.J., Delwart, E., Rhee, S.Y., Tsui, R., Zolopa, A.R., Taylor, J., Shafer, R.W., 2003. Lack of detectable human immunodeficiency virus type 1 superinfection during 1072 person-years of observation. J. Infect. Dis. 188, 397–405.
Goudsmit, J., Weverling, G.J., van der Hoek, L., de Ronde, A., Miedema, F., Coutinho, R.A., Lange, J.M., Boerlijst, M.C., 2001. Carrier rate of zidovudine-resistant HIV-1: the impact of failing therapy on transmission of resistant strains. AIDS 15, 2293–2301.
Grant, R.M., Hecht, F.M., Warmerdam, M., Liu, L., Liegler, T., Petropoulos, C.J., Hellmann, N.S., Chesney, M., Busch, M.P., Kahn, J.O., 2002. Time trends in primary HIV-1 drug resistance among recently infected persons. JAMA 288, 181–188.
Grant, R.M., Liegler, T., Spotts, G., Hecht, F.M., 2003. Declining nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor primary resistance in San Francisco, 2000–2003. XII International HIV Drug Resistance Workshop: Basic Principles & Clinical Implications, Los Cabos, Mexico.
Harrigan, P.R., Bloor, S., Larder, B.A., 1998. Relative replicative fitness of zidovudine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates in vitro. J. Virol. 72, 3773–3778.
Hethcote, H.W., Van Ark, J.W., 1987. Epidemiological models for heterogeneous populations proportionate mixing parameter estimation and immunization programs. Math. Biosci. 84, 85–118.
Hethcote, H.W., Van Ark, J.W., 1992. Modeling HIV transmission and AIDS in the United States. Lecture Notes in Biomathematics, vol. 95. Springer, Berlin, New York.
Hirsch, M.S., Conway, B., Daquila, R.T., Johnson, V.A., BrunVezinet, F., Clotet, B., Demeter, L.M., Hammer, S.M., Jacobsen, D.M., Kuritzkes, D.R., Loveday, C., Mellors, J.W., Vella, S., Richman, D.D., 1998. Antiretroviral drug resistance testing in adults with HIV infection: implications for clinical management. JAMA 279, 1984–1991.
Katz, M.H., Schwarcz, S.K., Kellogg, T.A., Klausner, J.D., Dilley, J.W., Gibson, S., McFarland, W., 2002. Impact of highly active antiretroviral treatment on HIV seroincidence among men who have sex with men: San Francisco. Am. J. Public Health 92, 388–394.
Koelsch, K.K., Smith, D.M., Little, S.J., Ignacio, C.C., Macaranas, T.R., Brown, A.J., Petropoulos, C.J., Richman, D.D., Wong, J.K., 2003. Clade B HIV-1 superinfection with wild-type virus after primary infection with drug-resistant clade B virus. AIDS 17, F11–F16.
Koopman, J., Simon, C., Jacquez, J., Joseph, J., Sattenspiel, L., Park, T., 1988. Sexual partner selectiveness effects on homosexual HIV transmission dynamics. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1, 486–504.
Law, M.G., Prestage, G., Grulich, A., Van de Ven, P., Kippax, S., 2001. Modelling the effect of combination antiretroviral treatments on HIV incidence. AIDS 15, 1287–1294.
Li, T.S., Tubiana, R., Katlama, C., Calvez, V., Ait Mohand, H., Autran, B., 1998. Long-lasting recovery in CD4 T-cell function and viral-load reduction after highly active antiretroviral therapy in advanced HIV-1 disease. Lancet 351, 1682–1686.
Little, S.J., Holte, S., Routy, J.P., Daar, E.S., Markowitz, M., Collier, A.C., Koup, R.A., Mellors, J.W., Connick, E., Conway, B., Kilby, M., Wang, L., Whitcomb, J.M., Hellmann, N.S., Richman, D.D., 2002. Antiretroviral-drug resistance among patients recently infected with HIV. N. Engl. J. Med. 347, 385–394.
Lloyd-Smith, J.O., Getz, W.M., Westerhoff, H.V., 2004. Frequency-dependent incidence in sexually transmitted disease: portrayal of pair-based transmission and effects of illness on contact behaviour. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 271(1539), 625–634.
Longini, I.M., Clark, W.S., Byers, R.H., Ward, J.W., Darrow, W.W., Lemp, G.F., Hethcote, H.W., 1989. Statistical analysis of the stages of HIV infection using a Markov model. Stat. Med. 8, 831–843.
Louie, J.K., Hsu, L.C., Osmond, D.H., Katz, M.H., Schwarcz, S.K., 2002. Trends in causes of death among persons with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy, San Francisco, 1994–1998. J. Infect. Dis. 186, 1023–1027.
Lukashov, V.V., de Ronde, A., de Jong, J.J., Goudsmit, J., 2000. Epidemiology of HIV-1 and emerging problems. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 16, 463–466.
Lukashov, V.V., Goudsmit, J., 2002. Recent evolutionary history of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype B: reconstruction of epidemic onset based on sequence distances to the common ancestor. J. Mol. Evol. 54, 680–691.
