Abstract
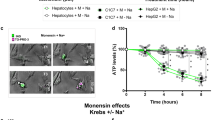
Although hypoosmotic stress-induced cell swelling activates phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, its impact on the downstream signal protein kinase B and cell growth is unknown. Activator protein-1 is in part phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase dependent, and is important in proliferation. We hypothesized that cell swelling modulates proliferation in HepG2 cells via the protein kinase B-dependent activation of activator protein-1. HepG2 cells pretreated with or without LY294002 were exposed for up to 30 minutes to hypoosmotic medium (160 mOsm/L). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (1.4 nmol/L) or normoosmolar medium (270 mOsm/L) served as positive and negative controls, respectively. Western immunoblots measured cytoplasmic phosphorylated and total protein kinase B. Electromobility shift assays measured nuclear activator protein-1. Methylene blue assays measured cell proliferation at 24, 48, and 72 hours after stimulation. Hypoosmotic stress phosphorylated protein kinase B by 10 minutes. Subsequently, hypoosmotic exposure stimulated activator protein-1 by 30 minutes. Pulse exposure to hypoosmotic stress potentiated HepG2 proliferation by 72 hours as compared to both negative controls and LY-inhibited cells (n = 4 per group, P = 0.009 and P = 0.004, respectively; P <0.001 analysis of variance. All three activation events were abolished with LY294002 pretreatment. In HepG2 cells, hypoosmotic stress-induced swelling stimulates proliferation via protein kinase B-mediated activation of activator protein-1. These data delineate a possible mechanism linking changes in cell volume to growth in human liver cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meyers WC. Neoplasms of the liver. In Sabiston D, ed. Textbook of Surgery, 15th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1997, pp 1068–1083.
Klohn PC, Bitsch A, Neumann HG. Mitochondrial permeability transition is altered in early stages of carcinogenesis of 2-acetylaminofluorene. Carcinogenesis 1998;19:1185–1190.
Jack EM, Bentley P, Bieri F, Muakkassah-Kelly SF, Staubli W, Suter J, Waechter F, Cruz-Orive LM. Increase in hepatocyte and nuclear volume and decrease in the population of binucleated cells in preneoplastic foci of rat liver: A stereological study using the nucleator method. Hepatology 1990;11:286–297.
Khasawinah AM, Grutsch JE. Chlordane: Thirty-month tumorigenicity and chronic toxicity test in rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 1989;10:95–109.
Yoshida M, Miyajima K, Shiraki K, Ando J, Kudoh K, Nakae D, Takahashi M, Maekawa A. Hepatotoxicity and consequently increased cell proliferation are associated with flumequine hepatocarcinogenesis in mice. Cancer Lett 1999;141:99–107.
Sparks RL, Pool TB, Smith NK, Cameron IL. Effects of amiloride on tumor growth and intracellular element content of tumor cells in vivo. Cancer Res 1983;43:73–77.
Noe B, Schliess F, Wettstein M, Heinrich S, Haussinger D. Regulation of taurocholate excretion by a hypo-osmolarity-activated signal transduction pathway in rat liver. Gastroenterology 1996;110:858–865.
Finkenzeller G, Newsome W, Lang F, Haussinger D. Increase of c-jun mRNA upon hypoosmotic cell swelling of rat hepatoma cells. FEBS Lett 1994;34O:163–166.
Kim RD, Darling CE, Cerwenka H, Chari RS. Hypoosmotic stress activates p38, ERK 1 and 2, and SAPK/JNK in rat hepatocytes. J Surg Res 2000;90:58–66.
Krasilnikov MA. Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase dependent pathways: The role in control of cell growth, survival, and malignant transformation. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2000;65:59–67.
Craddock BL, Orchiston EA, Hinton HJ, Welham MJ. Dissociation of apoptosis from proliferation, protein kinase B activation, and BAD phosphorylation in interleukin-3-mediated phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling. J Biol Chem 1999;274:10633–10640.
Duan C, Bauchat JR, Hsieh T. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is required for insulin-like growth factor-I-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Circ Res 2000;86:15–23.
Le F, Stomski F, Woodcock JM, Lopez AF, Gonda TJ. The role of disulfide-linked dimerization in interleukin-3 receptor signaling and biological activity. J Biol Chem 2000;275:5124–5130.
Biggs WH, Meisenhelder J, Hunter T, Cavenee WK, Arden KC. Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999;96:7421–7426.
