Abstract
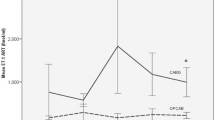
It is well established that endothelin-1 (ET-1) is a very potent mediator of vasoconstriction that leads to microcirculatory disturbances. The aim of the study was to evaluate the effect of a selective endothelin A receptor antagonist on severe ischemia/reperfusion injury in a pig model. Fourteen pigs were subjected to 120 minutes of complete vascular exclusion of the liver with a passive bypass. The animals were randomized into two groups: a control group, which was given isotonic saline solution, and a therapy group, which received the selective endothelin A receptor antagonist BSF 208075 at the beginning of reperfusion. On postoperative days 4 and 7, animals were relaparotomized to obtain tissue specimens. Blood monitoring included aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), glutamate dehydrogenase (GLDH), alkaline phosphatase, and ET-1. Partial oxygen tension (ptiO2) was measured by a Clarke-type electrode and blood flow by laser Doppler. A semiquantitative scoring index was used for assessment of histologic injury and for immunohistochemical analysis of ET-1. Treatment with the endothelin A receptor antagonist significantly reduced the severity of the ischemia/reperfusion injury, as evidenced by lower levels of AST, ALT, and GLDH. The dramatic increase in plasma ET-1 in the therapy group is clear evidence of effective receptor blockade. Analysis of PtiO2 and blood flow revealed a significant improvement in capillary perfusion and blood flow in the treated group and was associated with relevant reduction of tissue injury. In summary, in the control group we observed serious microcirculatory disturbances and severe histologic damage in the liver after reperfusion. Treatment with a selective endothelin A receptor antagonist attenuated the ischemia/reperfusion injury in a porcine model of severe ischemia/reperfusion, as demonstrated by improved microcirculation, a reduction in histologic damage, and an decrease in liver enzymes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bismuth H, Castaing D, Garden OJ. Major hepatic resection under total vascular exclusion. Ann Surg 1989;210:13–19.
Uhlmann D, Witzigmann H, Senninger N, et al. Protective role of an endothelin-converting enzyme inhibitor (FR901533) in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Microvasc Res 2001; 62:43–54.
Masuko H, Jin MB, Horiuchi H, et al. Protective effect of agiotensin II type I receptor antagonist, CV-11974, on ischemia and reperfusion injury of the liver. Transplantation 2001;71:1034–1039.
Nakamura N, Hamada N, Murata R, et al. Contribution of serotonin to liver injury following canine small-intestinal ischemia and reperfusion. J Surg Res 2001;99:17–24.
Scommotau S, Uhlmann D, Loffler BM, et al. Involvement of endothelin/nitric oxide balance in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Langenbecks Arch Surg 1999;384:65–70.
Nakamura S, Nishiyama R, Serizawa A, et al. Hepatic release of endothelin-1 after warm ischemia. Reperfusion injury and its hemodynamic effect. Transplantation 1995;59:679–684.
Goto M, Takei Y, Kawano S, et al. Endothelin-1 is involved in the pathogenesis of ischemia/reperfusion liver injury by hepatic microcirculatory disturbances. Hepatology 1994;19:675–681.
Kawamura E, Yamanaka N, Okamoto E, et al. Response of plasma and tissue endothelin-1 to liver ischemia and its implication in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Hepatology 1995; 21:1138–1143.
Okumura S, Takei Y, Kawano S, et al. Vasoactive effect of endothelin-1 on rat liver in vivo. Hepatology 1994;19:155–161.
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S, et al. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature 1988;332:411–415.
Clozel M, Gray GA, Breu V, et al. The endothelin ETB receptor mediates both vasodilation and vasoconstriction in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992;186:867–873.
Davenport AP. International Union of Pharmacology. XXIX. Update on endothelin receptor nomenclature. Pharmacol Rev 2002;54:219–226.
Zhang JX, Pegoli W Jr, Clemens MG. Endothelin-1 induces direct constriction of hepatic sinusoids. Am J Physiol 1994;266:G624-G632.
Imakita M, Yamanaka N, Kuroda N, et al. Effects of the endothelin receptor antagonist TAK-044 on hepatocyte element alterations in the ischemic-reperfused liver in Beagle dogs. J Hepatol 1998;28:204–211.
Uhlmann D, Uhlmann S, Spiegel HU. Important role for endothelins in acute hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Invest Surg 2001;14:31–45.
Koeppel TA, Kraus T, Thies JC, et al. Effects of mixed endothelin A and endothelin B-receptor antagonist (Ro-47-0203) on hepatic microcirculation after warm ischemia. Dig Dis Sci 1997;42:1316–1321.
Lopez Farre A, Riesco A, Espinosa G, et al. Effect of endothelin-1 on neutrophil adhesion to endothelial cells and perfused heart. Circulation 1993;88:1166–1171.
Foitzik T, Faulhaber J, Hotz HG, et al. Endothelin receptor blockade improves fluid sequestration, pancreatic capillary blood flow, and survival in severe experimental pancreatitis. Ann Surg 1998;228:670–675.
Ota T, Hirai R, Urakami A, et al. Endothelin-1 levels in portal venous blood in relation to hepatic tissue microcirculation disturbance and hepatic cell injury after ischemia/ reperfusion. Surg Today 1997;27:313–320.
Battistini B, Forget MA, Laight D. Potential roles for endothelins in systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a particular relationship to cytokines. Shock 1996;5:167–183.
Rockey DC, Fouassier L, Chung JJ, et al. Cellular localization of endothelin-1 and increased production in liver injury in the rat: potential for autocrine and paracrine effects on stellate cells. Hepatology 1998;27:472–480.
Ruetten H, Thiemermann C. Endothelin-1 stimulates the biosynthesis of tumour necrosis factor in macrophages: ETreceptors, signal transduction and inhibition by dexamethasone. J Physiol Pharmacol 1997;48:675–688.
Post S, Rentsch M, Gonzalez AP, et al. Importance of the first minutes of reperfusion in hepatic preservation injury. Transplant Proc 1995;27:727–728.
Wilhelm SM, Stowe NT, Robinson AV, et al. The use of the endothelin receptor antagonist, tezosentan, before or after renal ischemia protects renal function. Transplantation 2001;71:211–216.
Katsuramaki T, Kimura H, Isobe U, et al. Changes in hepatic venous oxygen saturation in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in pigs. Surg Today 2000;30:343–351.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Else Kröner-Fresenius Stiftung and by a junior research fund of the Medical Faculty at the University of Leipzig.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uhlmann, D., Armann, B., Gaebel, G. et al. Endothelin a receptor blockade reduces hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury after warm ischemia in a pig model. J Gastrointest Surg 7, 331–339 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(02)00417-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(02)00417-1