Abstract
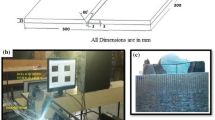
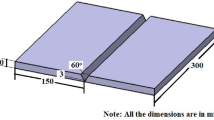
Armour grade quenched and tempered steel closely confirming to AISI 4340 is well known for its superior ballistic performance and hence used in the fabrication of combat vehicles. The traditional filers like austenitic stainless steel showed poor ballistic performance of these welded joints as compared to the base metal. Attempts have been made to deposit hardfaced interlayer between austenitic stainless steel weld metals. Though this method, marginal improvements in ballistic performance can be yielded, and cracks were observed in between base metal and hardfaced layer. Thickness of the hardfaced interlayer plays a vital role for the effective ballistic performance. Thus, an attempt has been made to investigate the effect of hardfaced interlayer thickness on ballistic performance of armour steel welds. The results of effect of buttering, low hydrogen ferritic (LHF) filer and three different hardfaced layer thicknesses (4, 5.5 and 7 mm) on ballistic performance of shielded metal arc welded armour steel joints were given.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ade F. Balistic Qualification ofArmour Steel Weldments [J]. Weld J, 1991, 70(9): 53.
Madhusudhan Reddy G, Mohandas T. Balistic Performance of High-Strength Low-Aloy Steel Weldments [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1996, 57 (1/2): 23.
Madhusudhan Reddy G, Mohandas T, Tagore G R N. Weldability Studies of High-Strength Low-Aloy Steel Using Austenitic Filers [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1995, 49(1/2): 213.
Alkemade S J. The Weld Cracking Susceptibility of High Hardness Armour Steel [R]. Australia: Defense Science and Technology Organization, 1996.
Magudeeswaran G, Balasubramanian V, Madhusudhan Reddy G. Hydrogen Induced Cold Cracking Studies on Armour Grade High Strength, Quenched and Tempered Steel Weldments [J]. International Journal for Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33 (7): 1897.
Madhusudhan Reddy G, Mohandas T, Sarma D S. Cold Cracking Studies on Low Aloy Steel Weldments: Effect of Filer Metal Composition [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2003, 8(6): 407.
Madhusudhan Reddy G, Mohandas T, Papukuty K K. Effect of Welding Process on the Balistic Performance of High-Strength Low-Aloy Steel Weldments [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1998, 74(1/2/3): 27.
Madhusudhan Reddy G, Mohandas T, Papukuty K K. Enhancement of Balistic Capabilities of Soft Welds Through Hardfacing [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1999, 22 (8): 775.
Mohandas T, Madhusudan Reddy G, Satish Kumar B. Heat-Afected Zone Softening in High-Strength Low-Aloy Steels [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1999, 88(1/2/3): 284.
Jena P K, Ramanjeneyulu K, Siva Kumar K, et al. Balistic Studies on Layered Structures [J]. Materials and Design, 2009, 30(6): 1922.
Seong-Hun Choo, Eung-Ryul Baek, Sunghak Lee. Balistic Impact Behavior of Multilayered Armor Plates Processed by Hardfacing [J]. Metalurgical and Materials Transactions, 1996, 27A(10): 3335.
Balakrishnan M, Balasubramanian V, Madhusudhan Reddy G, et al. Improving the Balistic Immunity of Armour Steel Weldments by Plasma Transferred Arc (PTA) Hardfacing [J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31(5): 2664.
Balakrishnan M, Balasubramanian V, Madhusudhan Reddy G, et al. Effect of Butering and Hardfacing on Balistic Performance of Shielded Metal Arc Welded Armour Steel Joints [J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32(2): 469.
Magudeeswaran G, Balasubramanian V, Balasubramanian T S, et al. Effect of Welding Processes and Consumables on Tensile and Impact Properties of High Strength Quenched and Tempered Steel Joint [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2008, 15(6): 87.
Magudeeswaran G, Balasubramanian V, Balasubramanian T S, et al. Effect of Welding Consumables on Tensile and Impact Properties of Shielded Metal Arc Welded High Strength, Quenched and Tempered Steel Joints [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2008, 13(2): 97.
SFA 5. 13. Specification for Surfacing Electrodes for Shielded Metal Arc Welding, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (an International Code), Sec II Part-C: Specification for Welding Rods, Filer Metals and Electrodes [M]. New York: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers New York, 2004: 303.
Unfried S J, Garzonb C M, Giraldoc J E. Numerical and Experimental Analysis of Microstructure Evolution During Arc Welding in Armor Plate Steels [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(4): 1688.
Pizana C, Murr L E, Baquera M T, et al. Solid-State Flow, Mechanical Alloying, and Melt-Related Phenomena for [0 0 1] Single-Crystal W Balistic Rod Penetrators Interacting With Steel Targets [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2006, 428(1/2): 301.
Crouch I G. Metalic ArmourGFrom Cast Aluminium Aloys to High Strength Steels [J]. Mater Forum, 1988, 12: 31.
Woodward R L. Materials for Projectile Disruption [J]. Mater Forum, 1988, 12: 26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balakrishnan, M., Balasubramanian, V. & Madhusudhan Reddy, G. Effect of Hardfaced Interlayer Thickness and Low Hydrogen Ferritic Capping on Ballistic Performance of Shielded Metal Arc Welded Armour Steel Joints. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20, 82–91 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(13)60220-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(13)60220-4