Abstract
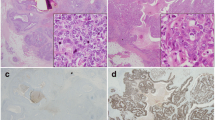
The murine double minutes 2 (MDM2) oncoprotein inhibits p53-mediated tumor suppression. MDM2 has been shown to be overexpressed in sarcomas and more recently was implicated in the pathogenesis of carcinomas. The purpose of this study was to determine the expression pattern of MDM2 in adenomas and colorectal adenocarcinomas and decide whether there is a correlation between MDM2 and p53 protein status. Paraffin-embedded tissues from 52 colorectal cancer (CRC) specimens and their adjacent normal tissue (N-CRC) were studied. In addition, 56 sporadic adenomas were investigated for the immunohistochemical expression of MDM2 and p53 proteins. Immunoreactivity of p53 indicating p53 gene mutation (p53 +) was significantly higher in CRC (44%) compared to adenomas (23.2%) (P <0.01). None of the N-CRC specimens expressed the immunoreactive p53 protein. MDM2 overexpression (MDM2+) was similar in adenomas (30.3%) and CRC (25%), but only 2 (3.8%) of 52 N-CRC specimens showed overexpression of MDM2. In most cases MDM2 expression was associated with negative p53 expression (wild-type p53) in both adenomas (r = 0.59, P <0.001) and CRC (r = 0.69, P <0.0001). No correlation was found between MDM2, p53 expression, and either the histologic grade, nodal stage or morphology of the tumors. There is greater p53 mutation in CRC compared to adenomas and N-CRC. The data indicate that MDM2 is overexpressed in CRC and is significantly associated with wild-type p53 compared to N-CRC specimens from the same patient. The MDM2 expression pattern is similar in adenomas and CRC, which may suggest that MDM2 overexpression is an early event in the progression of CRC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts and Figures, 1996. Atlanta: American Cancer Society (ACS), 1996. Publication No. 5008-96.
Greenberger NJ. Updates in gastroenterology. Ann Intern Med 1998;129:309–316.
Ransohoff DF. Colorectal cancer in digestive disease in the United States: Epidemiology and impact. In Everhart JE, ed. 1994, NIH Publication No. 94-1447 pp 207–223.
Boring CC, Squire TS, Tong T, Montgomery S. Cancer Sta- tistics, 1994. CA Cancer J Clin 1994;44:7–26.
Agency for Health Care Policy and Research (AHCPR). Re- search Activities 1997;200:15–18.
Fearon ER, Vogelstein B. A genetic model of colorectal tu- morigenesis. Cell 1990;61:759–767.
Wang XW, Harris CC. p53 tumor-suppressor gene: Clues to molecular carcinogenesis. J Cell Physiol 1997;173:247–255.
Cahilly-Snyder L, Yang-Feng T, Franke U, George DL. Mo- lecular analysis and chromosomal mapping of amplified genes isolated from transformed mouse 3T3 cell line. Somat Cell Mol Genet 1987;13:235–244.
Valassiadou KE, Stefanaki K, Tzardi M, Datseris G, Geor-goulias V, Mellissas J, Tsiftsis DD, Delides G, Kana Varos P. Immunohistochemical expression of p53, mdm2, and wafl/p21 proteins in colorectal adenocarcinomas. Antieancer Res 1997;17:2571–2576.
Hao XP, Gunther T, Roessner A, Price AB, Talbott IC: Ex- pression of mdm2 and p53 in epithelial neoplasms of the colo- rectum. Mol Pathol 1998;51:26–29.
Genta RM, Bleyzer I, Cate TR, Tandon AK, Yoffe B. In situ hybridization and immunohistochemical analysis of cy- tomegalovirus-associated ileal perforation. Gastroenterology 1993;104:1822–1827.
Oliner JD, Kanzler KW, Melzer PS, George D, Vogelstein B. Amplification of gene encoding a p53 associated protein in hu- man sarcomas. Nature 1992;358:80–83.
Merup M, Juliusson G, Xu XH, Jasson M, Stellan B, Rasool O, Roijer E, Stenman G, Gahrton G, Einhorn S. Amplification of multiple regions of chromosome 12, including 12ql3-15, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Eur J Hematol 1997;58:174–180.
Nilbert M, Rydholm A, Millen H, Mitelman F, Mandahl N. MDM2 gene amplification correlates with ring chromosomes in soft tissue tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1994;9:261–265.
