Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to assess whether, after anterior myocardial infarction, ST segment changes during percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) of the left anterior descending coronary artery correlated with the amount of ischemic myocardium in the area at risk, measured with 99mTc-labeled sestamibi single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) during ballon inflation.
Methods and Results
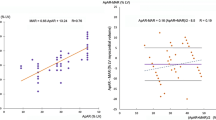
Quantitative continuous monitoring of the ST segment was performed during PTCA of the left anterior descending coronary artery in 11 patients, and corresponding SPECT imaging was compared with a rest acquisition performed before PTCA. SPECT was quantified by a bull’s-eye analysis according to main criteria: (1) the planimetered defect size during PTCA as an indicator of the size of the area at risk, (2) the change in the pathologic/normal area count ratio in the area at risk as an index of the severity of ischemia, and (3) the difference between the size of the defect during PTCA and at baseline. ST segment changes were correlated to the variation in pathologic/normal area count ratio (19%±14%; r=0.61; p<0.05) but not to the sizes of the scintigraphic defects.
Conclusion
ST segment changes induced by occlusion of the infarct-related coronary artery during PTCA are related mostly to the severity of ischemia rather than to the size of the area at risk.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lowe JE, Reimer KA, Jennings RB. Experimental infarct size as a function of the amount of myocardium at risk. Am J Pathol 1978;90:363–79.
Haronian HL, Remetz MS, Sinusas AJ, Baron JM, Miller HI, Cleman MW, et al. Myocardial risk area defined by Tc 99m sestamibi imaging during percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty: comparison with coronary angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993; 22:1033–43.
Gibson RS, Watson DD, Craddock GB, Crampton RS, Kaiser DL, Denny MJ, et al. Prediction of cardiac events after uncomplicated myocardial infarction: a prospective study comparing predischarge exercise thallium 201 scintigraphy and coronary angiography. Circulation 1983;68:321–36.
Leppo JA, O’Brien J, Rothendler JA, Getchell JD, Lee VW. Dipyridamole-thallium-201 scintigraphy in the prediction of future cardiac events after acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1984;310:1014–8.
Feiring AJ, Johnson MR, Kioschos JM, Kirchner PT, Marcus ML, White CW. The importance of the determination of the myocardial area at risk in the evaluation of the outcome of acute myocardial infarction in patients. Circulation 1987;75:980–7.
Wackers FJ, Gibbons RJ, Verani MS, Kayden DS, Pellika PA, Behrenbeck T, et al. Serial quantitative planar technetium-99m isonitrile imaging in acute myocardial infarction: efficacy for noninvasive assessment of thrombolytic therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 1989; 14:861–73.
Huber KC, Bresnahan JF, Bresnahan DR, Pellikka PA, Behrenbeck T, Gibbons RJ. Measurement of myocardium at risk by technetium 99m sestamibi: correlation with coronary angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992; 19:67–73.
Näslund U, Häggmark S, Johnasson G, Reiz S. Ischaemia and reperfusion induced transient QRS vector changes: relationship to size of the ischaemic territory. Cardiovasc Res 1993;27:327–33.
Margonato A, Chierchia SL, Xuereb RG, Xuereb M, Fragasso G, Cappelletti A, et al. Specificity and sensitivity of exercise-induced ST segment elevation for detection of residual viability: comparison with fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995; 25:1032–8.
Steg PG, Faraggi M, Himbert D, Juliard JM, Cohen-Solal A, Lebtahi R, et al. Comparison using dynamic vectorcardiography and MIBI-SPECT of ST-segment changes and myocardial MIBI uptake during percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty of the left anterior descending coronary artery. Am J Cardiol 1995; 75:998–1002.
Dellborg M, Riha M, Swedberg K. Dynamic QRS and ST-segment changes in acute myocardial infarction monitored by continuous on-line vectorcardiography. J Electrocardiol 1990;23(suppl):11–9.
Frank E. Accurate, clinically practical system for spatial vector-cardiography. Circulation 1956;13:737–44.
Goris ML, Boudier S, Briandet PA. Two dimensional mapping of three dimensional SPECT data: a preliminary step to the quantitation of thallium myocardial perfusion single photon emission tomography. Am J Physiol Imaging 1987;2:176–80.
Goris ML, Bretille J, Askienazy S, Purcell GP, Savelli V. Validation of diagnostic procedures on stratified populations: application on the quantification of thallium myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Am J Physiol Imaging 1989;4:11–5.