Mocroft, A., Vella, S., Benfield, T.L., Chiesi, A., Miller, V., Gargalianos, P., d’Arminio Monforte, A., Yust, I., Bruun, J.N., Phillips, A.N., Lundgren, J.D., 1998. Changing patterns of mortality across Europe in patients infected with HIV-1. EuroSIDA Study Group. Lancet 352, 1725–1730.
Omrani, A.S., Pillay, D., 2000. Multi-drug resistant HIV-1. J. Infect. 41, 5–11.
Palella Jr., F.J., Delaney, K.M., Moorman, A.C., Loveless, M.O., Fuhrer, J., Satten, G.A., Aschman, D.J., Holmberg, S.D., 1998. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV outpatient study investigators. N. Engl. J. Med. 338, 853–860.
Phillips, A.N., Youle, M., Johnson, M., Loveday, C., 2001. Use of a stochastic model to develop understanding of the impact of different patterns of antiretroviral drug use on resistance development. AIDS 15, 2211–2220.
Pillay, D., Taylor, S., Richman, D.D., 2000. Incidence and impact of resistance against approved antiretroviral drugs. Rev. Med. Virol. 10, 231–253.
Pomerantz, R.J., 2001. Initiating antiretroviral therapy during HIV infection: confusion and clarity. JAMA 286, 2597–2599.
Porco, T.C., Martin, J., Page-Shafer, K., Cheng, A., Charlebois, E., Grant, R.M., Osmond, D., 2004. Decline in HIV infectivity following the introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 18, 81–88.
Porter, K., Pillay, D., Cane, P., Dean, G., Churchill, D., Baily, G., Drake, S., Fisher, M., 2001. Analysis of prevalence of HIV-1 drug resistance in primary infections in the United Kingdom. BMJ 322, 1087–1088.
Quinn, T.C., Wawer, M.J., Sewankambo, N., Serwadda, D., Li, C.J., Wabwire-Mangen, F., Meehan, M.O., Lutalo, T., Gray, R.H., 2000. Viral load and heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. N. Engl. J. Med. 342, 921–929.
Ramos, A., Hu, D.J., Nguyen, L., Phan, K.O., Vanichseni, S., Promadej, N., Choopanya, K., Callahan, M., Young, N.L., McNicholl, J., Mastro, T.D., Folks, T.M., Subbarao, S., 2002. Intersubtype human immunodeficiency virus type 1 superinfection following seroconversion to primary infection in two injection drug users. J. Virol. 76, 7444–7452.
Robbins, K.E., Lemey, P., Pybus, O.G., Jaffe, H.W., Youngpairoj, A.S., Brown, T.M., Salemi, M., Vandamme, A.M., Kalish, M.L., 2003. U.S. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 epidemic: date of origin, population history, and characterization of early strains. J. Virol. 77, 6359–6366.
Sattenspiel, L., Koopman, J., Simon, C., Jacquez, J.A., 1990. The effects of population structure on the spread of the HIV infection. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 82, 421–429.
Schwarcz, S., Kellogg, T., McFarland, W., Louie, B., Kohn, R., Busch, M., Katz, M., Bolan, G., Klausner, J., Weinstock, H., 2001. Differences in the temporal trends of HIV seroincidence and seroprevalence among sexually transmitted disease clinic patients, 1989–1998: application of the serologic testing algorithm for recent HIV seroconversion. Am. J. Epidemiol. 153, 925–934.
Shapiro, M.F., Morton, S.C., McCaffrey, D.F., Senterfitt, J.W., Fleishman, J.A., Perlman, J.F., Athey, L.A., Keesey, J.W., Goldman, D.P., Berry, S.H., Bozzette, S.A., 1999. Variations in the care of HIV-infected adults in the United States: results from the HIV Cost and Services Utilization Study. JAMA 281, 2305–2315.
Stolte, I.G., Dukers, N.H., de Wit, J.B., Fennema, J.S., Coutinho, R.A., 2001. Increase in sexually transmitted infections among homosexual men in Amsterdam in relation to HAART. Sex. Transm. Infect. 77, 184–186.
Tsui, R., Herring, B.L., Barbour, J.D., Grant, R.M., Bacchetti, P., Kral, A., Edlin, B.R., Delwart, E.L., 2004. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 superinfection was not detected following 215 years of injection drug user exposure. J. Virol. 78, 94–103.
Velasco-Hernandez, J.X., Gershengorn, H.B., Blower, S.M., 2002. Could widespread use of combination antiretroviral therapy eradicate HIV epidemics? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2, 487–493.
Volberding, P.A., 2003. HIV therapy in 2003: consensus and controversy. AIDS 17(Suppl. 1), S4–S11.
Wainberg, M.A., Friedland, G., 1998. Public health implications of antiretroviral therapy and HIV drug resistance. JAMA 279, 1977–1983.
Yerly, S., Vora, S., Rizzardi, P., Chave, J.P., Vernazza, P.L., Flepp, M., Telenti, A., Battegay, M., Veuthey, A.L., Bru, J.P., Rickenbach, M., Hirschel, B., Perrin, L., 2001. Acute HIV infection: impact on the spread of HIV and transmission of drug resistance. AIDS 15, 2287–2292.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In memory of Eran Karmon, who passed away on March 5, 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez, M.S., Grant, R.M., Porco, T.C. et al. A decrease in drug resistance levels of the HIV epidemic can be bad news. Bull. Math. Biol. 67, 761–782 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2004.10.001
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2004.10.001