Ladanyi M, Lewis R, Rhanwar S, Gerald W, Huvos A, Healey J. MDM2 and CDK4 gene amplification in Ewing’s sarcoma. J Pathol 1995;53:16–18.
Nakayama T, Tbguchida J, Wadayama B, Kanoe H, Kotoura Y, Sasaki M. MDM2 gene amplification in bone and soft- tissue tumors: Association with tumor progression in differ- entiated adipose-tissue tumors. Int J Cancer 1995;64:342–346.
Giannikaki E, Kouvidou C, Tzardi M, Stefanaki K, Koutsoubi K, Gregoriou M, Zois E, Kakolyris S. p53 protein expression in breast carcinoma. Cooperative study with wild type p53 induced proteins MDM2 and p21/WAFl. Anticancer Res 1997;17:2123–2127.
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AL. The mdm2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell 1992;69:1237–1245.
Piette J, Neel H, Marechal V. Mdm2: Keeping p53 under con- trol. Oncogene 1997;15:1001–1010.
Higashyama M, Doi O, Ykokouchi H, Kasugal T, Ishiguro S, Takami K, Nakayama T, Nishisho I. MDM2 gene amplifica- tion and expression in non-small cell lung cancer: Immuno- histochemical expression of its protein is a favorable prognos- tic marker in patients without p53 accumulation. Br J Cancer 1997;75:1302–1308.
Drager BJ, Kushima M, Goebell P, Jax TW, Gerharz CD, Bultel H, Schulz WA, Ebert T, Ackermann R. P53 and MDM2 in the development and progression of bladder can- cer. Eur Urol 1997;32:487–493.
Barnes DM, Hanby AM, Gillett CE, Mohamed S, Hogson S, Bobrow LG, Leigh IM, Purkis T, MacGeoch C, Spurr- NK, Bartek J, Vojtesek B, Picksley SM, Lane DP. Abnormal ex- pression of wild type p53 protein in normal cells of cancer family patient. Lancet 1992;340:259–263.
Grimm M-O, Jurgens B, Schulz WA, Makri D, Schmitz-Drager BJ. Inactivation of tumor suppressor genes and dereg- ulation of the c-myc gene in urothelial cancer cell lines. Urol Res 1995;23:293–300.
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M. Mdm2 promotes rapid degradation of p53. Nature 1997;387:296–299.
Barak Y, Juven T, Haffner R, Oren M. MDM2 expression is induced by wild type p53 activity. EMBO J 1993;12:461–468.
Juven T, Barak Y, Zauberman A, George D, Oren M. Wild type p53 can mediate sequence specific transactivation of an internal promoter within the mdm2 gene. Oncogene 1993;8:3411–3416.
Khatib Z, Matsushime H, Valentine M, Shapiro D, Sherr C, Look A. Coamplification of the CDK4 gene with MDM2 and GL1 in human sarcomas. Cancer Res 1993;53:5535–5541.
DcCaprio JA, Furukawa YK, Ajchenbaum F, Griffin JF, Livingstone DM. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene produce becomes phosphorylated in multistages during cell cycle entry and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1992;89:1795–1798.
Zhang Y, Xiong Y, Yarbrough Y. ARF-promotes MDM2 degradation and stabilizes p53: ARF-locus deletion impairs both RB and p53 tumor suppressor pathways. Cell 1998;92:725–734.
Palmero I, Pantoja C, Serrano M. P19ARF links the tumour suppressor p53 to Ras. Nature 1998;395:125–126.
Pomerantz J, Schreiber-Agus N, Liegeois NJ, Silverman A, Alland L, Chin L, Potes J, Chen K, Orlow I, Lee HW, Cordon-Cardo C, DePinho RA. The INK4a tumor sup- pressor gene product, pl9 Arf, interacts with MDM2 and neutralizes MDM2’s inhibition of p53. Cell 1998; 92:713–723.
Bates S, Phillips AC, Clark P, Stott F, Peters G, Ludwig R, Vousden K. P14ARFlinks the rumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature 1998;395:124–125.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from The Methodist Hospital Foundation, Houston, Tex.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Fattah, G., Yoffe, B., Krishnan, B. et al. MDM2/p53 protein expression in the development of colorectal adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg 4, 109–114 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(00)80041-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(00)80041-4