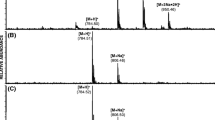
Abstract
Structural characterization of glycosphingolipids as their lithiated adducts using low-energy collisional-activated dissociation (CAD) tandem mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization (ESI) is described. The tandem mass spectra contain abundant fragment ions reflecting the long chain base (LCB), fatty acid, and the sugar constituent of the molecule and permit unequivocal identification of cerebrosides, di-, trihexosyl ceramides and globosides. The major fragmentation pathways arise from loss of the sugar moiety to yield a lithiated ceramide ion, which undergoes further fragmentation to form multiple fragment ions that confirm the structures of the fatty acid and LCB. The mechanisms for the ion formation and the possible configuration of the fragment ions, resulting from CAD of the lithiated molecular ions ([M + Li]+) of monoglycosylceramides are proposed. The mechanisms were supported by CAD and source CAD tandem mass spectra of various cerebrosides and of their analogous molecules prepared by H-D exchange. Constant neutral loss and precursor ion scannings to identify galactosylceramides with sphingosine or sphinganine LCB subclasses, and with specificN-2-hydroxyl fatty acid subclass in mixtures are also demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hakomori, S.; Igarashi, Y. Gangliosides and glycosphingolipids as modulators of cell growth, adhesion, and transmembrane signaling.Adv. Lipid Res. 1993,25, 147–162.
Yamashita, T.; Wada, R.; Sasaki, T.; Deng, C.; Bierfreund, U.; Sandhoff, K.; Proia, R. L. A vital role for glycosphingolipid synthesis during development and differentiation.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999,96, 9142–9147.
Fenderson, B. A.; Eddy, E. M.; Hakomori, S. Glycoconjugate expression during embryogenesis and its biological significance.Bioessays 1990,12, 173–179.
Schneider, J. S. GM1 ganglioside in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 1998,845, 363–373.
Schneider, J. S.; Pope, A.; Simpson, K.; Taggart, J.; Smith, M. G.; DiStefano, L. Recovery from experimental parkinsonism in primates with GM1 ganglioside treatment.Science 1992,256, 843–846.
Di Gregorio, F.; Ferrari, G.; Marini, P.; Siliprandi, R.; Gorio, A. The influence of gangliosides on neurite growth and regeneration.Neuropediatrics 1984,15Suppl, 93–96.
Gorio, A. Gangliosides as a possible treatment affecting neuronal repair processes.Adv. Neurol. 1988,47, 523–530.
Felding-Habermann, B.; Igarashi, Y.; Fenderson, B. A.; Park, L. S.; Radin, N. S.; Inokuchi, J.; Strassmann, G.; Handa, K.; Hakomori, S. A ceramide analogue inhibits T cell proliferative response through inhibition of glycosphingolipid synthesis and enhancement of N,N-dimethylsphingosine synthesis.Biochemistry 1990,29, 6314–6322.
Costello, C. E.; Vath, J. E. Tandem mass spectrometry of glycolipids.Methods Enzymol. 1990,193, 738–768.
Domon, B.; Costello, C. E. Structure elucidation of glycosphingolipids and gangliosides using high-performance tandem mass spectrometry.Biochemistry 1988,27, 1534–1543.
Kasama, T.; Handa, S. Structural studies of gangliosides by fast atom bombardment ionization, low-energy collision-activated dissociation, and tandem mass spectrometry.Biochemistry 1991,30, 5621–5624.
Ann, Q.; Adams, J. Structural-specific collision-induced fragmentations of ceramides cationized with alkali-metal ions.Anal. Chem. 1993,65, 7–13.
Ann, Q.; Adams, J. Structural determination of ceramides and neutral glycoshingolipids by collisional activation of [M + Li]+ ions.J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1992,3, 260–263.
Sullards, M. C.; Lynch, D. V.; Merrill, A. H.; Adams, J. Structural determination of soybean and wheat glucosylceramides by tandem mass spectrometry.J. Mass Spectrom. 2000,35, 347–353.
Guittard, J.; Hronowski, X. L.; Costello, C. E. Direct matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric analysis of glycosphingolipids on thin layer chromatographic plates and transfer membranes.Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999,13, 1838–1849.
Ii, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Nagai, Y. Structural elucidation of underivatized gangliosides by electrospray-ionization tandem mass spectrometry (ESIMS/MS).Carbohydr. Res. 1995,273, 27–40.
Olling, A.; Breimer, M. E.; Peltomaa, E.; Samuelsson, B. E.; Ghardashkhani, S. Electrospray ionization and collision-induced dissociation time-of-flight mass spectrometry of neutral glycosphingolipids.Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1998,12, 637–645.
Hsu, F. F.; Turk, J. Structural determination of sphingomyelin by tandem mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization.J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2000,11, 437–449.
Hsu, F. F.; Bohrer, A.; Turk, J. Formation of lithiated adducts of glycerophosphocholine lipids facilitates their identification by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry.J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1998,9, 516–526.
Hsu, F. F.; Bohrer, A.; Turk, J. Characterization of phosphatidylethanolamine as a lithiated adduct by triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization.J. Mass Spectrom. 2000,35, 596–606.
Hsu, F. F.; Turk, J. Structural characterization of triacylglycerols as lithiated adducts by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry using low-energy collisionally activated dissociation on a triple stage quadrupole instrument.J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1999,10, 587–599.
Levery, S. B.; Toledo, M. S.; Doong, R. L.; Straus, A. H.; Takahashi, H. K. Comparative analysis of ceramide structural modification found in fungal cerebrosides by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry with low energy collision-induced dissociation of Li+ adduct ions.Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2000,14, 551–563.
Heller, D. N.; Murphy, C. M.; Cotter, R. J.; Fenselau, C.; Uy, O. M. Constant neutral loss scanning for the characterization of bacterial phospholipids desorbed by fast atom bombardment.Anal. Chem. 1988,60, 2787–2791.
Cole, M. J.; Enke, C. G. Direct determination of phospholipid structures in microorganisms by fast atom bombardment triple quadrupole mass spectrometry.Anal. Chem. 1991,63, 1032–1038.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, FF., Turk, J. Structural determination of glycosphingolipids as lithiated adducts by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry using low-energy collisional-activated dissociation on a triple stage quadrupole instrument. J. Am. Soc. Spectrom. 12, 61–79 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1044-0305(00)00194-X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1044-0305(00)00194-X