Abstract
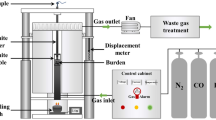
The behaviors of mixed burden in the cohesive zone of oxygen blast furnace were studied by softening and melting tests, and the influence of reducing gas and burden basicity on the softening and melting behaviors of mixed burden was also investigated. The results indicated that the softening range became wide, however, the melting range narrowed sharply in the atmosphere of oxygen blast furnace. The permeability of burden in the oxygen blast furnace was obviously improved comparing with the conventional blast furnace. In addition, the content of sulphur in the dripping iron of oxygen blast furnace was much lower than that of conventional blast furnace, however, the content of carbon increased. An optimum basicity of burden, which could lead to the appearance of the narrower melting range and better permeability of burden, was obtained in the atmosphere of oxygen blast furnace.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okamoto T, Tada T, Sugiura S. On the Highly Oxygen-Enriched Blast Furnace Operation Utilizing Top Gas for Ammonia Synthesis [J]. Tetsu-to-Hagane, 1972, 58(5): 637 (in Japanese).
Riley M F, Strayer T J, Zhao Y. Effect of Direct Oxygen Injection on Comhustion of Injected Coal [C] // 2nd International Congress on the Science and Technology of Ironmaking and 57th Ironmaking Conference. Toronto: [s. n.], 1998: 198.
Yamaoka H, Kamei Y. Theoretical Study on an Oxygen Blast Furnace Using Mathematical Simulation Model [J], ISIJ International, 1992, 32(6): 701.
Yamaoka H, Kamei Y. Experimental Study on an Oxygen Blast Furnace Process Using a Blast Furnace Test Plant [J], ISIJ International, 1992, 32(6): 709.
Fink F. Suspension Smelting Reduction—A New Method of Hot Iron Production [J]. Steel Times, 1996, 224(11): 398.
Lu W K, Kumar R V. The Feasibility of Nitrogen-Free Blast Furnace Operations [J]. Iron and Steel Society of AIME Transactions, 1984, 5: 25.
QIN Ming-sheng, GAO Zheng-kai, WANG Guan-lun, et al. Blast Furnace Operation With Full Oxygen Blast [J]. Iron-making and Steelmaking, 1988, 15(6): 287.
Ohno Y, Matsuura M, Mitsufuji H, et al. Process Characteristics of a Commercial-Scale Oxygen Blast Furnace Process With Shaft Gas Injection [J]. ISIJ International, 1992, 32(7): 838.
ZUO Guang-qing, Hirsch A. The Trial of the Top Gas Recycling Blast Furnace at LKAB’s EBF and Scale-Up [J]. Revue de Métallurgie, 2009, 106(9): 387.
Danloy G, Berthelemot A, Grant M, et al. ULCOS-Pilot Testing of the Low-CO2 Blast Furnace Process at the Experimental BF in Luleâ [J]. Revue de Métallurgie, 2009, 106(1): 1.
Austin P R, Nogami H, Yagi J. Prediction of Blast Furnace Performance With Top Gas Recycling [J], ISIJ International, 1998, 8(3): 239.
Danloy G, Stel J van der, Schmole P. Heat and Mass Balances in the ULCOS Blast Furnace [C] // Proceedings of the 4th Ulcos Seminar. Essen: [s. n. ], 2008: 706.
HAN Yi-hua, WANG Jing-song, LI Yan-zhen, et al. Comprehensive Mathematical Model for Ironmaking Process of Top Gas Recycling and Oxygen Blast Furnace [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2011, 33(10): 1280 (in Chinese).
Bakker T. Softening in the Blast Furnace Process [D], Netherlands: Delft University of Technology, 1999.
Nogueira P F. Blast Furnace Burden Softening and Melting Phenomena [D]. Pittsburgh; Carnegie Mellon University, 2003.
Kaushik P. Mixed Burden Softening and Melting Phenomena [D]. Pittsburgh: Carnegie Mellon University, 2006.
WANG Xiu-liu. Ferrous Metallurgy (Ironmaking) [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006 (in Chinese).
ZHANG Xing-he, Takahashi R, Akiyama T, et al. Carburization Rate Into Solid Iron at CO-CO2 Atmosphere [J]. Tesu-to-Hagane, 1997, 83(5): 299 (in Japanese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China (2012CB720401); National Key Technology Research and Development Program in 12th Five-Year Plan of China (2011BAC01B02)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, Xw., Wang, Js., Lan, Rz. et al. Softening and Melting Behavior of Mixed Burden for Oxygen Blast Furnace. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20, 11–16 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(13)60090-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(13)60090-4