Abstract
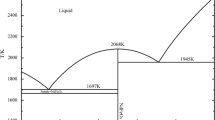
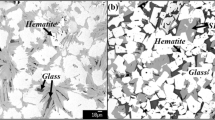
A high temperature equilibration experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of oxygen partial pressure on the phase equilibria and liquidus in CaO-Al2O3 -FeOx system with the intermediate oxygen partial pressures of 10. 13 Pa and 1. 01 · 10-3 Pa. The equilibrated phases and their compositions of the quenched samples were analyzed by using SEM/EPMA (Scanning Electron Microscope/Electron Probe Micro-Analysis) and XRD (X-Ray Diffraction). The phase equilibrium results include two cases, the two-phase coexistence and the three-phase coexistence in the high Al2 O3 region with oxygen partial pressure of either 10. 13 Pa or 1. 01 · 10-3 Pa. Effects of oxygen partial pressure and temperature on the liquidus along the primary phase fields of CaO ·Al2 O3 and CaO ·Al2 O3 were notable. With the decrease of oxygen partial pressure, the liquid area expands and the liquidus of CaO ·Al2 O3 and CaO ·Al2 O3 primary fields moves to the Al2O3-FeOx region. On the other hand, the liquid area of CaO-Al2O3-FeOm system extends extremely to the high Al2O3 region with the temperature increasing from 1 400 to 1 500 °C, especially at lower oxygen partial pressure. The present experiment results are in good agreement with the calculated ones by FactSage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Decterov S A, Kang Y B, Jung I H. Thermodynamic Database for the Al-Ca-Co-Cr-Fe-Mg-Mn-Ni-Si-OP-S System and Applications in Ferrous Process Metallurgy [J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria and Diffusion, 2009, 30(5): 443.
Wang N, Zou Z S, Zhang Z, et al. Effect of Oxygen Partial Pressure and Temperature on Liquidus for the CaO-SiO2-FeOx-Al2O3 System [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 295–297: 2279.
Jak E, Degterov S, Hayes P C, et al. Thermodynamic Modelling of the System Al2O3-SiO2-CaO-FeOFe2O3 to Predict the Flux Requirements for Coal Ash: Slags [J]. Fuel, 1998, 77(1/2): 77.
Muan A, Gee C L. Phase Equilibrium Studies in the System Iron Oxide-Al2 O3 in Air and at latm O2 Pressure [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1956, 39(6): 207.
Dayal R R, Glasser F P. Phase Relations in the System CaO-Al2O3-FezO3 [J]. Science of Ceramics,1967, 3: 191.
Newkirk T F, Thwaite R D. Pseudoternary System Calcium Oxide-Monocalcium Aluminate-Dicalcium Ferrite [J]. Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards, 1958, 61(4): 233.
Espejo V, Iwase M. A Thermodynamic Study of the System CaO-Al2O3-FerO at 1673 K [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 1995, 26B(4): 257.
Turkdogan E T. Physical Chemistry of High Temperature Technology [M], New York: Academic Press Inc, 1980.
Bale C W, Bélisle E, Chartrand P, et al. FactSage Thermochemical Software and Databases-Recent Development [J]. Calphad, 2009, 33: 295.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (50974034, 51074039)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, N., Huang, Wj., Chen, Sc. et al. Effect of Oxygen Partial Pressure on Phase Equilibria and Liquidus in CaO-Al2O3-FeOx System. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 19, 8–12 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(13)60013-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(13)60013-8