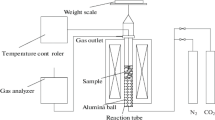
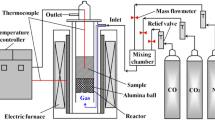
Abstract
Reasonable control on CRI (coke reaction index) is one of the key factors for BF (blast furnace) low-carbon smelting. However, there are contrary opinions. One is increasing CRI to improve reaction efficiency in BF and the other is decreasing CRI to suppress coke degradation in furnace. Different methods are adopted to realize effective catalysis (increasing CRI) and passivation (decreasing CRI) of coke. Simulation tests of coke in BF lumpy zone under gradual temperature rising have been done. Effect of CRI on gas composition, ore reduction, burden column permeability and heat reserve zone’s temperature under non-isothermal condition are studied. Then combined with iron making calculations, a novel BF operation suggestion is proposed as coke nut with small size be catalyzed and mixed with ore while skeletal coke with large size be passivated and separately charged into BF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshihito Shigeno, Jamse Williams Evans, Itsumei You. Infiltration of Metallurgical Coke by Pyrolysis of CH4 and Its Effect on Enhancement of CSR [J]. ISIJ International, 1998, 38(1): 28.
ZHANG Qun. Improve Coke Hot Properties to Suppress Coke Gasification Reaction [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Technology, 2003 (in Chinese).
ZHU Zi-zong, ZHANG Zhu-ming, TANG Qi-yong, et al. Industrial Experiment on Coke Spraying With ZBS Additive in Blast Furnace [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2006, 13(3): 14.
Kasai Akito, Matsui Yoshiyuki. Lowering of Thermal Reserve Zone Temperature in Blast Furnace by Adjoining Carbonaceous Material and Iron Ore [J]. ISIJ International, 2004, 44(12): 2073.
Seiji Nomura, Hisatsugu Kitaguchi, Kouichi Yamaguchi, et al. The Characteristics of Catalyst-Coated Highly Reactive Coke [J]. ISU International, 2007, 47(2): 245.
Seiji Nomura, Kenichi Higuchi, Kazuya Kunitomo, et al. Reaction Behavior of Formed Iron Coke and Its Effect on Decreasing Thermal Reserve Zone Temperature in Blast Furnace [J]. ISIJ International, 2010, 50(10): 1388.
Michael W Chapman, Brain J Monaghan, Sharon A Nightingale, et al. Observation of the Mineral Matter Present at the Coke/Iron Interface During Dissolution Into Iron [J]. ISIJ International, 2007, 47(7): 973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61271303); Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities of China (FRF-TP-12-029A)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Hb., Bai, Yq. & Cheng, Ss. Effect of Coke Reaction Index on Reduction and Permeability of Ore Layer in Blast Furnace Lumpy Zone Under Non-Isothermal Condition. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20, 6–10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(13)60074-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(13)60074-6