Abstract
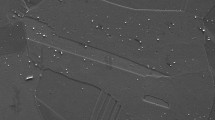
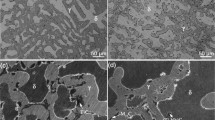
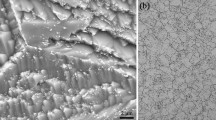
To investigate the effect of high temperature ageing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of S31042 steel, solid solution treatment at 700 °C was carried out for various time from 10 to 6 000 h. Experimental results showed that the change of mechanical properties is closely related to the amount of precipitated phases. During ageing from 10 to 300 h, precipitation in the tested steel increases rapidly, and correspondingly, the high temperature yield strength and room temperature hardness of tested steel increase rapidly. Meanwhile, the thickness of the secondary phase on grain boundaries widens sharply and the room temperature Charpy impact absorb energy decreases. Ageing beyond 300 h, the precipitation in the steel increases gradually and the precipitates coarsen to a certain extent. The high temperature yield strength of the steel keeps stable, and the room temperature Charpy impact energy and hardness decrease slowly. Ageing beyond 3 000 h, the mechanical properties of the steel tend to be stable. The main precipitates are M23C6, NbCrN and NbC in the tested steel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG Jing-zhong, LIU Zheng-dong, CHENG Shi-chang. Study on Hot Deformation Behaviors of S31042 Austenitic Heat-Resistant Steel [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2011, 18(10): 54.
TAN Shu-ping. Effect of Composition and Processing on Properties and Strengthening Mechanism of S30432 Steel [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009 (in Chinese).
Masuyama Fujimitsu. History of Power Plants and Progress in Heat Resistant Steels [J]. ISIJ International, 2001, 41(6): 612.
WANG Jing-zhong, LIU Zheng-dong, CHENG Shi-chang, et al. Effect of Elevated Temperature Aging on Ambient Tensile Properties of Steel S31042 [J]. Special Steel, 2011, 32(3): 61 (in Chinese).
Natori A. HR3C Tubes in Coal-Fired Boiler [J]. Stainless Steel Europe, 1992, 4(16): 20.
Iseda A, Okada H, Semba H, et al. Long Term Creep Properties and Microstructure of SUPER304H, TP347HFG and HR3C for A-USC Boilers [J]. Energy Materials: Materials Science and Engineering for Energy Systems, 2007, 2(4): 199.
Park I, Masuyama F, Endo T. Effect of Soluble Nitrogen on the Creep Strength of an Austenitic 25Cr-20Ni Steel [J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2000, 171–174: 445.
Barcik J. The Kinetics of Cr-Phase Precipitation in AIS1 310 and AIS1 316 Steels [J]. Metall Trans, 1983, 14A: 635.
Padilha A F, Escriba D M, Materna-Morris E, et al. Precipitation in AISI 316L(N) During Creep Tests at 550 and 600 °C up to 10 Years [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2007, 362(1): 132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Science and Technology Support Plan of China (2007BAE51B02)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Jz., Liu, Zd., Bao, Hs. et al. Effect of Ageing at 700 °C on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of S31042 Heat Resistant Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20, 54–58 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(13)60082-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(13)60082-5