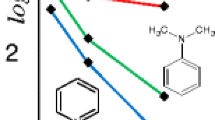
Abstract
We show results from experiments designed to determine the relative importance of gas phase processes and solution phase processes into ionization suppression observed in biological sample extracts. The data indicate that gas phase reactions leading to the loss of net charge on the analyte is not likely to be the most important process involved in ionization suppression. The results point to changes in the droplet solution properties caused by the presence of nonvolatile solutes as the main cause of ionization suppression in electrospray ionization of biological extracts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matuszewski, B. K.; Constanzer, M. L.; Chavez-Eng, C. M. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 882–889.
Buhrman, D. L.; Price, P. I.; Rudewicz, P. J. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1996, 7, 1099–1105.
Pfeifer, R. J.; Hendricks, C. D. AIAA J. 1968, 6, 496–502.
Fernández de la Mora, J. J. Fluid Mech. 1992, 243, 561–574.
Kebarle, P.; Tang, L. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 972–986A.
Ikonomou, M. G.; Blades, A. T.; Kebarle, P. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 1989–1998.
Kebarle, P.; Yeunghow, H. In Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry; Cole, R. B., Ed.; Wiley: New York, 1997; pp 3–63.
Wang, G.; Cole, R. B. In Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry; Cole, R. B., Ed.; Wiley: New York, 1997; p 137.
Bruins, A. P.; Covey, T. R.; Henion, J. D. Anal. Chem. 1987, 59, 2642–2646.
Banks, J. F.; Shen, S.; Whitehouse, C. M.; Fenn, J. B. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 406–414.
Banks, J. F.; Quinn, J. P.; Whitehouse, C. M. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 3688–3695.
Kostiainen, R.; Bruins, A. P. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1994, 8, 549–558.
Dole, M.; Mack, L. L.; Hines, R. L.; Mobley, R. C.; Ferguson, L. D.; Alice, M. B. J. Chem. Phys. 1968, 49, 2240–2249.
Iribarne, J. V.; Thompson, R. A. J. Chem. Phys. 1976, 64, 2287.
Thompson, R. A.; Iribarne, J. V. J. Chem. Phys. 1979, 71, 4451–4463.
Schmelzeisen-Redeker, G.; Bütfering, L.; Röllgen, F. W. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Processes 1989, 90, 139–150.
Gomez, A.; Tang, K. Phys. Fluids 1994, 6, 404–414.
Sunner, J.; Nicol, G.; Kebarle, P. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 1300–1307.
Fenn, J. B. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1993, 4, 524–535.
Bonfiglio, R.; King, R. C.; Olah, T. V.; Merkle, K. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 13, 1175–1185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, R., Bonfiglio, R., Fernandez-Metzler, C. et al. Mechanistic investigation of ionization suppression in electrospray ionization. J. Am. Soc. Spectrom. 11, 942–950 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1044-0305(00)00163-X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1044-0305(00)00163-X