Dilsizian V, Rocco TP, Strauss HW, Boucher CA. Technetium-99m isonitrile myocardial uptake at rest, I: relation to severity of coronary artery stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 1989;14:1673–7.
Beanlands RSB, Dawood F, Wen W-H, McLaughlin PR, Butany J, D’Amati G, et al. Are the kinetics of technetium-99m methoxyisobutyl isonitrile affected by cell metabolism and viability? Circulation 1990;82:1802–14.
Freeman I, Grunwald AM, Hoory S, Bodenheimer MM. Effect of coronary occlusion and myocardial viability on myocardial activity of technetium-99m-sestamibi. J Nucl Med 1991;32:292–8.
Pfisterer M, Müller-Brand J, Spring P, Bassignana V, Kiowski W. Assessment of the extent of jeoparized myocardium during acute coronary occlusion followed by reperfusion imaging in man using technetium-99m isonitrile imaging. Am Heart J 1991;122:7–12.
Borges-Neto S, Puma J, Jones RH, Sketch MH, Stack R, Hanson MW, et al. Myocardial perfusion and ventricular function measurements during total coronary occlusion in humans: a comparison with rest and exercise radionuclide studies. Circulation 1994; 89:278–84.
Gallik DM, Obermueller SD, Swarna US, Guidry GW, Mahmarain JJ, Verani MS. Simultaneous assessment of myocardial perfusion and left ventricular function during transient coronary occlusion. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995;25–7:1529–38.
Akiyama T, Hodges M, Biddle TL, Zawrotny B, Vangellow C. Measurement of ST segment elevation in acute myocardial infarction in man: comparison of a precordial mapping technique and the Frank vector system. Am J Cardiol 1975;36:155–62.
Berry C, Zalewski A, Kovach R, Savage M, Goldberg S. Surface electrocardiogram in the detection of transmural myocardial ischemia during coronary artery occlusion. Am J Cardiol 1989;63:21–6.
Dellborg M, Emanuelsson H, Riha M, Swedberg K. Dynamic QRS complex and ST-segment monitoring by continuous vectorcar-diography during coronary angioplasty. Coron Artery Dis 1991;2:43–52.
Wagner NB, Sevilla DC, Krucoff MW, Lee KL, Pieper KS, Kent KM, et al. Transient alterations of the QRS complex and ST segment during percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty of the left anterior descending artery. Am J Cardiol 1988;62:1038–42.
Krucoff M. Identification of high-risk patients with silent myocardial ischemia after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty by multilead monitoring. Am J Cardiol 1988;61:29F-34F.
Cohen M, Scharpf S, Rentrop P. Prospective analysis of electrocardiographic variables as markers for extent and location of acute wall motion abnormalities observed during coronary angioplasty in human subjects. J Am Coll Cardiol 1987;10:17–24.
Margonato A, Ballarotto C, Bonetti F, Cappelletti A, Sciammarella M, Cianflone D, et al. Assessment of residual tissue viability by exercise testing in recent myocardial infarction: comparison of the electrocardiogram and myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992; 19:948–52.
Koning R, Cribier A, Korsatz L, Stix G, Chan C, Eltchaninoff H, et al. Progressive decrease in myocardial ischemia assessed by intracoronary electrocardiogram during successive and prolonged coronary occlusions in angioplasty. Am Heart J 1993;125:56–61.
Taylor AJ, Sackett MC, Beller GA. The degree of ST-segment depression on symptom limited exercise testing: relation to the myocardial ischemic burden as determined by thallium 201 scintigraphy. Am J Cardiol 1995;75:228–31.
Cuocolo A, Pace L, Ricciardelli B, Chiariello M, Trimarco B, Salvatore M. Identification of viable myocardium in patients with chronic artery disease: comparison of thallium 201 scintigraphy with reinjection and technetium 99m-methoxyisobutylisonitrile. J Nucl Med 1992;33:501–11.
Dilsizian V, Arrighi JA, Diodati JG, Quyyumi AA, Alavi K, Bacharach SL, et al. Myocardial viability in patients with chronic coronary artery disease: comparison of 99mTc-sestamibi with thallium reinjection and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose. Circulation 1994;89:578–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faraggi, M., Steg, P.G., Francois, D. et al. Residual area at risk after anterior myocardial infarction: Are ST segment changes during coronary angioplasty a reliable indicator? A comparison with technetium 99m-labeled sestamibi single-photon emission computed tomography. J Nucl Cardiol 4, 11–17 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1071-3581(97)90044-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1071-3581(97)90044-1