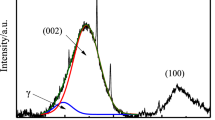
Abstract
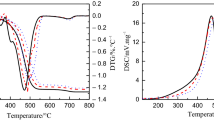
Non-isothermal combustion kinetics of two kinds of low volatile pulverized coals (HL coal and RU coal) were investigated by thermogravimetric analysis. The results show that the combustibility of HL coal was better than that of RU coal, and with increasing heating rate, ignition and burnout characteristics of pulverized coal were improved. The volume model (VM), the random pore model (RPM), and the new model (NEWM) in which the whole combustion process is considered to be the overlapping process of volatile combustion and coal char combustion, were used to fit with the experimental data. The comparison of these three fitted results indicated that the combustion process of coal could be simulated by the NEWM with highest precision. When calculated by the NEWM, the activation energies of volatile combustion and coal char combustion are 130.5 and 95.7 kJ • mol−1 for HL coal, respectively, while they are 114.5 and 147.6 kJ • mol−1 for RU coal, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. M. Fisher, C. Dupont, L. I. Darvell, J. M. Commandre, A. Saddawi, J. M. Jones, M. Grateau, T. Nocquet, S. Salvador, Bioresour. Technol. 119 (2012) 119–157.
R. Barranco, A. Rojas, J. Barraza, E. Lester, Fuel 88 (2009) 2335–2339.
S. Porada, Fuel 83 (2004) 1191–1196.
P. R. Solomon, M. A. Serio, G. V. Despande, E. Kroo, Energ. Fuel 4 (1990) 42–54.
S. Porada, Fuel 83 (2004) 1071–1078.
J. Tomeczek, S. Gil, Fuel 82 (2003) 285–292.
J. Y. Zhang, B. Wang, Y. J. Yan, Z. L. Zhen, J. S. Gao, J. East Chin. Univ. Sci. Technol. 26 (2000) 642–645.
T. P. Griffin, J. B. Howard, W. A. Peters, Energ. Fuel 7 (1993) 297–305.
T. P. Griffin, J. B. Howard, W. A. Peters, Fuel 73 (1994) 591–601.
C. Q. Zhang, X. M. Jiang, L. H. Wei, H. Wang, Energy Convers. Manage. 48 (2007) 797–802.
S. Kasaoka, Y. Sakata, C. Tong, Int. Chem. Eng. 25 (1985) 160–175.
S. J. Yuh, E. E. Wolf, Fuel 63 (1984) 1604–1609.
S. K. Bhatia, D. D. Perlmutter, AIChE J. 26 (1980) 379–386.
S. K. Bhatia, D. D. Perlmutter, AIChE J. 27 (1981) 247–254.
J. R. Fernandez, F. Oliva, R. A. Vazquez, Energ. Fuel 25 (2011) 2039–2048.
H. N. Sharma, L. Pahalagedara, A. Joshi, S. L. Suib, A. B. Mhadeshwar, Energ. Fuel 26 (2012) 5613–5625.
N. Zouaoui, J. F. Brilhac, F. Mechati, M. Jeguirim, B. Djelloulli, P. Gilot, J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 102 (2010) 837–849.
A. Khawam, D. R. Flanagan, J. Phys. Chem. B 110 (2006) 17315–17328.
Y. G. Xu, C. Zhang, J. Xia, Y. H. Duan, J. J. Yin, G. Chen, Asia-Pacific Jrnl of Chem. Eng 5 (2010) 435–440.
R. H. Essenhigh, M. K. Misra, D. W. Shaw, Combust. Flame 77 (1989) 3–30.
X. M. Jiang, J. B. Li, J. R. Qiu, Proceedings of CSEE 20 (2000) No. 6, 71–78.
C. L. Qi, J. L. Zhang, X. H. Lin, Q. Y. Liu, X. L. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18 (2011) No. 8, 1–8.
J. L. Zhang, G. W. Wang, X. D. Xing, Q. H. Pang, J. G. Shao, S. Ren, J. Iron Steel Res. 25 (2013) No. 4, 9–14.
S. G. Long, F. Cao, S. W. Wang, L. H. Sun, J. M. Pang, Y. P. Sun, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 15 (2008) No. 1, 6–9.
S. F. Zhang, C. G. Bai, L. Y. Wen, B. G. Qiu, X. W. Lü, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 17 (2010) No. 10, 8–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China (2012CB720401); National Key Technology Research and Development Program in the 12th Five-year Plan of China (2011BAC01B02)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Jg., Zhang, Jl., Wang, Gw. et al. Combustion Property and Kinetic Modeling of Pulverized Coal Based on Non-Isothermal Thermogravimetric Analysis. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21, 1002–1008 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60175-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60175-8