Walker TR, Moore SM, Lawson MF, Panettieri RAJ, Chil-vers ER. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB and thrombin activate phosphoinositide 3-kinase and protein kinase B: Role in mediating airway smooth muscle proliferation. Mol Pharmacol 1998;54:1007–1015.
Paramio JM, Navarro M, Segrelles C, Gomez-Casero E, Jor-cano JL. PTEN tumour suppressor is linked to the cell cycle control through the retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene 1999; 18:7462–7468.
Westwick JK, Weitzel C, Leffert HL, Brenner DA. Activation of Jun kinase is an early event in hepatic regeneration. J Clin Invest 1995;95:803–810.
Dong Z, Huang C, Ma WY. PI-3 kinase in signal transduction, cell transformation, and as a target for chemoprevention of cancer. Anticancer Res 1999;19:3743–3747.
Reddy SA, Huang JH, Liao WS. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in interleukin 1 signaling. Physical interaction with the interleukin 1 receptor and requirement in NFкB and AP-1 activation. J Biol Chem 1997;272:29167–29173.
Sadoshima J, Qiu Z, Morgan JP, Izumo S. Tyrosine kinase activation is an immediate and essential step in hypotonie cell swelling-induced ERK activation and c-fos gene expression in cardiac myocytes. EMBO J 1996;15:5535–5546.
Dignam JD, Lehovitz RM, Roeder RG. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res 1983;11:1475–1489.
Sen R, Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell 1986;46:705–716.
Oliver MH, Harrison NK, Bishop JE, Cole PJ, Laurent GJ. A rapid and convenient assay for counting cells cultured in microwell plates: Application for assessment of growth factors. J Cell Sci 1989;92:513–518.
Krause U, Rider MH, Hue L. Protein kinase signaling pathway triggered by cell swelling and involved in the activation of glycogen synthase and acetyl-CoA carboxylasc in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 1996;271:16668–16673.
Dixon M, Agius L, Yeaman SJ, Day CP. Inhibition of rat hepatocyte proliferation by transforming growth factor beta and glucagon is associated with inhibition of ERK2 and p70 S6 kinase. Hepatology 1999;29:1418–1424.
Michalke M, Cariers A, Schliess F, Haussinger D. Hypoosmolarity influences the activity of transcription factor NF-kB in rat II4II3 hepatoma cells. FEBS Lett 2000;465:64–68.
Brenner DA. Signal transduction during liver regeneration. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1998;13(Suppl):S93-S95.
Feingold KR, Grunfeld C. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates hepatic lipogenesis in the rat in vivo. J Clin Invest 1987; 80:184490.
Gao C, Jokerst R, Gondipalli P, Cai SR, Kennedy S, Flye MW, Ponder KP. Lipopolysaccharidc potentiates the effect of hepatocyte growth factor on hepatocyte replication in rats by augmenting AP-1 activity. Hepatology 1999;30:1405–1416.
Qian D, Brosnan JT. Administration of Escherichia coli endotoxin to rat increases liver mass and hepatocyte volume in vivo. Biochem J 1996;313:479–486.
Eder AM, Dominiez L, Franke TF, Ashwell JD. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulation of T cell receptor-mediated interleukin-2 gene expression in normal T cells. J Biol Chem 1998;273:28025–28O31.
Tacchini L, Dansi P, Matteucci E, Desiderio MA. Hepatocyte growth factor signal coupling to various transcription factors depends on triggering of Met receptor and protein kinase transducers in human hepatoma cells IIepG2. Exp Cell Res 2000;256:272–281.
Freeman TL, Ngo HQ, Mailliard ME. Inhibition of system A amino acid transport and hepatocyte proliferation following partial hepatectomy in the rat. Hepatology 1999;30:437–444.
Dartsch PC, Ritter M, Gschwentner M, Lang HJ, Lang F. Effects of calcium channel blockers on NIH 3T3 fibroblasts expressing the Ha-ras oncogene. EurJ Cell Biol 1995;67:372–378.
Settmacher U, Volk HD, von Baehr R, Wolff II, Jahn S. In vitro stimulation of human fetal lymphocytes by mitogens and interleukins. Immunol Lett 1993;35:147–152.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, R.D., Roth, T.P., Darling, C.E. et al. Hypoosmotic stress stimulates growth in HepG2 cells via protein kinase B-dependent activation of activator protein-1. J Gastrointest Surg 5, 546–555 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(01)80094-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(01)80094-9