Abstract
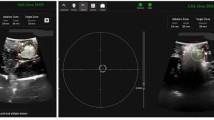
Radiofrequency ablation requires accurate probe placement using ultrasound guidance. The purpose of this study was to develop an in vivo tumor-mimic model for learning open and laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation. Tumor-mimics were created in ex vivo porcine livers by injecting a mixture of 3% agarose, 3% cellulose, 7% glycerol, and 0.05% methylene blue, which formed 1 cm hyperechoic, discrete lesions on ultrasound. Open and laparoscopic (using a box-trainer) ablation techniques were practiced. In vivo experiments were then conducted in 10 pigs. Three tumor-mimics were created in each animal using a laparoscopic approach. Lesions were characterized sonographically, ablated using an open (n = 5) or laparoscopic (n = 5) approach, and examined pathologically. An ablation in normal liver tissue was performed as a control. Tissue impedance was recorded. Target creation took 81 minutes per animal and 96% of injections were successful. Tissue impedance (48.8 ±5.8 vs. 49.6 ±5.4) and ablation size (25.1 ±3.4 vs. 24.3 ±5.1) were not significantly different for controls (n = 8) and tumor-mimics (n = 26), respectively. One animal died of a pulmonary embolism following injection of agarose into a hepatic vein. The agarose-based tissue-mimic creates realistic sonographic targets for learning ultrasound-guided open and laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation in an in vivo model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curley SA, Izzo F, Delrio P, Ellis LM, Granchi J, Vallone P, Fiore F, Pignata S, Daniele B, Cremona F. Radiofrequency ab- lation of unresectable primary and metastatic hepatic malig- nancies: Results in 123 patients. Ann Surg 1999;230:l-8.
Jiao LR, Hansen PD, Havilk R, Mitry RR, Pignatelli M, Habib N. Clinical short-term results of radiofrequency abla- tion in primary and secondary liver tumors. Am J Surg 1999;177:303–306.
Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F, Di Stasi M, Quaretti P, Rago M, Zangrandi A, Andreola S, Silverman D, Buscarini L. Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an ex- pandable RF needle electrode. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998; 170:1015–1022.
Solbiati L, Goldberg SN, Ierace T, Dellanoce M, Livraghi T, Gazelle GS. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatic metastases: Postprocedural assessment with a US microbubble contrast agent—early experience. Radiology 1999;211:643–649.
Scudamore CH, Lee SI, Patterson EJ, Buczkowski AK, July LV, Chung SC, Buckley AR, Ho SGF, Owen DA. Radiofre- quency ablation followed by resection of malignant liver tu- mors. AmJ Surg 1999;177:411–417.
Siperstein AE, Rogers SJ, Hansen PD, Gitomirsky A. Lapa- roscopic thermal ablation of hepatic neuroendocrine tumor metastases. Surgery 1997:122:1147–1155.
Pearson AS, Izzo F, Fleming RYD, Ellis LM, Delrio P, Roh MS, Granchi J, Curley SA. Intraoperative radiofrequency ab- lation or cryoablarion for hepatic malignancies. Am J Surg 1999;178:592–599.
Curley SA, Davidson BS, Fleming RY, Izzo F, Stephens LC, Tinkey P, Cromeens D. Laparoscopically guided bipolar ra- diofrequency ablation of areas of porcine liver. Surg Endosc 1997;ll:729–733.
Mahvi DM, Lee FT. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatic ma- lignancies: Is heat better than cold? Ann Surg 1999;230:9–11.
Falcone RA, Fegelman EJ, Nussbaum MS, Brown DL, Bebbe TM, Merhar GL, Johannigman JA, Luchette FA, Davis KHJM. A prospective comparison of laparoscopic ultrasound vs intraoperative cholangiogram during laparoscopic chole- cystectomy. Surg Endosc 1999;13:784–788.
John TG, GreigJD, Crosbie JL, Miles WFA, Garden OJ. Su- perior staging of liver tumors with laparoscopy and laparo- scopic ultrasound. Ann Surg 1994;6:711–719.
Rickey DW, Picot PA, Christopher DA, Fenster A. A wall-less vessel phantom for Doppler ultrasound studies. Ultrasound Med Biol 1995;21:1163–1176.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding was provided by the Southwestern Center for Minimally Invasive Surgery as supported in part by an educational grant from United States Surgical—A Division of Tyco Healthcare Group.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, D.J., Young, W.N., Watumull, L.M. et al. Development of an in vivo tumor-mimic model for learning radiofrequency ablation. J Gastrointest Surg 4, 620–625 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(00)80112-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(00)80112-2